Protein practice MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one
... 19) The minimum energy that reactants need in order for the molecules to be in the correct orientation is called: A) collision energy B) dissociation energy C) activation energy D) orientation energy ...
... 19) The minimum energy that reactants need in order for the molecules to be in the correct orientation is called: A) collision energy B) dissociation energy C) activation energy D) orientation energy ...
T7-O-me-RNA-Polymerase
... aptamers, in particular as an active agent in innovative therapeutic approaches. However, these applications require the modification of RNA which otherwise shows poor resistance to cellular nucleases. To this end, typically the ribose 2´hydroxyl moieties are substituted by O-methyl groups. This ste ...
... aptamers, in particular as an active agent in innovative therapeutic approaches. However, these applications require the modification of RNA which otherwise shows poor resistance to cellular nucleases. To this end, typically the ribose 2´hydroxyl moieties are substituted by O-methyl groups. This ste ...
amino acid
... •Reactants have more energy than the products •Reactants are larger, less stable, and more complex than products •More energy is released when new bonds are formed in the products than was needed to break the old bonds in the reactants ...
... •Reactants have more energy than the products •Reactants are larger, less stable, and more complex than products •More energy is released when new bonds are formed in the products than was needed to break the old bonds in the reactants ...
Name: ENZYME FUNCTION LAB 9 PURPOSE To explore the role of
... Hydrogen peroxide is stored in a brown bottle to deep out light, which speeds up this reaction. Certain chemicals can also dramatically increase the speed at which this reaction takes place. In this lab you will work with some of them. Caution: Be careful not to get the hydrogen peroxide on your ski ...
... Hydrogen peroxide is stored in a brown bottle to deep out light, which speeds up this reaction. Certain chemicals can also dramatically increase the speed at which this reaction takes place. In this lab you will work with some of them. Caution: Be careful not to get the hydrogen peroxide on your ski ...
General Biology I (BIOLS 102)
... Accomplished by bringing the substrates into contact with one another under mild conditions Does not get consumed by the reaction nor does it alter the equilibrium of the reaction, thus it remains intact ...
... Accomplished by bringing the substrates into contact with one another under mild conditions Does not get consumed by the reaction nor does it alter the equilibrium of the reaction, thus it remains intact ...
Enzymes: The Biological Catalysts of Life
... activation energy. A simple and succinct definition of an enzyme is that it is a biological catalyst that accelerates a chemical reaction without altering its equilibrium. During the reactions the enzymes themselves undergo transient changes. In the overall process, enzymes do not undergo any net ch ...
... activation energy. A simple and succinct definition of an enzyme is that it is a biological catalyst that accelerates a chemical reaction without altering its equilibrium. During the reactions the enzymes themselves undergo transient changes. In the overall process, enzymes do not undergo any net ch ...
Enzymes what are they
... 2. Explain how the structure of the protein is linked to its ability to act as an enzyme? 3. How does heating a mixture increase the chance that a chemical reaction Will occur? Why can’t this approach be used in cells? 4. Write a paragraph in your own words describing how enzymes act as catalysts by ...
... 2. Explain how the structure of the protein is linked to its ability to act as an enzyme? 3. How does heating a mixture increase the chance that a chemical reaction Will occur? Why can’t this approach be used in cells? 4. Write a paragraph in your own words describing how enzymes act as catalysts by ...
Pinpointing dynamic coupling in enzymes for efficient drug design
... increase of ∼10%, and the catalytic properties of this heavy enzyme are compared with the natural light version [11,12] . Isotope substitution does not change the chemistry of the catalyzed reaction but slows motions of the catalyst, from femtosecond bond vibrational frequencies through millisecond ...
... increase of ∼10%, and the catalytic properties of this heavy enzyme are compared with the natural light version [11,12] . Isotope substitution does not change the chemistry of the catalyzed reaction but slows motions of the catalyst, from femtosecond bond vibrational frequencies through millisecond ...
Active Transport - stephen fleenor
... Internal Membranes Membrane-bound organelles also help organize chemical reactions. ...
... Internal Membranes Membrane-bound organelles also help organize chemical reactions. ...
Enzymes
... Classwork 2.3: Enzymes • You will have 15 minutes to work on this assignment. • Graded for accuracy! ...
... Classwork 2.3: Enzymes • You will have 15 minutes to work on this assignment. • Graded for accuracy! ...
Name: Date: ______ Block: ______ ENZYMES A CATALYST is a
... A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of ACTIVATION ENERGY needed to start that reaction. ENZYMES are the biological molecules (proteins or RNA) that act as catalysts in a living organism. The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to relea ...
... A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of ACTIVATION ENERGY needed to start that reaction. ENZYMES are the biological molecules (proteins or RNA) that act as catalysts in a living organism. The seemingly simple act of breaking down food molecules to relea ...
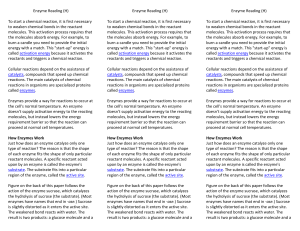
Enzyme Reading - BizierDiemHonorsBiology
... As with any other protein, an enzyme's structure and shape are essential to its function. And like other proteins, an enzyme's shape is sensitive to changes in its surrounding environment. Therefore, factors such as pH and temperature can greatly affect how well an enzyme works or if it can work at ...
... As with any other protein, an enzyme's structure and shape are essential to its function. And like other proteins, an enzyme's shape is sensitive to changes in its surrounding environment. Therefore, factors such as pH and temperature can greatly affect how well an enzyme works or if it can work at ...
which pennies are turned over by pennyase?
... Name: ___________________________________________ Date: ___________ Pd: _____ ...
... Name: ___________________________________________ Date: ___________ Pd: _____ ...
Amylase Experiment
... and Tables. The figures should be very clearly labeled and each should have a descriptive title. The Discussion section should report any difficulties with the experiment and any conclusions. Was Vmax established for your sample? How do you know? If not, what is your estimate of the true Vmax? Is yo ...
... and Tables. The figures should be very clearly labeled and each should have a descriptive title. The Discussion section should report any difficulties with the experiment and any conclusions. Was Vmax established for your sample? How do you know? If not, what is your estimate of the true Vmax? Is yo ...
Enzyme Review Sheet
... reaction can proceed. In a synthesizing reaction, before the reactants can combine, a little energy has to be added to overcome the mutual repulsion of the negatively-charged electron clouds surrounding the atoms. Activation energy is often supplied in the form of heat that the reactants absorb from ...
... reaction can proceed. In a synthesizing reaction, before the reactants can combine, a little energy has to be added to overcome the mutual repulsion of the negatively-charged electron clouds surrounding the atoms. Activation energy is often supplied in the form of heat that the reactants absorb from ...
Biology Chapter 2 Test Review Questions
... Compare enzyme activity to a lock and key? The enzyme has an active site which symbolizes the lock and the key would be the substrate that fits into the active site of the enzyme. Without a perfect match, the chemical reaction cannot occur. Likewise, without the right key, the lock cannot open. ...
... Compare enzyme activity to a lock and key? The enzyme has an active site which symbolizes the lock and the key would be the substrate that fits into the active site of the enzyme. Without a perfect match, the chemical reaction cannot occur. Likewise, without the right key, the lock cannot open. ...
Review for Practical (Solutions) Enzyme A will outcompete Enzyme
... (98 g)/(1.87 g/ml) = 52.4 ml. So, I’d add 52.4 ml to water and bring the volume up to 1 L. Percentages: 98g/1000 ml = 9.8g/100 ml = 9.8%(w/v); 52.4 ml/1000 ml = 5.24 ml/100 ml = 5.24% (v/v) Normality: 1 M solution = 3N ...
... (98 g)/(1.87 g/ml) = 52.4 ml. So, I’d add 52.4 ml to water and bring the volume up to 1 L. Percentages: 98g/1000 ml = 9.8g/100 ml = 9.8%(w/v); 52.4 ml/1000 ml = 5.24 ml/100 ml = 5.24% (v/v) Normality: 1 M solution = 3N ...
Enzymes Notes #2- Enzyme Substrate Complexes and Factors
... Enzymes are specific for one particular reaction or group of related reactions. Many reactions cannot occur without the correct enzyme present. They are often named by adding “ASE" to the name of the substrate. Example: Dehydrogenases are enzymes that remove hydrogen. ...
... Enzymes are specific for one particular reaction or group of related reactions. Many reactions cannot occur without the correct enzyme present. They are often named by adding “ASE" to the name of the substrate. Example: Dehydrogenases are enzymes that remove hydrogen. ...
The effect of calcium on conformational change of thimet
... same conditions, the overall enzyme efficiency is opposite for the different substrates, while the effect of calcium on binding affinity does not change. The mca-NT substrate is a special case. The C-terminal of this peptide has been modified from a COO- to NH2, which changes how it interacts with t ...
... same conditions, the overall enzyme efficiency is opposite for the different substrates, while the effect of calcium on binding affinity does not change. The mca-NT substrate is a special case. The C-terminal of this peptide has been modified from a COO- to NH2, which changes how it interacts with t ...
Pepsin and Salivary Amylase Activity at Different pH Values
... Biology students investigated various human digestive enzymes. The table below summarizes the functions of several different digestive enzymes. Enzyme ...
... Biology students investigated various human digestive enzymes. The table below summarizes the functions of several different digestive enzymes. Enzyme ...
lecture3
... hence may either intensify or tend to nullify allosteric regulatory effects. Regulation by covalent modulation is well documented in animals. In mammalian systems, the 2 most common forms of covalent modification are Partial proteolysis and Phosphorylation and De-phosphorylation. B/C Cells lack the ...
... hence may either intensify or tend to nullify allosteric regulatory effects. Regulation by covalent modulation is well documented in animals. In mammalian systems, the 2 most common forms of covalent modification are Partial proteolysis and Phosphorylation and De-phosphorylation. B/C Cells lack the ...
Gene fusion analysis
... Steps in analyzing fusions of domains to known enzymes Triage into ‘essentially known’, ‘unknown and unpromising’, and ‘unknown and promising’ categories 1. Is the fusion real, i.e. does it occur in several independent genomes? (Run a Blast search at NCBI.) Are those genomes high-quality? Those that ...
... Steps in analyzing fusions of domains to known enzymes Triage into ‘essentially known’, ‘unknown and unpromising’, and ‘unknown and promising’ categories 1. Is the fusion real, i.e. does it occur in several independent genomes? (Run a Blast search at NCBI.) Are those genomes high-quality? Those that ...
Enzymes
... •Enzymes increase reaction rates by decreasing the amount of energy required to form a complex of reactants that is competent to produce reaction products. This complex is known as the activated state or transition state complexfor the reaction. •Enzymes and other catalysts accelerate reactions by l ...
... •Enzymes increase reaction rates by decreasing the amount of energy required to form a complex of reactants that is competent to produce reaction products. This complex is known as the activated state or transition state complexfor the reaction. •Enzymes and other catalysts accelerate reactions by l ...
Learning Target: I can analyze and teach my classmates about Radon.
... substrates. The substrates are the reactants that undergo the chemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. The location where substrates bind to or interact with the enzyme is known as the active site, because that is the site where the chemistry occurs. When the substrate binds to its active site at ...
... substrates. The substrates are the reactants that undergo the chemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. The location where substrates bind to or interact with the enzyme is known as the active site, because that is the site where the chemistry occurs. When the substrate binds to its active site at ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.