穨 Ams1a
... radiation : stream of fast moving electron travelling with speed of light. The electron is emitted by splitting a neutron in radioactive decay. Ionize gas through which they pass. ...
... radiation : stream of fast moving electron travelling with speed of light. The electron is emitted by splitting a neutron in radioactive decay. Ionize gas through which they pass. ...
Dalton Model Reading
... he sets out the relative weights of the atoms of a number of elements, derived from analysis of water, ammonia, carbon dioxide, etc. by chemists of the time. In 1803 Dalton orally presented his first list of relative atomic weights for a number of substances. This paper was published in 1805, but he ...
... he sets out the relative weights of the atoms of a number of elements, derived from analysis of water, ammonia, carbon dioxide, etc. by chemists of the time. In 1803 Dalton orally presented his first list of relative atomic weights for a number of substances. This paper was published in 1805, but he ...
summary sheet
... SUMMARY Electrons in Atoms (Section 29.1) The Bohr model fails to fully describe atoms because it combines elements of classical physics with some principles of quantum mechanics. To explain the observed properties of an atom, electrons must be described with a wave function that is determined by so ...
... SUMMARY Electrons in Atoms (Section 29.1) The Bohr model fails to fully describe atoms because it combines elements of classical physics with some principles of quantum mechanics. To explain the observed properties of an atom, electrons must be described with a wave function that is determined by so ...
Metric Unit – Chapter 1
... combine in simple wholenumbered ratios to form 5. In chemical reactions, atoms ___________________________. are _____________________ 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are _______________________. ___________________________ ___________________________. ...
... combine in simple wholenumbered ratios to form 5. In chemical reactions, atoms ___________________________. are _____________________ 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are _______________________. ___________________________ ___________________________. ...
History of Atomic Theories (No Videos)
... Joseph Proust (1779) Develops Law of Definite Composition- all samples of a specific substance contain the same mass ratio of the same elements a. ex: all samples of CO2 contains 27.3% carbon and 72.7% oxygen b. therefore ‘elements’ are combining in a whole number ratio ...
... Joseph Proust (1779) Develops Law of Definite Composition- all samples of a specific substance contain the same mass ratio of the same elements a. ex: all samples of CO2 contains 27.3% carbon and 72.7% oxygen b. therefore ‘elements’ are combining in a whole number ratio ...
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
... atoms of a transition element The ground-state configuration of a negative ion of a halogen The ground-state configuration of a common ion of an alkaline earth element ...
... atoms of a transition element The ground-state configuration of a negative ion of a halogen The ground-state configuration of a common ion of an alkaline earth element ...
CHAPTER 3 Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... – All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms – Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties – Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed – Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds – In chemical reac ...
... – All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms – Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties – Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed – Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds – In chemical reac ...
Chapter 2 - Speedway High School
... Elements and Compounds • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
... Elements and Compounds • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
Chemistry Atomic structure Chapter 4, and Chapter 5, p. 146-148
... Webquest on atomic emission spectra ...
... Webquest on atomic emission spectra ...
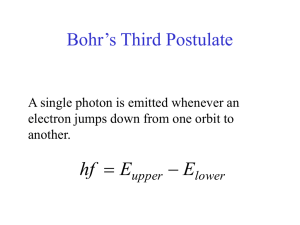
Bohr´s Third Postulate
... don’t all the photoelectrons have the same kinetic energy when they leave the metal’s surface? 4. What property of the emitted electrons depends on the intensity of incident light?What property of the emitted photoelectrons depends on the frequency of incident light? ...
... don’t all the photoelectrons have the same kinetic energy when they leave the metal’s surface? 4. What property of the emitted electrons depends on the intensity of incident light?What property of the emitted photoelectrons depends on the frequency of incident light? ...
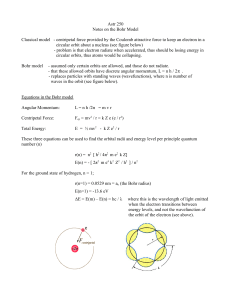
Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model
... Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model - centripetal force provided by the Coulomb attractive force to keep an electron in a circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms wo ...
... Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model - centripetal force provided by the Coulomb attractive force to keep an electron in a circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms wo ...
Week 1: Nuclear timeline (pdf, 233 KB)
... Much of the material here can be expanded upon by examining the Wikapedia site found by searching on the name of the various discoverers. These articles not only describe the other discoveries made by these scientists but also describe their personalities and other activities. They make for very int ...
... Much of the material here can be expanded upon by examining the Wikapedia site found by searching on the name of the various discoverers. These articles not only describe the other discoveries made by these scientists but also describe their personalities and other activities. They make for very int ...
Semester 1 Exam Review Part 1
... atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus A = Atomic Number These are all equal to each P = Proton Number other E = Electron Number ...
... atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus A = Atomic Number These are all equal to each P = Proton Number other E = Electron Number ...
TIMELINE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... light by electrons changing their circular orbits while orbiting a positive nucleus. model can actually predict wavelength of light based on equations representing his mechanical model of the atom. This was an incredible advancement in physics. This model, was very simple at first, electrons in circ ...
... light by electrons changing their circular orbits while orbiting a positive nucleus. model can actually predict wavelength of light based on equations representing his mechanical model of the atom. This was an incredible advancement in physics. This model, was very simple at first, electrons in circ ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
Ideas of Modern Physics
... 4. A quantum particle in a box is in the lowest energy (ground) state. If the size of the box is decreased, momentum uncertainty of the particle? a. becomes larger b. becomes smaller c. is unchanged d. becomes negative e. cannot be measured 5. A photon is found to have 100 eV of energy. Which answer ...
... 4. A quantum particle in a box is in the lowest energy (ground) state. If the size of the box is decreased, momentum uncertainty of the particle? a. becomes larger b. becomes smaller c. is unchanged d. becomes negative e. cannot be measured 5. A photon is found to have 100 eV of energy. Which answer ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.