Boardworks Enzyme Inhibitors
... Uses of inhibitors: drugs The antibiotics penicillin and vancomycin inhibit enzymes involved in the production of bacterial cell walls. Methotrexate is used in the treatment of cancer and some autoimmune diseases. It inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved with the metabolism ...
... Uses of inhibitors: drugs The antibiotics penicillin and vancomycin inhibit enzymes involved in the production of bacterial cell walls. Methotrexate is used in the treatment of cancer and some autoimmune diseases. It inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which is involved with the metabolism ...
Fuel for the Future
... the MnO2 itself is broken down to form the oxygen ). Enzymes as catalysts are capable of increasing the reaction rate by as much as 1020. They are able to do this in many ways: reduce the activation energy, reduce energy of transition state, temporarily react with the chemical creating a compound fo ...
... the MnO2 itself is broken down to form the oxygen ). Enzymes as catalysts are capable of increasing the reaction rate by as much as 1020. They are able to do this in many ways: reduce the activation energy, reduce energy of transition state, temporarily react with the chemical creating a compound fo ...
MACROMOLECULES OF LIFE
... Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and ...
... Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and ...
MACROMOLECULES OF LIFE
... Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and ...
... Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and ...
Enzymes
... Catalytic activity of Allosteric enzymes: Regulated through reversible binding of endproduct to a site other than the active site Feedback relations may be very complex if branched pathways are involved In branched pathway first enzyme after branch is usually the allosteric enzyme ...
... Catalytic activity of Allosteric enzymes: Regulated through reversible binding of endproduct to a site other than the active site Feedback relations may be very complex if branched pathways are involved In branched pathway first enzyme after branch is usually the allosteric enzyme ...
Enzymes - stephen fleenor
... Watch the video, and complete the following sentence in your notebook: Two abiotic factors which can denature enzymes are ________ and __________. https://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation _4145881127&feature=iv&src_vid=XUn64HY5bug&v=qgV FkRn8f10 ...
... Watch the video, and complete the following sentence in your notebook: Two abiotic factors which can denature enzymes are ________ and __________. https://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation _4145881127&feature=iv&src_vid=XUn64HY5bug&v=qgV FkRn8f10 ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products. ...
... • Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of new bonds in products. ...
Enzymes: Molecules That Speed Up Reactions - juan-roldan
... which is the energy required to break down existing bonds between atoms Enzymes speed up two types of reactions: 1. Exergonic Reactions 2. Endergonic Reactions ...
... which is the energy required to break down existing bonds between atoms Enzymes speed up two types of reactions: 1. Exergonic Reactions 2. Endergonic Reactions ...
Enzyme Notes
... A. All reactions require some energy to start: activation energy. Example: if some reactions that release energy did not require activation energy, what could happen to the pages of your text book as you sit here reading? They could spontaneously combust into flames. ...
... A. All reactions require some energy to start: activation energy. Example: if some reactions that release energy did not require activation energy, what could happen to the pages of your text book as you sit here reading? They could spontaneously combust into flames. ...
Review of Biochemistry
... function is usually about 35-40 C. • reactions proceed slowly below optimal temperatures • above 45 C most enzymes are denatured (change in their shape so the enzyme active site no longer fits with the substrate and the enzyme can't function) ...
... function is usually about 35-40 C. • reactions proceed slowly below optimal temperatures • above 45 C most enzymes are denatured (change in their shape so the enzyme active site no longer fits with the substrate and the enzyme can't function) ...
Effect of Catalase Concentration on the
... Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts in a wide variety of lifesustaining chemical reactions that take place in cells. As catalysts, enzymes lower the amount of energy required to make a reaction occur. We call this energy the activation ...
... Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts in a wide variety of lifesustaining chemical reactions that take place in cells. As catalysts, enzymes lower the amount of energy required to make a reaction occur. We call this energy the activation ...
Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide
... Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts in a wide variety of lifesustaining chem-ical reactions that take place in cells. As catalysts, enzymes lower the amount of energy required to make a reaction occur. We call this energy the activatio ...
... Measuring the Effect of Enzyme Concentration Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts in a wide variety of lifesustaining chem-ical reactions that take place in cells. As catalysts, enzymes lower the amount of energy required to make a reaction occur. We call this energy the activatio ...
Biochemistry 3100 Sample Problems Binding proteins, Kinetics & Catalysis eg
... (a) Draw and label a single graph, indicating the approximate O2 binding curves for both myoglobin and hemoglobin. (b) Draw and label a single graph, representing the Hill plot for the binding of O2 to both proteins. (3) What is cooperativity and how is it quantified. (4) Derive the equilibrium expr ...
... (a) Draw and label a single graph, indicating the approximate O2 binding curves for both myoglobin and hemoglobin. (b) Draw and label a single graph, representing the Hill plot for the binding of O2 to both proteins. (3) What is cooperativity and how is it quantified. (4) Derive the equilibrium expr ...
Document
... Enzymes, which are a type of protein, are biological catalysts found in all living things. What do enzymes do? An enzyme’s job is to change molecules. An enzyme may add atoms to a molecule, remove atoms from a molecule, split a large molecule into two smaller molecules, or join together smaller mole ...
... Enzymes, which are a type of protein, are biological catalysts found in all living things. What do enzymes do? An enzyme’s job is to change molecules. An enzyme may add atoms to a molecule, remove atoms from a molecule, split a large molecule into two smaller molecules, or join together smaller mole ...
