Enzymes: Biological Catalysts
... Michaelis-Menten Kinetics • Equation above represents the minimal equation needed to describe a simple one-substrate, one-product reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. • This assumes the reverse reaction between E and P is negligible and is a simple, first-order reaction whose rate is determined by [ES] ...
... Michaelis-Menten Kinetics • Equation above represents the minimal equation needed to describe a simple one-substrate, one-product reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. • This assumes the reverse reaction between E and P is negligible and is a simple, first-order reaction whose rate is determined by [ES] ...
Bio Boot Camp - Tredyffrin/Easttown School District
... A scientist observed that, when the pH of the environment surrounding an enzyme is changed the rate the enzyme catalyzes a reaction greatly decreases. Which statement best describes how a change in pH can affect an enzyme? ...
... A scientist observed that, when the pH of the environment surrounding an enzyme is changed the rate the enzyme catalyzes a reaction greatly decreases. Which statement best describes how a change in pH can affect an enzyme? ...
Lecture Resource ()
... Important Features that Contribute to the Catalytic Ability of Enzymes • Reacting groups are brought together at the active site in the proper orientation for reaction • Some of the amino acids in the enzyme serve as catalytic groups; many enzymes have metal ions as catalysts • Groups on the enzyme ...
... Important Features that Contribute to the Catalytic Ability of Enzymes • Reacting groups are brought together at the active site in the proper orientation for reaction • Some of the amino acids in the enzyme serve as catalytic groups; many enzymes have metal ions as catalysts • Groups on the enzyme ...
Experiment 7 (Lab Period 8) Quantitative Determination of
... Influence of pH on phosphatase activity: For most enzymes, pH can influences the catalytic site directly by altering the charge of the protein in this region. The pH will also affect tertiary structure of the enzyme, and may also affect the ability of the enzyme to bind ("embrace") the substrate. As ...
... Influence of pH on phosphatase activity: For most enzymes, pH can influences the catalytic site directly by altering the charge of the protein in this region. The pH will also affect tertiary structure of the enzyme, and may also affect the ability of the enzyme to bind ("embrace") the substrate. As ...
8 Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity NOTES I. Pepsin a
... Which statement best expresses the amount of product that will be formed at each temperature if the experiment is repeated at a pH of 4? (1) The amount of product formed will be equal to that produced at pH 6. (2) The amount of product formed will be greater than that produced at pH 6. (3) The amoun ...
... Which statement best expresses the amount of product that will be formed at each temperature if the experiment is repeated at a pH of 4? (1) The amount of product formed will be equal to that produced at pH 6. (2) The amount of product formed will be greater than that produced at pH 6. (3) The amoun ...
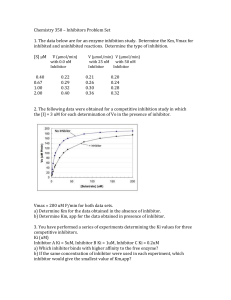
Chemistry 350 – Inhibitors Problem Set 1. The data below are for an
... c) If the value for Km is 1 uM, what is the ratio of Ki/Km for each inhibitor? How is this related to the competing equilibria for binding of the substrate vs. the inhibitor to the enzyme? 4. An enzyme is discovered to be implicated in a disease process. The enzyme is known to have Km = 1.0 mM, and ...
... c) If the value for Km is 1 uM, what is the ratio of Ki/Km for each inhibitor? How is this related to the competing equilibria for binding of the substrate vs. the inhibitor to the enzyme? 4. An enzyme is discovered to be implicated in a disease process. The enzyme is known to have Km = 1.0 mM, and ...
Reagent Grade Enzymes for Nitrate Determination
... Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts. They tend to be large and complex molecules, often with attached “cofactors” that facilitate catalytic function. Some B vitamins are enzyme cofactors; others are metal complexes such as hemoglobin or chlorophyll. Enzymes are named and grouped by catal ...
... Enzymes are proteins that function as catalysts. They tend to be large and complex molecules, often with attached “cofactors” that facilitate catalytic function. Some B vitamins are enzyme cofactors; others are metal complexes such as hemoglobin or chlorophyll. Enzymes are named and grouped by catal ...
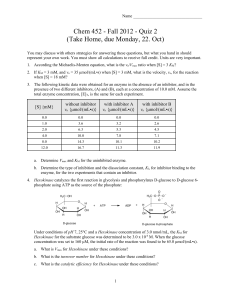
Chem452_Quiz_2
... Under conditions of pH 7, 25°C and a Hexokinase concentration of 3.0 nmol/mL, the KM for Hexokinase for the substrate glucose was determined to be 3.0 x 10-4 M. When the glucose concentration was set to 160 μΜ, the initial rate of the reaction was found to be 65.0 μmol/(mL•s). a. What is Vmax for He ...
... Under conditions of pH 7, 25°C and a Hexokinase concentration of 3.0 nmol/mL, the KM for Hexokinase for the substrate glucose was determined to be 3.0 x 10-4 M. When the glucose concentration was set to 160 μΜ, the initial rate of the reaction was found to be 65.0 μmol/(mL•s). a. What is Vmax for He ...
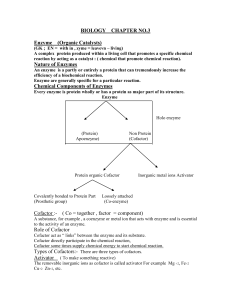
Nature of Enzymes
... Induce – Fit Model :Daniel Koshland proposed his induce fit theory to explain mechanism of enzyme Action (1959) “ According to this theory when a substrate combines with an enzyme, it induce (produces ) changes in the enzyme structure.” The change in structure allows the enzyme to perform its cataly ...
... Induce – Fit Model :Daniel Koshland proposed his induce fit theory to explain mechanism of enzyme Action (1959) “ According to this theory when a substrate combines with an enzyme, it induce (produces ) changes in the enzyme structure.” The change in structure allows the enzyme to perform its cataly ...
Extra slides (lecture Wed. 11/4)
... One biologically important use of proteases: to cleave inactive proenzymes (or zymogens) to produce the mature, active form of an enzyme In some cases, such cleavages act one after another on a series of enzymes. This leads to a ‘cascade’, which can produce a geometric explosion of enzymatic activi ...
... One biologically important use of proteases: to cleave inactive proenzymes (or zymogens) to produce the mature, active form of an enzyme In some cases, such cleavages act one after another on a series of enzymes. This leads to a ‘cascade’, which can produce a geometric explosion of enzymatic activi ...
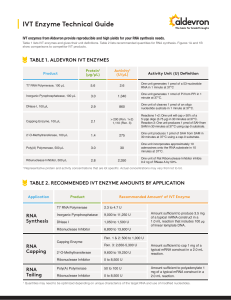
IVT Enzyme Technical Guide
... Inorganic Pyrophosphatase activity was determined by measuring the formation of a phosphate-molybdate complex in the presence of reducing agent and inorganic pyrophosphate as substrate. Ribonuclease Inhibitor inhibits the catalytic activity of RNase A and its homologs. One unit of Ribonuclease Inhib ...
... Inorganic Pyrophosphatase activity was determined by measuring the formation of a phosphate-molybdate complex in the presence of reducing agent and inorganic pyrophosphate as substrate. Ribonuclease Inhibitor inhibits the catalytic activity of RNase A and its homologs. One unit of Ribonuclease Inhib ...
Matter is anything which has mass and takes up space
... the iodine because the enzyme has converted all of the starch to maltose. 7. Test both test tubes with Benedict’s solution. 8. A shows no reaction to it. 9. B changes the blue benedict’s solution to brick red. This shows that test tube B now contains sugar. This must be due to the presence of the en ...
... the iodine because the enzyme has converted all of the starch to maltose. 7. Test both test tubes with Benedict’s solution. 8. A shows no reaction to it. 9. B changes the blue benedict’s solution to brick red. This shows that test tube B now contains sugar. This must be due to the presence of the en ...
SG 4,5,6,11
... transitions, effectors and modulators. What is positive cooperativity; know an example. Discuss denaturation, what causes it, how it causes it, can it be reversed. Chapter 6 What is an enzyme and importance to living systems? How do catalysts effect reaction rate, quantify? Discuss effect in terms o ...
... transitions, effectors and modulators. What is positive cooperativity; know an example. Discuss denaturation, what causes it, how it causes it, can it be reversed. Chapter 6 What is an enzyme and importance to living systems? How do catalysts effect reaction rate, quantify? Discuss effect in terms o ...
Case 39 Inhibition of Alcohol Dehydrogenase Focus concept The
... ordered bisubstrate mechanism. The mechanism is diagramed in Figure 39.2; use the diagram to write a description of the mechanism. How does N-1,5-dimethylhexylformamide inhibit the activity of the ADH enzyme? How does N-1,5-dimethylhexylformamide differ from the “classic” inhibitors of this type tha ...
