Document
... An oversimplified (but less mind-bending for the symbolically challenged) way to look at this is that the equilibrium constant depends on the relative concentrations of the reactants (A and B) and products (C and D) at the point in the reaction where neither is changing any further. So a reaction’s ...
... An oversimplified (but less mind-bending for the symbolically challenged) way to look at this is that the equilibrium constant depends on the relative concentrations of the reactants (A and B) and products (C and D) at the point in the reaction where neither is changing any further. So a reaction’s ...
Testing the activity of enzymes
... The vast majority of enzymes are proteins. Their function is directly related to their very precise 3-D shape (configuration). If that 3-D shape is altered, the enzyme will not function. The enzyme and its substrate must fit together like a lock and key. In some cases, cells control the activity of ...
... The vast majority of enzymes are proteins. Their function is directly related to their very precise 3-D shape (configuration). If that 3-D shape is altered, the enzyme will not function. The enzyme and its substrate must fit together like a lock and key. In some cases, cells control the activity of ...
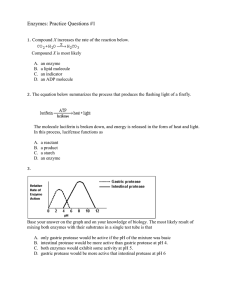
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
... The graph shows the relative rates of action of four enzymes, A, B, C, and D. A solution with a pH of 6 contains enzyme C and its substrate. If a base is gradually added to this solution, the rate of action of enzyme C would most likely A. B. C. D. ...
... The graph shows the relative rates of action of four enzymes, A, B, C, and D. A solution with a pH of 6 contains enzyme C and its substrate. If a base is gradually added to this solution, the rate of action of enzyme C would most likely A. B. C. D. ...
Chemical Reactions
... How many molecules are in a chemical formula/equation? Photosynthesis: Put a box around the products and circle reactants ...
... How many molecules are in a chemical formula/equation? Photosynthesis: Put a box around the products and circle reactants ...
Catalase enzyme lab
... Salt concentration: If the salt concentration is very low or zero, the charged amino acid side-chains of the enzyme will stick together. The enzyme will denature and form an inactive precipitate. If, on the other hand, the salt concentration is very high, normal interaction of charged groups will be ...
... Salt concentration: If the salt concentration is very low or zero, the charged amino acid side-chains of the enzyme will stick together. The enzyme will denature and form an inactive precipitate. If, on the other hand, the salt concentration is very high, normal interaction of charged groups will be ...
Harmless digestive enzyme evolved into venom in two species
... much more extreme compound that causes paralysis and death in prey that is bitten." In the first part of the study, Aminetzach and her A harmless digestive enzyme can be turned into a toxin colleagues compared a toxin found in the salivary glands of the insectivorous North American shrew in two unre ...
... much more extreme compound that causes paralysis and death in prey that is bitten." In the first part of the study, Aminetzach and her A harmless digestive enzyme can be turned into a toxin colleagues compared a toxin found in the salivary glands of the insectivorous North American shrew in two unre ...
Macromolecules Lab 1
... cells. A bacterium like E. coli has about 1,000 different types of enzymes floating around in the cytoplasm at any given time. Enzymes have extremely interesting properties that make them little chemical-reaction machines. The purpose of an enzyme in a cell is to allow the cell to carry out chemical ...
... cells. A bacterium like E. coli has about 1,000 different types of enzymes floating around in the cytoplasm at any given time. Enzymes have extremely interesting properties that make them little chemical-reaction machines. The purpose of an enzyme in a cell is to allow the cell to carry out chemical ...
week3-3
... the production of Isoleucine from Thereonine by Thereonine deaminase:• The end product acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme in the pathway. • When the product is abundant متوفر, the pathway is turned off, when rare قليلthe pathway is active. ...
... the production of Isoleucine from Thereonine by Thereonine deaminase:• The end product acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme in the pathway. • When the product is abundant متوفر, the pathway is turned off, when rare قليلthe pathway is active. ...
Exploration Activity: Enzymes
... Graph (a) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of temperatures? Graph (b) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of temperatures? Graph (c) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of pH? Graph (d) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of pH? ...
... Graph (a) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of temperatures? Graph (b) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of temperatures? Graph (c) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of pH? Graph (d) shows that this enzyme will work best at what type of pH? ...
Enzymology Lecture 5 - ASAB-NUST
... The plot of v versus [S] is not linear; although initially linear at low [S], it bends over to saturate at high [S]. Before the modern era of nonlinear curve-fitting on computers, this nonlinearity could make it difficult to estimate KM and Vmax accurately. Therefore, several researchers developed l ...
