Document
... ______ 13. Used Planck’s idea of quantization to explain the line spectrum of hydrogen. ______ 14. Stated that the position and momentum of a moving object cannot be simultaneously measured and known exactly. ______ 15. Labeled each energy level in his atomic model with the principal quantum number, ...
... ______ 13. Used Planck’s idea of quantization to explain the line spectrum of hydrogen. ______ 14. Stated that the position and momentum of a moving object cannot be simultaneously measured and known exactly. ______ 15. Labeled each energy level in his atomic model with the principal quantum number, ...
Discovery of the Electron, Models & Theories
... Bohr based his model on experiments done by Ernest Rutherford; he saw Rutherford’s model wasn’t quite right and changed it ...
... Bohr based his model on experiments done by Ernest Rutherford; he saw Rutherford’s model wasn’t quite right and changed it ...
- Catalyst
... is the smallest body that retains the unique identity of the element. 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element hav ...
... is the smallest body that retains the unique identity of the element. 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element hav ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... with the coal? The elements (carbon in coal; hydrogen and oxygen in water) only combine as sugar when _________bonds form Sugar cannot be easily separated into its components. So…Can you break gold down into a simpler substance??? NO…because it is an element Atoms are the basic building blocks of al ...
... with the coal? The elements (carbon in coal; hydrogen and oxygen in water) only combine as sugar when _________bonds form Sugar cannot be easily separated into its components. So…Can you break gold down into a simpler substance??? NO…because it is an element Atoms are the basic building blocks of al ...
For a “black body” - The University of Sheffield
... •Unlike convection and conduction, transfer of heat by thermal radiation doesn’t require a “medium” •So, for example, heat can reach Earth from the Sun through millions of kilometres of empty space. •Rate at which an object, surface area A, temperature T, radiates energy is given by Stefan’s Law ...
... •Unlike convection and conduction, transfer of heat by thermal radiation doesn’t require a “medium” •So, for example, heat can reach Earth from the Sun through millions of kilometres of empty space. •Rate at which an object, surface area A, temperature T, radiates energy is given by Stefan’s Law ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... charged particles that respond to an applied magnetic field. – used by Thomson to discover electron, first subatomic particle and measure its charge/mass ratio, led to Plum pudding model – used in CRT televisions Tiny oil drop exposed to radiation to give it a charge. Size of charge measured by bala ...
... charged particles that respond to an applied magnetic field. – used by Thomson to discover electron, first subatomic particle and measure its charge/mass ratio, led to Plum pudding model – used in CRT televisions Tiny oil drop exposed to radiation to give it a charge. Size of charge measured by bala ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
Fall Exam 1
... Cathode rays are composed of electrons. B. The path of cathode rays can be altered by imposing both magnetic and electric fields. 18. Millikan’s oil drop experiment ...
... Cathode rays are composed of electrons. B. The path of cathode rays can be altered by imposing both magnetic and electric fields. 18. Millikan’s oil drop experiment ...
Matter
... properties from the elements of which they are composed. Chemical bonds are the forces that hold the elements together in a compound creating a state of stability. ...
... properties from the elements of which they are composed. Chemical bonds are the forces that hold the elements together in a compound creating a state of stability. ...
Atomic
... atomic theory that he created using the laws of matter and previously known atomic theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties 3. Atoms can not be divided, created or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in s ...
... atomic theory that he created using the laws of matter and previously known atomic theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties 3. Atoms can not be divided, created or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in s ...
Unit IV: Nature of Matter
... Demitri Mendeleev used this theory when he constructed the first working periodic table. ...
... Demitri Mendeleev used this theory when he constructed the first working periodic table. ...
Physical Chemistry
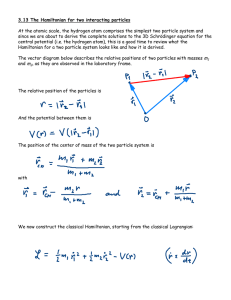
... • (1) Atoms can exist in stable “states” without radiating. The states have discrete energies En, n= 1, 2, 3,..., where n= 1 is the lowest energy state (the most negative, relative to the dissociated atom at zero energy), n= 2 is the next lowest energy state, etc. The number “n” is an integer, a qua ...
... • (1) Atoms can exist in stable “states” without radiating. The states have discrete energies En, n= 1, 2, 3,..., where n= 1 is the lowest energy state (the most negative, relative to the dissociated atom at zero energy), n= 2 is the next lowest energy state, etc. The number “n” is an integer, a qua ...
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
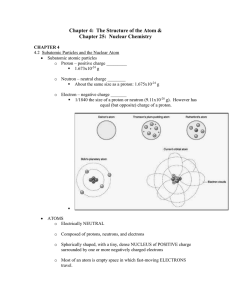
... o Gamma radiation is made of GAMMA RAYS (high energy radiation) No mass or charge Symbol is _______________ ...
... o Gamma radiation is made of GAMMA RAYS (high energy radiation) No mass or charge Symbol is _______________ ...
Atomic Structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
The New Alchemy
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
Dalton`s Laws worksheet
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter 1. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. All atoms are identical b. All atoms of a given element are identical c. All atoms differ from one another d. Atoms of the same element can have a different shape 2. Dalton suggested ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter 1. Which of the following statements is part of Dalton’s atomic theory of matter? a. All atoms are identical b. All atoms of a given element are identical c. All atoms differ from one another d. Atoms of the same element can have a different shape 2. Dalton suggested ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... Law of Multiple Proportions • The masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the second element are in a ratio of small whole numbers. Compare CO and CO2 ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions • The masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the second element are in a ratio of small whole numbers. Compare CO and CO2 ...
Chapt38_VGO
... Classical Physics Studies of the light emitted by gas discharge tubes helped bring classical physics to an end. Chapter Goal: To understand how scientists discovered the properties of atoms and how these discoveries led to the need for a new theory of light and matter. ...
... Classical Physics Studies of the light emitted by gas discharge tubes helped bring classical physics to an end. Chapter Goal: To understand how scientists discovered the properties of atoms and how these discoveries led to the need for a new theory of light and matter. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.