Chemistry: The Basics
... – Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. – Actual mass = 1.67 x 10-24 grams – No charge ...
... – Discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. – Actual mass = 1.67 x 10-24 grams – No charge ...
Elementary my dear Watson review
... are involved and the numbers tell us how many atoms of each kind are involved. For example, water (H20) is made up of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen. ...
... are involved and the numbers tell us how many atoms of each kind are involved. For example, water (H20) is made up of 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen. ...
Test 1 Guide
... 1) Neutrons have almost no mass (in amu) and no charge. 2) The fact that 2 different elements may have atoms with the same atomic mass violates Dalton’s atomic theory. 3) Deuterium differs from hydrogen in the number of protons it has. 4) In the quantum mechanical model of the atom, electrons are co ...
... 1) Neutrons have almost no mass (in amu) and no charge. 2) The fact that 2 different elements may have atoms with the same atomic mass violates Dalton’s atomic theory. 3) Deuterium differs from hydrogen in the number of protons it has. 4) In the quantum mechanical model of the atom, electrons are co ...
Chemistry Honors Unit 2 Study Guide Atomic Theory Mr. Brown Use
... Law of Definite Proportions/Composition = Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the amount or source of the sample. EX. NaCl always contain 39.34% by mass of Na and 60.66% by mass of Cl. Law of Multiple Proportions = If two or more ...
... Law of Definite Proportions/Composition = Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the amount or source of the sample. EX. NaCl always contain 39.34% by mass of Na and 60.66% by mass of Cl. Law of Multiple Proportions = If two or more ...
Modern Physics
... from the nucleus for the hydrogen atom is 2 ao. Find the probability of finding the 1-s electron at a distance greater than 2 ao according to quantum mechanics. ...
... from the nucleus for the hydrogen atom is 2 ao. Find the probability of finding the 1-s electron at a distance greater than 2 ao according to quantum mechanics. ...
Topic 7: Atomic and nuclear physics 7.1 The atom
... is somehow excited, then the electrons will leave the ground state and move to a higher energy state. As soon as this happens they transition back to lower energy states radiating energy in the process. The set of wavelengths of light emitted by the atoms of the element is called its emission spectr ...
... is somehow excited, then the electrons will leave the ground state and move to a higher energy state. As soon as this happens they transition back to lower energy states radiating energy in the process. The set of wavelengths of light emitted by the atoms of the element is called its emission spectr ...
Problem Set 05
... a nitrogen molecule (N2) from its ground state (n=0) to the n=1 rotational state (for N2, d=0.11 nm). [You can check your result by noting that rotational spectra for small molecules are generally in the microwave region: 0.1mm→10cm]. ...
... a nitrogen molecule (N2) from its ground state (n=0) to the n=1 rotational state (for N2, d=0.11 nm). [You can check your result by noting that rotational spectra for small molecules are generally in the microwave region: 0.1mm→10cm]. ...
3. Represents an atom that has four valence electrons.
... 9. Which of the responses contains all the statements that are consistent with the Bohr theory of the atom (and no others)? (I) Only orbits of specific radii, corresponding to certain definite energies, are permitted for electrons in an atom. (II) An electron in a permitted orbit has a specific ener ...
... 9. Which of the responses contains all the statements that are consistent with the Bohr theory of the atom (and no others)? (I) Only orbits of specific radii, corresponding to certain definite energies, are permitted for electrons in an atom. (II) An electron in a permitted orbit has a specific ener ...
File
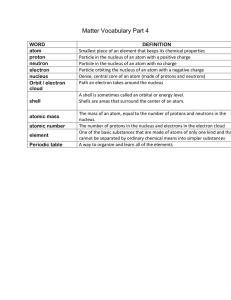
... atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no ...
... atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no ...
Models of the Atom:
... Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements are not the same. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one another in simple wholenumber ratios to form COMPOUNDS. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements are not the same. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one another in simple wholenumber ratios to form COMPOUNDS. ...
Nuclear - Orangefield ISD
... ◦ Aristotle rejected Atomic Theory Respected for ideas on nature, physics, astronomy, etc., so most ignored Democritus’ ideas ...
... ◦ Aristotle rejected Atomic Theory Respected for ideas on nature, physics, astronomy, etc., so most ignored Democritus’ ideas ...
Ch 2 Atomic History
... given a negative charge. Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops upward. When a drop is perfectly balanced, the weight of the drop is equal to the electrostatic force of attraction between the drop and the positive ...
... given a negative charge. Gravity forces the drops downward. The applied electric field forces the drops upward. When a drop is perfectly balanced, the weight of the drop is equal to the electrostatic force of attraction between the drop and the positive ...
power point notes
... WAY! He thought that only 4 elements actually exist: water, air, fire and earth ...
... WAY! He thought that only 4 elements actually exist: water, air, fire and earth ...
Simple Harmonic Oscillator
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. - Niels Bohr ...
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. - Niels Bohr ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.