... The plot of v versus [S] is not linear; although initially linear at low [S], it bends over to saturate at high [S]. Before the modern era of nonlinear curve-fitting on computers, this nonlinearity could make it difficult to estimate KM and Vmax accurately. Therefore, several researchers developed l ...
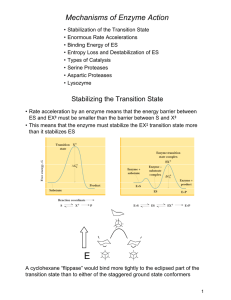
Mechanisms of Enzyme Action - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... which increases the sites available to S • Ligands such as S are positive homotropic effectors • Molecules that influence the binding of something other than themselves are heterotropic effectors ...
... which increases the sites available to S • Ligands such as S are positive homotropic effectors • Molecules that influence the binding of something other than themselves are heterotropic effectors ...
Epjj Lecture 4
... of the inhibitor. The concentration of S which will be required to overcome the effect of the competitive inhibitor will depend on the [Ic] (ie. concentration of the competitive inhibitor) and the Ki (ie. the binding constant of the inhibitor to enzyme). ...
... of the inhibitor. The concentration of S which will be required to overcome the effect of the competitive inhibitor will depend on the [Ic] (ie. concentration of the competitive inhibitor) and the Ki (ie. the binding constant of the inhibitor to enzyme). ...
Today: Membrane Structure continued Membrane Transport Exam
... intermediates. Phosphorylation usually makes a molecule less stable/more reactive. ...
... intermediates. Phosphorylation usually makes a molecule less stable/more reactive. ...
Chapter 6
... • ATP not suitable for long term energy storage – Fats and carbohydrates better – Cells store only a few seconds worth of ATP ...
... • ATP not suitable for long term energy storage – Fats and carbohydrates better – Cells store only a few seconds worth of ATP ...
Topic 16 IB Chemistry Definitions
... The rate is always proportional to the concentration of a reactant raised to a power, where the power is the order of the reaction with respect to that reactant. The constant of proportionality in the rate expression. Unit is: (mol dm-3)1 – overall order ...
... The rate is always proportional to the concentration of a reactant raised to a power, where the power is the order of the reaction with respect to that reactant. The constant of proportionality in the rate expression. Unit is: (mol dm-3)1 – overall order ...
1. What are enzymes? Be able to describe the chemical nature of
... Lactate Dehydrogenase: The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the removal of hydrogen from L-lactate but not from D-lactate. ...
... Lactate Dehydrogenase: The enzyme lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the removal of hydrogen from L-lactate but not from D-lactate. ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Enzyme Activity
... I. ARE ENZYMES SPECIFIC AND WHAT IS MEANT BY LOCK AND KEY MECHANISM? An enzyme and four different molecules are shown in the diagram below: ...
... I. ARE ENZYMES SPECIFIC AND WHAT IS MEANT BY LOCK AND KEY MECHANISM? An enzyme and four different molecules are shown in the diagram below: ...
metabolism - Chavis Biology
... increase in the reaction rate. Reaction rate will eventually level off as all available substrates are used up. Draw this: ...
... increase in the reaction rate. Reaction rate will eventually level off as all available substrates are used up. Draw this: ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Analysis of Single Ionizing Group
... the stoichiometric release of one of the products that is much faster than the steady state Vmax The p-nitrophenol released in the initial pre-steady state 'burst' is stoichiometric to the concentration of active sites present (mole:mole) Rate then slows down to Vmax Suggests an initial phase of rap ...
... the stoichiometric release of one of the products that is much faster than the steady state Vmax The p-nitrophenol released in the initial pre-steady state 'burst' is stoichiometric to the concentration of active sites present (mole:mole) Rate then slows down to Vmax Suggests an initial phase of rap ...
Ch.08An Introduction to Metabolism
... (b) Mechanical work: ATP binds noncovalently to motor proteins, then is hydrolyzed ...
... (b) Mechanical work: ATP binds noncovalently to motor proteins, then is hydrolyzed ...
Bio1A Unit 1-5 Metabolism Notes File
... Metabolism Metabolic Pathway: series of steps from reactants to products, usually enzyme catlyzed Enzyme 1 A ...
... Metabolism Metabolic Pathway: series of steps from reactants to products, usually enzyme catlyzed Enzyme 1 A ...
biochemistry 14_15 - Pleasantville High School
... It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between en ...
... It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between en ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.