Enzyme
... • Reaction rate increases as enzyme concentration increase • (at constant and very high substrate concentration) • At higher enzyme concentration more substrate will bind with enzyme ...
... • Reaction rate increases as enzyme concentration increase • (at constant and very high substrate concentration) • At higher enzyme concentration more substrate will bind with enzyme ...
What Are Enzymes?
... Irreversible egg protein denaturation caused by high temperature (while cooking it). ...
... Irreversible egg protein denaturation caused by high temperature (while cooking it). ...
Chapter 20 Carbohydrate Biosynthesis in Plants and Bacteria
... Ans: The condensation of molecular oxygen with ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate yields 3phosphoglycerate and the two-carbon compound phosphoglycolate. Phosphoglycolate has no known metabolic role; its carbon is salvaged by a series of reactions that consume O2 and produce CO2 the “photorespiration” proce ...
... Ans: The condensation of molecular oxygen with ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate yields 3phosphoglycerate and the two-carbon compound phosphoglycolate. Phosphoglycolate has no known metabolic role; its carbon is salvaged by a series of reactions that consume O2 and produce CO2 the “photorespiration” proce ...
Epjj Lecture 4
... These six classes are: 1. Oxidoreductases - enzymes catalyzing oxidation reduction reactions. 2. Transferases - enzymes catalyzing transfer of functional groups. 3. Hydrolases - enzymes catalyzing hydrolysis reactions. 4. Lyases - enzymes catalyzing group elimination reactions to form double bonds. ...
... These six classes are: 1. Oxidoreductases - enzymes catalyzing oxidation reduction reactions. 2. Transferases - enzymes catalyzing transfer of functional groups. 3. Hydrolases - enzymes catalyzing hydrolysis reactions. 4. Lyases - enzymes catalyzing group elimination reactions to form double bonds. ...
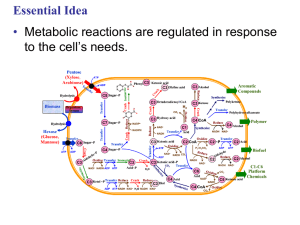
Control of metabolism
... – Regulation is accomplished by altering the activity of at least one pacemaker enzyme (or rate-determining step) of the pathway. ...
... – Regulation is accomplished by altering the activity of at least one pacemaker enzyme (or rate-determining step) of the pathway. ...
Digestion of Dietary Proteins
... Inability to digest lactose of milk due to deficiency of lactase enzyme So, diarrhea will occur on ingestion of milk or milk products For infants (up to two years old): are treated by lactose-free milk 2- Intestinal diseases or drugs that injure the mucosa of the small intestine ...
... Inability to digest lactose of milk due to deficiency of lactase enzyme So, diarrhea will occur on ingestion of milk or milk products For infants (up to two years old): are treated by lactose-free milk 2- Intestinal diseases or drugs that injure the mucosa of the small intestine ...
Catalase enzyme lab
... Enzymes are biological catalysts that carry out the thousands of chemical reactions that occur in living cells. They are generally large proteins made up of several hundred amino acids, and often contain a non-proteinaceous group called the prosthetic group that is important in the actual catalysis. ...
... Enzymes are biological catalysts that carry out the thousands of chemical reactions that occur in living cells. They are generally large proteins made up of several hundred amino acids, and often contain a non-proteinaceous group called the prosthetic group that is important in the actual catalysis. ...
Avidin Based Enzyme Immobilization on Gold Nanoelectrodes
... Over the last decade, a considerable amount of research have been conducted in the field of biological electrochemistry, one example in particular is biosensors. Biosensors are used to analyze the composition of a solution and to detect the presence and concentration of a particular compound of inte ...
... Over the last decade, a considerable amount of research have been conducted in the field of biological electrochemistry, one example in particular is biosensors. Biosensors are used to analyze the composition of a solution and to detect the presence and concentration of a particular compound of inte ...
Enzymes: Catalytic Strategies
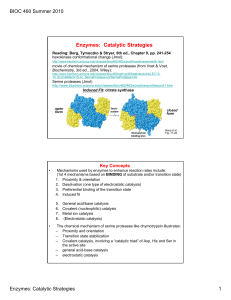
... reactive intermediate in the reaction that was supposed to transfer its reactive group to another substrate. 3. TIGHT TRANSITION STATE BINDING • used to be called "strain and distortion" • Enzyme binds transition state very tightly, tighter than substrate (stabilizes T.S.) • Free energy of transitio ...
... reactive intermediate in the reaction that was supposed to transfer its reactive group to another substrate. 3. TIGHT TRANSITION STATE BINDING • used to be called "strain and distortion" • Enzyme binds transition state very tightly, tighter than substrate (stabilizes T.S.) • Free energy of transitio ...
f212 molecules biodiversity food health 2.1.3 enzymes
... • Furthermore, the H+ ions can alter the essential & specific charges on amino acid R-groups that make up the active site. This will reduce bonding and slow down the enzyme-controlled reaction. • All enzymes have an optimum pH; the concentration of H+ ions in the solution that give the enzyme it’s b ...
... • Furthermore, the H+ ions can alter the essential & specific charges on amino acid R-groups that make up the active site. This will reduce bonding and slow down the enzyme-controlled reaction. • All enzymes have an optimum pH; the concentration of H+ ions in the solution that give the enzyme it’s b ...
Enzymes & pH - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
... What is pH? – Measures how acidic or basic a solution is Acids – compounds that release H+ ions in solution (corrosive) Bases – compounds that remove H+ from solution pH scale - measures how acidic a solution is – pH = usually between 0 -14 – pH 0 = very acidic (high H+ concentration) – pH 14 = very ...
