Easy explanation
... • X-rays were discovered to ionize air • Until then, only ions observed were in solution (e.g., Na+, Cl-) ...
... • X-rays were discovered to ionize air • Until then, only ions observed were in solution (e.g., Na+, Cl-) ...
3.4oquantum.4u
... The study of quantum mechanics is a branch of mathematics which studies the properties of electrons. In this class we will use the results of the calculations. (You can do them later in 3rd and 4th year university) Wave Mechanics tells us there are certain regions in space around the nucleus where t ...
... The study of quantum mechanics is a branch of mathematics which studies the properties of electrons. In this class we will use the results of the calculations. (You can do them later in 3rd and 4th year university) Wave Mechanics tells us there are certain regions in space around the nucleus where t ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
Midterm Review Sheet
... 3. Lavoisier - Law of conservation of mass. 4. Proust - Law of definite composition. 5. Dalton - Law of multiple proportions also developed atomic theory, much of which is still in use today. 6. Crookes - using Crookes' tube discovered "cathode rays" as negative particles/radiation. This was the fir ...
... 3. Lavoisier - Law of conservation of mass. 4. Proust - Law of definite composition. 5. Dalton - Law of multiple proportions also developed atomic theory, much of which is still in use today. 6. Crookes - using Crookes' tube discovered "cathode rays" as negative particles/radiation. This was the fir ...
Slide 1 - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
1 - Schoolwires.net
... 5) Atomic mass unit (amu) – one-twelfth the mass of carbon-12 atom. o Relative vs. Actual Masses 6) Atomic number (Z) – number of protons. 7) Protons must equal Electrons. 8) Mass number (A) – number of protons and neutrons. 9) Neutrons = Mass number (p+ & n0) – Atomic number (p+) A-Z 10) Use of the ...
... 5) Atomic mass unit (amu) – one-twelfth the mass of carbon-12 atom. o Relative vs. Actual Masses 6) Atomic number (Z) – number of protons. 7) Protons must equal Electrons. 8) Mass number (A) – number of protons and neutrons. 9) Neutrons = Mass number (p+ & n0) – Atomic number (p+) A-Z 10) Use of the ...
Section 13.2 - CPO Science
... between the two levels. • The energy comes out as different colors of light. ...
... between the two levels. • The energy comes out as different colors of light. ...
Activity 17 Follow-up
... neutrons, but always has the same number of protons •The atomic weight is the average weight of all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
... neutrons, but always has the same number of protons •The atomic weight is the average weight of all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
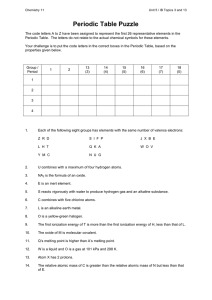
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the ...
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the ...
F = mv r
... The qualitative results of the model carry over into the modern version of q.m. so we will examine it in detail. First, we find an expression for r angular momentum ≡ mvr, but by postulate 1, it is given by nh/2π ...
... The qualitative results of the model carry over into the modern version of q.m. so we will examine it in detail. First, we find an expression for r angular momentum ≡ mvr, but by postulate 1, it is given by nh/2π ...
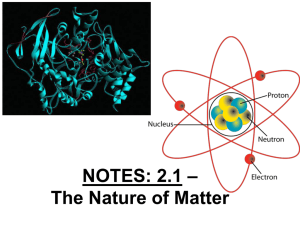
The Nature of Molecules
... • Diagram of typical atomic structure: • Atomic #/mass of: H, He, C, O, N, S, P, Ne ...
... • Diagram of typical atomic structure: • Atomic #/mass of: H, He, C, O, N, S, P, Ne ...
J. J. Thomson
... Determined the mass-to-charge ratio of an electron Proposed the "plum-pudding" model of the atom Argued that the number of electrons in an atom was approximately equal to the atomic weight of that element Worked on the conduction of electricity in gases One of Thomson's greatest contribution ...
... Determined the mass-to-charge ratio of an electron Proposed the "plum-pudding" model of the atom Argued that the number of electrons in an atom was approximately equal to the atomic weight of that element Worked on the conduction of electricity in gases One of Thomson's greatest contribution ...
08_lecture_ppt
... 1. All matter = indivisible atoms 2. An element is made up of identical atoms. 3. Different elements have atoms with different masses. 4. Chemical compounds are made of atoms in specific integer ratios. 5. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... 1. All matter = indivisible atoms 2. An element is made up of identical atoms. 3. Different elements have atoms with different masses. 4. Chemical compounds are made of atoms in specific integer ratios. 5. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
08_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 1. All matter = indivisible atoms 2. An element is made up of identical atoms. 3. Different elements have atoms with different masses. 4. Chemical compounds are made of atoms in specific integer ratios. 5. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... 1. All matter = indivisible atoms 2. An element is made up of identical atoms. 3. Different elements have atoms with different masses. 4. Chemical compounds are made of atoms in specific integer ratios. 5. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.