CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Successes and Failures of the Bohr Model Characteristic X-Ray Spectra and Atomic Number Atomic Excitation by Electrons In the present first part of the paper the mechanism of the binding of electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theor ...
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Successes and Failures of the Bohr Model Characteristic X-Ray Spectra and Atomic Number Atomic Excitation by Electrons In the present first part of the paper the mechanism of the binding of electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theor ...
CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Successes and Failures of the Bohr Model Characteristic X-Ray Spectra and Atomic Number Atomic Excitation by Electrons In the present first part of the paper the mechanism of the binding of electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theor ...
... The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom Successes and Failures of the Bohr Model Characteristic X-Ray Spectra and Atomic Number Atomic Excitation by Electrons In the present first part of the paper the mechanism of the binding of electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theor ...
CHEMISTRY
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
QUIZ: History of Atomic Structure
... D) The cathode ray tube proved that electrons have a negative charge. 4. Which was used to determine the value for charge of the electron? A) the gold foil experiment B) deflection of cathode rays by electric and magnetic fields C) The oil drop experiment D) the periodic table E) the mass spectromet ...
... D) The cathode ray tube proved that electrons have a negative charge. 4. Which was used to determine the value for charge of the electron? A) the gold foil experiment B) deflection of cathode rays by electric and magnetic fields C) The oil drop experiment D) the periodic table E) the mass spectromet ...
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... ELEMENT: a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom; a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions ...
... ELEMENT: a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom; a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions ...
Chemistry Science Notebook
... The quantum concept concludes that matter can gain or lose only in small, specific amounts called ...
... The quantum concept concludes that matter can gain or lose only in small, specific amounts called ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... The Structure and Stability of Atoms LEARNING OBJECTIVE SUMMARIES 1. Understand the fundamental properties and behavior of substances, including: a. Matter is composed of atoms that combine in whole number ratios to form molecules This fact, called Dalton’s atomic theory, historically was deduced fr ...
... The Structure and Stability of Atoms LEARNING OBJECTIVE SUMMARIES 1. Understand the fundamental properties and behavior of substances, including: a. Matter is composed of atoms that combine in whole number ratios to form molecules This fact, called Dalton’s atomic theory, historically was deduced fr ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... 11. Which of these types of nuclear radiation has the greatest penetrating power? (1) alpha (3) neutron (2) beta (4) gamma 12. Alpha particles and beta particles differ in (1) mass, only (2) charge, only (3) both mass and charge (4) neither mass nor charge 13. Which equation represents a fusion reac ...
... 11. Which of these types of nuclear radiation has the greatest penetrating power? (1) alpha (3) neutron (2) beta (4) gamma 12. Alpha particles and beta particles differ in (1) mass, only (2) charge, only (3) both mass and charge (4) neither mass nor charge 13. Which equation represents a fusion reac ...
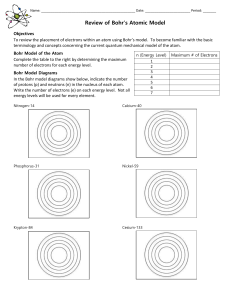
Name: ______ Date: Period: ______ Review of Bohr`s Atomic Model
... Review of Bohr’s Atomic Model Objectives ...
... Review of Bohr’s Atomic Model Objectives ...
4. Structure of the Atom
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. - Niels Bohr ...
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. - Niels Bohr ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... In our biosphere, everything is made of atoms Through the interaction of chemicals we can better understand our biosphere Give an example from what we have already done in Bio. ...
... In our biosphere, everything is made of atoms Through the interaction of chemicals we can better understand our biosphere Give an example from what we have already done in Bio. ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? Bonus question: Give possibilities for the compounds. ...
... What is the ratio of oxygen in the two compounds for a fixed amount of nitrogen? Bonus question: Give possibilities for the compounds. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.