... What is pH? – Measures how acidic or basic a solution is Acids – compounds that release H+ ions in solution (corrosive) Bases – compounds that remove H+ from solution pH scale - measures how acidic a solution is – pH = usually between 0 -14 – pH 0 = very acidic (high H+ concentration) – pH 14 = very ...
Glycolysis Worksheet High School Biology Use the
... a)The transfer of an inorganic phosphate group (Pi) from one substrate to another by way of an enzyme b) the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule c) the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. d)metabolic pathway in whic ...
... a)The transfer of an inorganic phosphate group (Pi) from one substrate to another by way of an enzyme b) the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule c) the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. d)metabolic pathway in whic ...
Enzyme Activity
... _____ 2. Based on your answer above, what would you say about enzymes? a. Enzymes are very specific b. Enzymes are nonspecific c. A specific enzyme can regulate only one type of reaction d. A specific enzyme can regulate several different types of reactions e. Both a and c Base your answers to quest ...
... _____ 2. Based on your answer above, what would you say about enzymes? a. Enzymes are very specific b. Enzymes are nonspecific c. A specific enzyme can regulate only one type of reaction d. A specific enzyme can regulate several different types of reactions e. Both a and c Base your answers to quest ...
Harmless digestive enzyme evolved into venom in two species
... enzyme kallikrein. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze, or increase the rates of, chemical reactions; this rate enhancement occurs at a specific region on an enzyme called the active site. (PhysOrg.com) -- Biologists have shown that independent but similar molecular changes turned Aminetzach found th ...
... enzyme kallikrein. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze, or increase the rates of, chemical reactions; this rate enhancement occurs at a specific region on an enzyme called the active site. (PhysOrg.com) -- Biologists have shown that independent but similar molecular changes turned Aminetzach found th ...
National 4- Production of cheese
... The temperature at which an enzyme is most active is said to be that enzymes optimum temperature. The pH at which an enzyme is most active is said to be that enzymes optimum pH. Each enzyme has a particular optimum temperature and pH at which it is most active. This temperature and pH is different f ...
... The temperature at which an enzyme is most active is said to be that enzymes optimum temperature. The pH at which an enzyme is most active is said to be that enzymes optimum pH. Each enzyme has a particular optimum temperature and pH at which it is most active. This temperature and pH is different f ...
The following Text was taken from the Student Lab Manual for
... Enzymes are a diverse and important class of proteins. Biologists refer to enzymes as biological catalysts because they increase the velocity or rate of chemical reactions in living cells. You may have already used MitochondriaLab to learn about basic principles of enzyme activity, metabolic pathway ...
... Enzymes are a diverse and important class of proteins. Biologists refer to enzymes as biological catalysts because they increase the velocity or rate of chemical reactions in living cells. You may have already used MitochondriaLab to learn about basic principles of enzyme activity, metabolic pathway ...
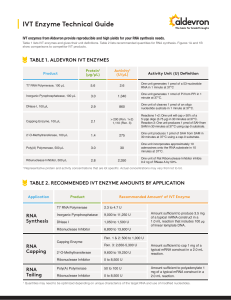
IVT Enzyme Technical Guide
... activity was measured using the EPIgeneous™ Methyltransferase Assay (Cisbio). ...
... activity was measured using the EPIgeneous™ Methyltransferase Assay (Cisbio). ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... which enzyme catalyzed the transfer of a specific functional group, X, from one of the substrates to the other: ...
... which enzyme catalyzed the transfer of a specific functional group, X, from one of the substrates to the other: ...
enzyme names end in “ase”
... An example of mixed inhibitor types is aspirin (ASA) and Ibuprofen (IBU). ASA is an UNcompetitive inhibitor of COX-1 (CycloOXygenase type 1). ASA and IBU inhibit cyclooxygenase variants which is the main enzyme in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Prostaglandins mediate pain, Inflammation, blood pressure, ...
... An example of mixed inhibitor types is aspirin (ASA) and Ibuprofen (IBU). ASA is an UNcompetitive inhibitor of COX-1 (CycloOXygenase type 1). ASA and IBU inhibit cyclooxygenase variants which is the main enzyme in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Prostaglandins mediate pain, Inflammation, blood pressure, ...
survey of biochemistry - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • General acid catalysis H+ transfer from an acid lowers the free energy of the transition state ...
... • General acid catalysis H+ transfer from an acid lowers the free energy of the transition state ...
Document
... Enzymes are amazing natural catalysts. Without them the rate of virtually all chemical reactions in the cell would be very low or even negligible. They are exceptionally efficient, some of them are able to increase rate of the reaction up to 10 17 times, other convert up to 10 6 substrate molecules ...
... Enzymes are amazing natural catalysts. Without them the rate of virtually all chemical reactions in the cell would be very low or even negligible. They are exceptionally efficient, some of them are able to increase rate of the reaction up to 10 17 times, other convert up to 10 6 substrate molecules ...
8.1 Metabolism
... 7. The isoleucine concentration in the cell falls and so the Isoleucine that is attached to the enzyme detaches. This amino acid is also used up in the various cellular processes. 8. With the inhibitor removed the the active site then becomes active again and the pathway switches back on. 9. The iso ...
... 7. The isoleucine concentration in the cell falls and so the Isoleucine that is attached to the enzyme detaches. This amino acid is also used up in the various cellular processes. 8. With the inhibitor removed the the active site then becomes active again and the pathway switches back on. 9. The iso ...
White Cell Enzymes
... regression and/or hepatosplenomegaly. n It does not rule out all storage disorders, let alone all ...
... regression and/or hepatosplenomegaly. n It does not rule out all storage disorders, let alone all ...
Isomerase

Isomerases are a general class of enzymes which convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases can either facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed or they can catalyze conformational changes. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:A–B → B–AThere is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangements. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism.