Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... c. The atoms of different elements differ in fundamental ways (e.g., different masses, different chemical behavior). d. Compounds form when atoms of different elements join together in simple whole number ratios. Thus, a given compound always contains the same relative number and types of atoms. e. ...
... c. The atoms of different elements differ in fundamental ways (e.g., different masses, different chemical behavior). d. Compounds form when atoms of different elements join together in simple whole number ratios. Thus, a given compound always contains the same relative number and types of atoms. e. ...
SG2 Atoms and Atomic Structure
... (i) Describe observations and conclusions (ii) Ground state vs. excited state (iii)Bohr model of hydrogen atom 1. Did not prove true for multi-electron atoms 2. Did not explain the chemical behavior of atoms (2) Explain why matter emits light when heated (a) Calculate the energy of light (aka. photo ...
... (i) Describe observations and conclusions (ii) Ground state vs. excited state (iii)Bohr model of hydrogen atom 1. Did not prove true for multi-electron atoms 2. Did not explain the chemical behavior of atoms (2) Explain why matter emits light when heated (a) Calculate the energy of light (aka. photo ...
DEVELOPMENT OF THE ATOMIC THEORY PROJECT due Friday
... and his contribution to the atomic theory on the atom. In succeeding layers, you will add detail to your atom and name the scientist who developed this part of the atomic theory. You will also include a picture or a brief description of the method the scientist used. You must include development of ...
... and his contribution to the atomic theory on the atom. In succeeding layers, you will add detail to your atom and name the scientist who developed this part of the atomic theory. You will also include a picture or a brief description of the method the scientist used. You must include development of ...
Atomic Structure 1. Historical perspective of the model of the atom a
... a.) In 1803, John Dalton proposed the atomic theory which stated that all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same type of element have the same chemical properties, compounds are formed by two or more different types of atoms, and that a chemical reaction involves either, joining, separating, or ...
... a.) In 1803, John Dalton proposed the atomic theory which stated that all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same type of element have the same chemical properties, compounds are formed by two or more different types of atoms, and that a chemical reaction involves either, joining, separating, or ...
Earth`s Chemistry
... Chemical Bonds Chemical bonds = forces that hold atoms together to make compounds Ionic bonds = electrons are transferred from one atom to another Ion = an atom or group of atoms that carry an electrical charge ( positive or negative) Covalent bond = share electrons Chemical formulas = a representa ...
... Chemical Bonds Chemical bonds = forces that hold atoms together to make compounds Ionic bonds = electrons are transferred from one atom to another Ion = an atom or group of atoms that carry an electrical charge ( positive or negative) Covalent bond = share electrons Chemical formulas = a representa ...
Section 1 Review
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
The Atom - Williamstown Independent Schools
... are composed of the same two elements then ratios of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... are composed of the same two elements then ratios of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
File - Mr. Sault`s Classroom
... All matter is made up of very small particles All particles in a pure substance are the same. Different substances are made of different particles There is space between particles The particles are always moving. As the particles gain energy, they move faster The particles in a substance are ...
... All matter is made up of very small particles All particles in a pure substance are the same. Different substances are made of different particles There is space between particles The particles are always moving. As the particles gain energy, they move faster The particles in a substance are ...
Minerals * Chemistry Review
... • An element is a substance that can not be made into simpler form by ordinary chemical means • The smallest unit is an atom ...
... • An element is a substance that can not be made into simpler form by ordinary chemical means • The smallest unit is an atom ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... A neutron has no charge and a relative mass of one. TOPIC TWO: COMPOUNDS & BONDING (PAGE 2) Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative number of each type of atom. The subscript always follows the symbol for the element. Example: In a water molecule, H2O, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and ...
... A neutron has no charge and a relative mass of one. TOPIC TWO: COMPOUNDS & BONDING (PAGE 2) Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative number of each type of atom. The subscript always follows the symbol for the element. Example: In a water molecule, H2O, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and ...
lect10
... world, at the quantum level, is governed by statistical law. It rules out “classical” or “naïve” realist views of nature. As an example, consider the following applet demonstrating the Hydrogen atom. ...
... world, at the quantum level, is governed by statistical law. It rules out “classical” or “naïve” realist views of nature. As an example, consider the following applet demonstrating the Hydrogen atom. ...
The Quantum Atom (section 18)
... Section 18: The Quantum Atom JJ Thomson 1899 – discovered electron using cathode ray tube (diagrams p210 Adams& Allday, p784 Muncaster). Particles given off from cathode always have the same charge to mass ratio, no matter what element the cathode is made of. Conclusion – they are subatomic particle ...
... Section 18: The Quantum Atom JJ Thomson 1899 – discovered electron using cathode ray tube (diagrams p210 Adams& Allday, p784 Muncaster). Particles given off from cathode always have the same charge to mass ratio, no matter what element the cathode is made of. Conclusion – they are subatomic particle ...
OBJECTIVE WORKSHEET Quantum Theory 1. How did
... 3. How many energy levels for electrons does the chapter discuss? 4. Who discovered the QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL? 5. What shape does the s and p orbitals have? 6. What does "n" stand for when we discuss atomic orbitals? 7. What is the maximum number of electrons allowed in when n=4? 8. What is "neon ...
... 3. How many energy levels for electrons does the chapter discuss? 4. Who discovered the QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL? 5. What shape does the s and p orbitals have? 6. What does "n" stand for when we discuss atomic orbitals? 7. What is the maximum number of electrons allowed in when n=4? 8. What is "neon ...
History of Atomic Theory PowerPoint
... ▪ Atoms are tiny, solid, homogenous, indestructible, and indivisible ▪ Different kinds of atoms have different sizes and shapes ▪ Size, shape, and movements of atoms determines the properties of matter ▪ Matter is made of atoms, which move through empty ...
... ▪ Atoms are tiny, solid, homogenous, indestructible, and indivisible ▪ Different kinds of atoms have different sizes and shapes ▪ Size, shape, and movements of atoms determines the properties of matter ▪ Matter is made of atoms, which move through empty ...
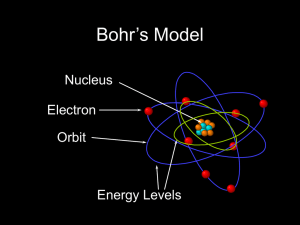
Bohr Atom
... the history of science, was at first prompted by and later partially disproved by experimentation. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Chemistry ...
... the history of science, was at first prompted by and later partially disproved by experimentation. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Chemistry ...
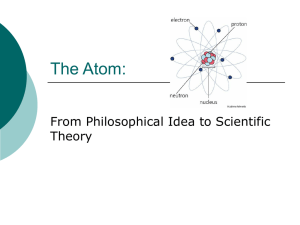
Atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a nucleus
... defined, quantized orbits, and could jump between these, but could not freely spiral inward or outward in intermediate states. An electron must absorb or emit specific amounts of energy to transition between these fixed orbits. Bohr's model successfully explained spectroscopic data of hydrogen very ...
... defined, quantized orbits, and could jump between these, but could not freely spiral inward or outward in intermediate states. An electron must absorb or emit specific amounts of energy to transition between these fixed orbits. Bohr's model successfully explained spectroscopic data of hydrogen very ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and oxygen. - A chemical compound is a distinct substance made up of atoms or two or more elements (like water above) 4) ...
... small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and oxygen. - A chemical compound is a distinct substance made up of atoms or two or more elements (like water above) 4) ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.