lecture3
... Inhibition of a regulatory enzyme does not conform to any normal inhibition pattern and the inhibitor does not bear any obvious structural relationship to the substrate. The enzyme exhibits extreme specificity with regard to the regulator molecule. Allosteric enzymes have an oligomeric organization. ...
... Inhibition of a regulatory enzyme does not conform to any normal inhibition pattern and the inhibitor does not bear any obvious structural relationship to the substrate. The enzyme exhibits extreme specificity with regard to the regulator molecule. Allosteric enzymes have an oligomeric organization. ...
Figure 15-1a Mechanisms of keto–enol tautomerization. (a
... 3. Proton transfer to the C-terminal fragment, which is released by cleavage of the C-N bond. The N-terminal peptide is bound through acyl linkage to serine. 4. A water molecule binds to the enzyme in place of the departed polypeptide. 5. The water molecule transfers its proton to His 57. Again, a t ...
... 3. Proton transfer to the C-terminal fragment, which is released by cleavage of the C-N bond. The N-terminal peptide is bound through acyl linkage to serine. 4. A water molecule binds to the enzyme in place of the departed polypeptide. 5. The water molecule transfers its proton to His 57. Again, a t ...
Chapter 2 Notes – The Chemistry of Life
... Enzymes Some chemical reactions that make life possible are too ___________ or have activation energies that are too ___________ to make them practical for living ...
... Enzymes Some chemical reactions that make life possible are too ___________ or have activation energies that are too ___________ to make them practical for living ...
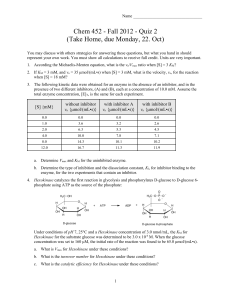
Chem452_Quiz_2
... e. What determines the ultimate speed limit of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction? That is, what is it that imposes a physical limit on catalytic perfection? f. ...
... e. What determines the ultimate speed limit of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction? That is, what is it that imposes a physical limit on catalytic perfection? f. ...
30 Review for test
... *Turn in toothpickase lab if you haven’t already *I have no tutorial today *Please stay in your seats until the bell rings ...
... *Turn in toothpickase lab if you haven’t already *I have no tutorial today *Please stay in your seats until the bell rings ...
metabolism - Chavis Biology
... SUBSTRATE Concentration Effects Enzyme Activity Assuming the amount of enzyme is constant, an increase in substrate concentration causes a diminishing increase in the reaction rate. A maximum rate is obtained at a certain substrate concentration where all enzymes are occupied by substrate. The react ...
... SUBSTRATE Concentration Effects Enzyme Activity Assuming the amount of enzyme is constant, an increase in substrate concentration causes a diminishing increase in the reaction rate. A maximum rate is obtained at a certain substrate concentration where all enzymes are occupied by substrate. The react ...
Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Reaction in Liver
... Name:_____________________________________________ Date:__________ Introduction: All organisms rely on enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions. An enzyme is a biological catalyst that increases the rate of chemical reaction by lowering the level of activation energy necessary to start the reaction. W ...
... Name:_____________________________________________ Date:__________ Introduction: All organisms rely on enzymes to catalyze chemical reactions. An enzyme is a biological catalyst that increases the rate of chemical reaction by lowering the level of activation energy necessary to start the reaction. W ...
Lecture * 4 The Kinetics of Enzyme
... • Reversible inhibitors are termed competitive if their presence increases the value of Km but does not alter vmax The effect of such inhibitors can be countered or reversed by increasing the substrate concentration. • On the other hand, by rendering the enzyme or the enzyme-substrate complex inacti ...
... • Reversible inhibitors are termed competitive if their presence increases the value of Km but does not alter vmax The effect of such inhibitors can be countered or reversed by increasing the substrate concentration. • On the other hand, by rendering the enzyme or the enzyme-substrate complex inacti ...
Fuel for the Future
... Instructing Concepts: (Fuel for the Future) Enzymes Enzymes: Enzymes are specialized proteins acting as “biological catalysts”. Proteins are organic compounds made of subunits known as amino acids. A protein is really a polymer containing 50 or more amino acids held together by peptide bonds. The s ...
... Instructing Concepts: (Fuel for the Future) Enzymes Enzymes: Enzymes are specialized proteins acting as “biological catalysts”. Proteins are organic compounds made of subunits known as amino acids. A protein is really a polymer containing 50 or more amino acids held together by peptide bonds. The s ...
Enzymes II – How Enzymes Work
... in metabolic pathways. Often, it is crucial for cells to regulate metabolic pathways very stringently, so that the product of a pathway is not produced in excess of what is needed by the cell. In many cases, allosteric enzymes catalyze early steps in a metabolic pathway. In addition, the end product ...
... in metabolic pathways. Often, it is crucial for cells to regulate metabolic pathways very stringently, so that the product of a pathway is not produced in excess of what is needed by the cell. In many cases, allosteric enzymes catalyze early steps in a metabolic pathway. In addition, the end product ...
Activity-Modeling_Cell_Respiration
... materials during decomposition. Tell them to pretend they are a cell in a decomposer, such as bacteria, yeast or mold cell, so they will be showing how the dead plant and animal material is used by the cell. There are lots of questions at the end of the model building activity. Provide students with ...
... materials during decomposition. Tell them to pretend they are a cell in a decomposer, such as bacteria, yeast or mold cell, so they will be showing how the dead plant and animal material is used by the cell. There are lots of questions at the end of the model building activity. Provide students with ...