... ordered bisubstrate mechanism. The mechanism is diagramed in Figure 39.2; use the diagram to write a description of the mechanism. How does N-1,5-dimethylhexylformamide inhibit the activity of the ADH enzyme? How does N-1,5-dimethylhexylformamide differ from the “classic” inhibitors of this type tha ...
Macromolecules ppt
... Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and ...
... Building blocks of all cells Made up of the atoms: Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and ...
Proteins Act As Catalysts
... • Inhibitor binds only to free enzyme (E) not (ES) • Substrate cannot bind when I is bound at active site (S and I “compete” for the enzyme active site) • Vmax is the same with or without I (high S can still saturate the enzyme even in the presence of I) • Apparent KM (KMapp) measured in the presenc ...
... • Inhibitor binds only to free enzyme (E) not (ES) • Substrate cannot bind when I is bound at active site (S and I “compete” for the enzyme active site) • Vmax is the same with or without I (high S can still saturate the enzyme even in the presence of I) • Apparent KM (KMapp) measured in the presenc ...
Document
... group. Right next to it. Right there. Right there where it should be. The rate constant goes from 6x10-6 to 1.5x10-5. The increase is 2x1011. And that is similar to what enzymes do. They force the substrate into a confirmation that resembles a transition state or resembles something that has to reac ...
... group. Right next to it. Right there. Right there where it should be. The rate constant goes from 6x10-6 to 1.5x10-5. The increase is 2x1011. And that is similar to what enzymes do. They force the substrate into a confirmation that resembles a transition state or resembles something that has to reac ...
Effect of Temp on Enzyme Activity Pre-Lab
... Increases in the temperature of a system results from increases in the kinetic energy of the system (meaning the molecules move around more) 1) More energetic collisions between Molecules When molecules collide, the kinetic energy of the molecules can be great enough to reach the activation energy o ...
... Increases in the temperature of a system results from increases in the kinetic energy of the system (meaning the molecules move around more) 1) More energetic collisions between Molecules When molecules collide, the kinetic energy of the molecules can be great enough to reach the activation energy o ...
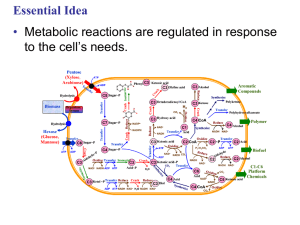
8.1 Metabolism
... 1. This is changed to product 1. • Enzyme (2) is specific to product1 which becomes the substrate and converted to product 2. • Enzyme (3) is specific to products which becomes the substrate and converted t o product 3. ...
... 1. This is changed to product 1. • Enzyme (2) is specific to product1 which becomes the substrate and converted to product 2. • Enzyme (3) is specific to products which becomes the substrate and converted t o product 3. ...
ETA Position Paper Biotechnology, Enzymes and Allergies
... all living cells produce and need enzymes to live and grow. However, enzymes themselves are not living organisms. Enzymes are catalysts: substances which speed up chemical reactions by being present in very small amounts and without being changed in the reaction. What is an allergy? The purpose of t ...
... all living cells produce and need enzymes to live and grow. However, enzymes themselves are not living organisms. Enzymes are catalysts: substances which speed up chemical reactions by being present in very small amounts and without being changed in the reaction. What is an allergy? The purpose of t ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... isoenzymes CYP3A4 plays a major role in metabolism of xenobiotics as it is the most abundant CYP in human liver (approx. 28 %) and it is involved in metabolism of more than 50 % of all pharmaceuticals applied in present-day medication. SupersomesTM (human recombinant enzymes) are microsomes prepared ...
... isoenzymes CYP3A4 plays a major role in metabolism of xenobiotics as it is the most abundant CYP in human liver (approx. 28 %) and it is involved in metabolism of more than 50 % of all pharmaceuticals applied in present-day medication. SupersomesTM (human recombinant enzymes) are microsomes prepared ...
File
... • Enzymes are a specific type of protein (polypeptide) • Quaternary level structure • Speed up all types of chemical reactions by reducing the activation energy required • Do not get destroyed during reactions, but get re-used over and over again. • Are highly specific in their behavior which is det ...
... • Enzymes are a specific type of protein (polypeptide) • Quaternary level structure • Speed up all types of chemical reactions by reducing the activation energy required • Do not get destroyed during reactions, but get re-used over and over again. • Are highly specific in their behavior which is det ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.