Pre-‐lab AP Lab: Enzyme Catalysis Name
... For example, suppose you wanted to compare the effectiveness of catalase obtained from potato with that of catalase obtained from liver. Would you want to compare the two reactions during the first few minutes when the rate is constant or later when the rates are changing? Answer: It is best to comp ...
... For example, suppose you wanted to compare the effectiveness of catalase obtained from potato with that of catalase obtained from liver. Would you want to compare the two reactions during the first few minutes when the rate is constant or later when the rates are changing? Answer: It is best to comp ...
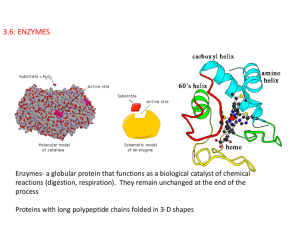
3.6: ENZYMES
... Enzyme action is influenced by pH because the amino acids that make up an enzyme contain many +/- regions, some around the active site. An excess of H+ ions in an acidic solution can lead to bonding between the H+ ions and the negative charges in the active site. (same with OH- in basic solutions wh ...
... Enzyme action is influenced by pH because the amino acids that make up an enzyme contain many +/- regions, some around the active site. An excess of H+ ions in an acidic solution can lead to bonding between the H+ ions and the negative charges in the active site. (same with OH- in basic solutions wh ...
Catalase OR Re
... ______°C (degrees), there is _____ reaction. d. Explain why temperature affects catalase activity in the way you described in part (c). The function of an enzyme is to _________________ the rate of a reaction. When the temperature is too _________, the enzyme ___________ function. This is because th ...
... ______°C (degrees), there is _____ reaction. d. Explain why temperature affects catalase activity in the way you described in part (c). The function of an enzyme is to _________________ the rate of a reaction. When the temperature is too _________, the enzyme ___________ function. This is because th ...
ENZYME ACTIVITY LAB What factors affect enzyme activity? Please
... chemical, into 2 harmless substances--water and oxygen. The reaction is: 2 H2O2 ----> 2 H2O + O2 This reaction is important to cells because hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced as a byproduct of many normal cellular reactions. If the cells did not break down the hydrogen peroxide, they would be poi ...
... chemical, into 2 harmless substances--water and oxygen. The reaction is: 2 H2O2 ----> 2 H2O + O2 This reaction is important to cells because hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced as a byproduct of many normal cellular reactions. If the cells did not break down the hydrogen peroxide, they would be poi ...
this lecture as PDF here
... Enzymes undergo physical changes during the reaction but revert to their original form at the end of the reaction. ...
... Enzymes undergo physical changes during the reaction but revert to their original form at the end of the reaction. ...
... acir alone and in combination with other natural ingredients an weight loss . The study was conducted under controlled circumstances on 60 moderately obese subjects . The findings afte ; 8 weeks of HCA supplemertation were that appetite, Body Mass Index, total cholesterol, low- density lipoproteins, ...
What Are Enzymes?
... enzyme or inhibitory protein). (3) Phosphorylation is a good example of how enzymes are activated and inactivated by covalent post-translational ...
... enzyme or inhibitory protein). (3) Phosphorylation is a good example of how enzymes are activated and inactivated by covalent post-translational ...
Enzymes II – How Enzymes Work
... enzymes. Allosteric enzymes are enzymes with multiple binding sites. Often, these binding sites are found on different subunits of the enzyme. In other words, many allosteric enzymes have quaternary structure. Some of the binding sites on an allosteric enzyme are active, or catalytic, sites and bind ...
... enzymes. Allosteric enzymes are enzymes with multiple binding sites. Often, these binding sites are found on different subunits of the enzyme. In other words, many allosteric enzymes have quaternary structure. Some of the binding sites on an allosteric enzyme are active, or catalytic, sites and bind ...
Chemistry 326 Name_____________________ Fall 2009 Check
... _____i. TPP is involved in redox reactions. _____j. Biotin and lipoic acid must be covalently bound to the enzyme to function. _____k. Enzymes are generally comparable in size to the substrates on which they act. _____l. Enzymes can be classed on the basis of the types of reactions they catalyze. __ ...
... _____i. TPP is involved in redox reactions. _____j. Biotin and lipoic acid must be covalently bound to the enzyme to function. _____k. Enzymes are generally comparable in size to the substrates on which they act. _____l. Enzymes can be classed on the basis of the types of reactions they catalyze. __ ...
White Cell Enzymes
... Pipette sonicate dilutions into tubes. 7 patients = >200 individual tubes. Start enzyme reaction by timed addition of appropriate substrate. Incubation times depend on enzyme. Stop reactions at same timed intervals by addition of an inhibitor ...
... Pipette sonicate dilutions into tubes. 7 patients = >200 individual tubes. Start enzyme reaction by timed addition of appropriate substrate. Incubation times depend on enzyme. Stop reactions at same timed intervals by addition of an inhibitor ...
UNIT 2: The Chemistry of Life
... 3. Which of the chemical reactions has a lower activation energy in the graph above, the catalyzed or the uncatalyzed reaction? ______________________________________ 4. Which of the chemical reactions (catalyzed of uncatalyzed) in the graph above will happen at a faster rate? ______________________ ...
... 3. Which of the chemical reactions has a lower activation energy in the graph above, the catalyzed or the uncatalyzed reaction? ______________________________________ 4. Which of the chemical reactions (catalyzed of uncatalyzed) in the graph above will happen at a faster rate? ______________________ ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.