* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download what are enzymes
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Lactoylglutathione lyase wikipedia , lookup
Transferase wikipedia , lookup
Beta-lactamase wikipedia , lookup
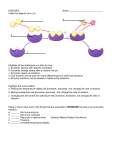
Name: ________________________________________ Period: ____ WHAT ARE ENZYMES? Enzymes are complex proteins that act as biological catalysts. This means that enzymes speed up the rate of chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks and weeks to digest our food, and our muscles, nerves, and bones would not work properly. Essentially, we would not be living! 1 A catalyst is any substance that makes a chemical reaction go faster, without being changed itself. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction – it does not get used up. Because enzymes are a biological catalyst, they also speed up the rate of chemical reactions, however enzymes are easily denatured. Denaturation is a structural change in the molecules caused by extreme conditions (like heat, pH, or other factors). Enzymes must have the correct structure (shape) to do their job, so if the enzyme is denatured, it can no longer function as a catalyst. So, enzymes must have the right environmental conditions to avoid denaturation. This is why some people say that enzymes work like a key in a lock. If the key has been melted by heat or dissolved in acid, it will no longer work. INDUCED FIT Just like a key is specific to one lock, an enzyme is specific to one chemical reaction. For example, human saliva contains an enzyme called amylase. This enzyme speeds up the chemical reaction that turns starch into a sugar called maltose. In this chemical reaction, starch is called the substrate. The substrate is the molecule that the enzyme is working on. So, when you take a bite of food, amylase (enzyme) catalyzes (speeds up) the chemical reaction that turns starch (substrate) into sugar while the food is in your mouth. However, you swallow this mouthful of food and it reaches your stomach, the amylase stops working. This is because your stomach acid is too acidic (pH 1.5 – 2), which causes the enzyme to be denatured, and no longer be able to function. 2 Enzymes in the human alimentary canal and what they digest: Enzyme Amylase Maltase Sucrase Lipase Pepsin Catalase Substrate Starch Maltose Sucrose Fats Proteins Hydrogen peroxide GUIDED READING QUESTIONS 1. Which type of biomolecule are enzymes? 4. What environmental conditions cause an enzyme to denature? 2. What is an enzyme and how does it function? 5. How does denaturation affect the function of an enzyme? 3. Do enzymes get used up after a reaction? NOTES What are Enzymes? Enzymes are a type of _________________ that helps control and manage cell metabolism by making __________________ ___________________ happen more _____________________. Enzymes ____________ _____ chemical reactions by __________________ the activation energy, which is the amount of energy that is needed to initiate (or start) a chemical reaction. Parts of Enzymes Substrate: the molecules an enzyme ____________________ (the reactants) Active Site: the ______________ on the enzyme where the substrate attaches o The active site is a groove or depression on the surface of an enzyme. o Even the slightest change in the form of this site will alter the enzyme's function. Products: the molecules that the enzyme is ________________ __________ into, the result of the reaction Induced Fit: the way in which the enzyme and substrate bond to one another o Each enzyme is only capable of metabolizing (breaking down) one type of substrate. o The enzyme and the substrate must fit together like a lock and key in order for the enzyme to induce (or start) the chemical reaction. What Factors can Affect Enzyme Function? Enzymes function best in ________________ _______________________; environmental factors within the cell can affect how well the enzyme functions. o Each particular enzyme has an ideal environment that it is most efficient in. Temperature: extreme temperatures can ________________ (change the shape) an enzyme. pH: Each enzyme has a particular pH range for _______________ performance. Salts ______________ (or prevent) enzyme action. Graphing Practice 1. A student studying reactions with enzymes uses the graph to form a conclusion. What is the best conclusion a student can make based on the information on the graph? a. The amount of activation energy is lower in reactions without enzymes. b. The amount of activation energy needed is greater in reactions with enzymes. c. A reaction with an enzyme lowers the activation energy needed. d. As the reaction continues the amount of energy needed increases. 2. Which statement does not describe the role of enzymes? a. b. c. d. Enzymes synthesize molecules Enzymes are specific to the molecules in a reaction. Enzymes reactions are maximized within a specific range of conditions. Enzymes decrease the activation energy necessary for cell metabolism. Use the diagram to the right to answer questions 3 and 4. 3. Which structure is indicated by letter B? a. Active Site b. Substrate c. Enzyme-Substrate Complex d. Competitive Inhibitor 4. Which structure is indicated by letter A? a. Active Site b. Substrate c. Enzyme-Substrate Complex d. Competitive Inhibitor 5. An enzyme is an example of which of the following biomolecules? a. Carbohydrate c. Protein b. Lipid d. Nucleic Acid 6. An enzyme is a type of molecule that speeds up chemical reactions, which is referred to as a/an – a. Catalysts c. Product b. Reactant d. Inhibitor 7. The area on the enzyme that the substrate attaches to, creating an induced fit, is known as the – a. Surface Area c. Active Site b. Initiator d. Protein channel 8. If an enzyme is placed in an extremely hot environment, this causes the enzyme to change shape. What is that change in shape called? a. Melting c. Diverging b. Extraction d. Denaturation 9. Enzymes function by lowering the __________________ that is needed to initiate the chemical reaction. a. Temperature c. pH b. Activation Energy d. Salt levels 10. What do enzymes do to a chemical reaction? a. Slow it down b. Speed it up c. Stop the reaction d. None of the above