Rutherford–Bohr model
... existence of excited states in mercury atoms, helping to confirm the quantum theory which predicted that electrons occupied only discrete, quantized energy states. Electrons were accelerated by a voltage toward a positively charged grid in a glass envelope filled with mercury vapor. Past the grid wa ...
... existence of excited states in mercury atoms, helping to confirm the quantum theory which predicted that electrons occupied only discrete, quantized energy states. Electrons were accelerated by a voltage toward a positively charged grid in a glass envelope filled with mercury vapor. Past the grid wa ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS (also called the LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION): All pure samples of a given compound contain the same proportion of elements by mass ...
... LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS (also called the LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION): All pure samples of a given compound contain the same proportion of elements by mass ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... 12. Put together the Atomic Theory, established the Law of Multiple Proportions, and explained the difference between a mixture and a compound. ______________________ 13. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, an undergraduate student who worked with Geiger._________________________ ...
... 12. Put together the Atomic Theory, established the Law of Multiple Proportions, and explained the difference between a mixture and a compound. ______________________ 13. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, an undergraduate student who worked with Geiger._________________________ ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... • Early Models of the Atom atom - smallest particles of an element that retains it's identity in a chemical reaction • Democritu's Atomic Philosophy (460 BC - 370 BC) - Atoms are: - Indivisible - Indestructible - He didn't: - Explain chemical behavior - have experimental support • Dalton's Atomic Th ...
... • Early Models of the Atom atom - smallest particles of an element that retains it's identity in a chemical reaction • Democritu's Atomic Philosophy (460 BC - 370 BC) - Atoms are: - Indivisible - Indestructible - He didn't: - Explain chemical behavior - have experimental support • Dalton's Atomic Th ...
File
... b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflected right back b. some alpha parti ...
... b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflected right back b. some alpha parti ...
Quantum Mechanics
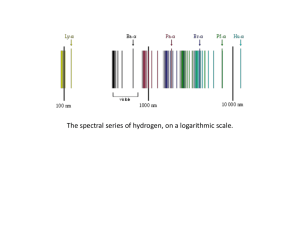
... Discharge tubes are used that contains very little gas at low pressure A high voltage is applied across the atoms, which cause them to interact to create light (one of the four interactions of photons) For hydrogen, there is an equation for wavelength of light emitted ...
... Discharge tubes are used that contains very little gas at low pressure A high voltage is applied across the atoms, which cause them to interact to create light (one of the four interactions of photons) For hydrogen, there is an equation for wavelength of light emitted ...
Slide 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom 7.1 The Wave Nature of Light 7.2 Quantum Effects and Photons 7.3 The Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 7.4 Quantum Mechanics 7.5 Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals ...
... Chapter 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom 7.1 The Wave Nature of Light 7.2 Quantum Effects and Photons 7.3 The Bohr Theory of the Hydrogen Atom 7.4 Quantum Mechanics 7.5 Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals ...
JJ Thompson Webquest
... elements ascending of their atomic weight, their chemical properties show characteristic periodicity and this later become known as the Periodic Law. Later this table was named the periodic table of elements. He Arranged elements into 7 groups with similar properties. ...
... elements ascending of their atomic weight, their chemical properties show characteristic periodicity and this later become known as the Periodic Law. Later this table was named the periodic table of elements. He Arranged elements into 7 groups with similar properties. ...
Slide 1
... photo-electric effect: light behaves as a particle Discovery of the nucleus: Rutherford scattering experiment Today: Atomic spectra: emission and absorption. Evidence for atomic energy levels Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom Continuous emission: black-body radiation ...
... photo-electric effect: light behaves as a particle Discovery of the nucleus: Rutherford scattering experiment Today: Atomic spectra: emission and absorption. Evidence for atomic energy levels Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom Continuous emission: black-body radiation ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... (2) Atoms of a given element are ___________ in all ways. (3) Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical __________. (4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form _________. (5) In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but are never ________ ...
... (2) Atoms of a given element are ___________ in all ways. (3) Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical __________. (4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form _________. (5) In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, but are never ________ ...
Chemistry 102B What`s in an atom? Before “Chemistry” Other Early
... Before “Chemistry” • Alchemy/Alchemists - a pseudoscience built around trying to turn cheap metals into GOLD! (400 B.C.-1400 A.D.) • Metallurgy – systematic extraction of metals from ores laid some groundwork for modern chemistry. (1500s) • The first “chemist” was Robert Boyle who worked on pressure ...
... Before “Chemistry” • Alchemy/Alchemists - a pseudoscience built around trying to turn cheap metals into GOLD! (400 B.C.-1400 A.D.) • Metallurgy – systematic extraction of metals from ores laid some groundwork for modern chemistry. (1500s) • The first “chemist” was Robert Boyle who worked on pressure ...
Glencoe Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom for the Wiki
... Law of definite proportions • Joseph Proust specific substances always contain elements in the same ratio by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element ...
... Law of definite proportions • Joseph Proust specific substances always contain elements in the same ratio by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element ...
The Atomic Theory of Matter
... • There were conflicting views about cathode rays. It wasn’t clear whether they were a stream of particles or a form of radiation. Experiments showed that they were deflected by electric or magnetic fields in a consistent way of their being a stream of negative charge. The British Scientists J.J. Th ...
... • There were conflicting views about cathode rays. It wasn’t clear whether they were a stream of particles or a form of radiation. Experiments showed that they were deflected by electric or magnetic fields in a consistent way of their being a stream of negative charge. The British Scientists J.J. Th ...
Goal 4.01
... Alpha particles are a positive type of radiation with four times the mass of a hydrogen. It was thought that all alpha particles would pass through the gold foil because nothing would be big or strong enough to deflect them. ...
... Alpha particles are a positive type of radiation with four times the mass of a hydrogen. It was thought that all alpha particles would pass through the gold foil because nothing would be big or strong enough to deflect them. ...
the atomic theory
... 1. John Dalton 2. J.J. Thomson 3. Ernest Rutherford 4. James Chadwick 5. Neils Bohr 6. nucleus 7. proton 8. neutron 9. electron 10. shell 11. atomic number 12. atomic mass 13. Bohr Model 14. subatomic particle 15. isotope 16. empty bus seat rule B/ THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM: - John Dalton ...
... 1. John Dalton 2. J.J. Thomson 3. Ernest Rutherford 4. James Chadwick 5. Neils Bohr 6. nucleus 7. proton 8. neutron 9. electron 10. shell 11. atomic number 12. atomic mass 13. Bohr Model 14. subatomic particle 15. isotope 16. empty bus seat rule B/ THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM: - John Dalton ...
BEAT_Sheet_for_Atoms_2016_ACA
... Name:______________________________________________Period:______#:_______ ...
... Name:______________________________________________Period:______#:_______ ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.