Slide 1
... populations more than others. For example, the development of lactose-free milk available in Europe and North America would have greater benefit in Africa/ Asia where lactose intolerance is more prevalent. The development of techniques requires financial investment. Should knowledge be shared when t ...
... populations more than others. For example, the development of lactose-free milk available in Europe and North America would have greater benefit in Africa/ Asia where lactose intolerance is more prevalent. The development of techniques requires financial investment. Should knowledge be shared when t ...
Catalytic Strategies I
... a. Compares the rates of reactions one could perform without enzymes in a test tube with biological reaction rates using the enzymatic approach III. What role does Transition State stabilization play in enzyme catalysis [S4] a. There is a free energy to create a product known as DELTA-G. b. You have ...
... a. Compares the rates of reactions one could perform without enzymes in a test tube with biological reaction rates using the enzymatic approach III. What role does Transition State stabilization play in enzyme catalysis [S4] a. There is a free energy to create a product known as DELTA-G. b. You have ...
Enzymes
... to them before they can catalyse reactions Co-enzymes •Small, non-protein, organic “helper” molecules ...
... to them before they can catalyse reactions Co-enzymes •Small, non-protein, organic “helper” molecules ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... appears to level off as it approaches a maximum value with increase in substrate.This plateau is known as maximum velocity (V max). This behavior shows that at low substrate concentrations, the enzyme quickly converts all the substrate to product, but as more substrate is added, the enzyme becomes s ...
... appears to level off as it approaches a maximum value with increase in substrate.This plateau is known as maximum velocity (V max). This behavior shows that at low substrate concentrations, the enzyme quickly converts all the substrate to product, but as more substrate is added, the enzyme becomes s ...
is a substance that
... (water)from the individual molecules so that a bond may form between them and result in a more complex molecule is called ___________ ...
... (water)from the individual molecules so that a bond may form between them and result in a more complex molecule is called ___________ ...
PowerPoint
... (water)from the individual molecules so that a bond may form between them and result in a more complex molecule is called ___________ ...
... (water)from the individual molecules so that a bond may form between them and result in a more complex molecule is called ___________ ...
Document
... important point is that enzymes always change molecules. The term “chemical reaction” means a change in a molecule, so the best way to define enzymes is to say enzymes are proteins that carry out chemical reactions. Enzymes act as catalysts to increase the rates of chemical reactions. Without the en ...
... important point is that enzymes always change molecules. The term “chemical reaction” means a change in a molecule, so the best way to define enzymes is to say enzymes are proteins that carry out chemical reactions. Enzymes act as catalysts to increase the rates of chemical reactions. Without the en ...
Enzymes
... Metabolic pathways are often localized in cell • Cellular structures organize and concentrate components of enzymatic pathways – e.g. organelles (mitochondria, chloroplast, lysosomes) ...
... Metabolic pathways are often localized in cell • Cellular structures organize and concentrate components of enzymatic pathways – e.g. organelles (mitochondria, chloroplast, lysosomes) ...
Enzymes revision
... Properties of Enzymes: Enzymes are specific i.e. each enzyme will catalyse only one particular reaction, for example, sucrASE acts on the sugar, sucrOSE. Enzymes are very efficient and have a high TURNOVER NUMBER. • This means that they can convert many molecules of substrate per unit time, for exa ...
... Properties of Enzymes: Enzymes are specific i.e. each enzyme will catalyse only one particular reaction, for example, sucrASE acts on the sugar, sucrOSE. Enzymes are very efficient and have a high TURNOVER NUMBER. • This means that they can convert many molecules of substrate per unit time, for exa ...
1.4 Enzymes
... Properties of Enzymes: Enzymes are specific i.e. each enzyme will catalyse only one particular reaction, for example, sucrASE acts on the sugar, sucrOSE. Enzymes are very efficient and have a high TURNOVER NUMBER. • This means that they can convert many molecules of substrate per unit time, for exa ...
... Properties of Enzymes: Enzymes are specific i.e. each enzyme will catalyse only one particular reaction, for example, sucrASE acts on the sugar, sucrOSE. Enzymes are very efficient and have a high TURNOVER NUMBER. • This means that they can convert many molecules of substrate per unit time, for exa ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... urease catalyzed reaction occurs at a rate of 3 x 104 s-1 20 oC (half life of 23 microseconds) which represents close to 1014-fold acceleration in rate. ...
... urease catalyzed reaction occurs at a rate of 3 x 104 s-1 20 oC (half life of 23 microseconds) which represents close to 1014-fold acceleration in rate. ...
Analysis of Single Ionizing Group
... than the steady state Vmax The p-nitrophenol released in the initial pre-steady state 'burst' is stoichiometric to the concentration of active sites present (mole:mole) Rate then slows down to Vmax Suggests an initial phase of rapid acylation of chymotrypsin then a slow hydrolysis of acylenzyme inte ...
... than the steady state Vmax The p-nitrophenol released in the initial pre-steady state 'burst' is stoichiometric to the concentration of active sites present (mole:mole) Rate then slows down to Vmax Suggests an initial phase of rapid acylation of chymotrypsin then a slow hydrolysis of acylenzyme inte ...
Testing the activity of enzymes
... Once you and your colleagues have designed such an experiment, you must present it to your instructor who is a highly skilled biologist who can comment on your procedural outline and determine if you have designed an experiment that will answer your question and which adequately controls unwanted va ...
... Once you and your colleagues have designed such an experiment, you must present it to your instructor who is a highly skilled biologist who can comment on your procedural outline and determine if you have designed an experiment that will answer your question and which adequately controls unwanted va ...
Isomerase

Isomerases are a general class of enzymes which convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases can either facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed or they can catalyze conformational changes. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:A–B → B–AThere is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangements. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism.