Chapter Title Headline text: arial bold 27pt
... The Rise of Ancient Rome Section 2: The Roman Empire Ruling an Empire Augustus began an even greater expansion of the Roman Empire. Added territories were divided into provinces, which were governed by a Roman, but which were allowed to maintain their ways of life. Beginning in A.D. 96, Rome was rul ...
... The Rise of Ancient Rome Section 2: The Roman Empire Ruling an Empire Augustus began an even greater expansion of the Roman Empire. Added territories were divided into provinces, which were governed by a Roman, but which were allowed to maintain their ways of life. Beginning in A.D. 96, Rome was rul ...
Roman Society
... answer the following questions 1. Describe the early settlements of Rome 2. How did the patricians control the Roman Republic 3. Why did Marcus feel that Lucius and the other patricians had taken advantage of them? 4. What changes did Marcus and the other plebeians want to make in Roman government 5 ...
... answer the following questions 1. Describe the early settlements of Rome 2. How did the patricians control the Roman Republic 3. Why did Marcus feel that Lucius and the other patricians had taken advantage of them? 4. What changes did Marcus and the other plebeians want to make in Roman government 5 ...
3 ROME - Duluth High School
... – More democratic form of government – All adult, Roman males could attend and vote ...
... – More democratic form of government – All adult, Roman males could attend and vote ...
Roman Social Classes and The Roman Republic
... The Roman Republic • Roman government was under patrician control • Legislative Branch • Assembly of Centuries • The Senate (300 powerful patricians who served for life) ...
... The Roman Republic • Roman government was under patrician control • Legislative Branch • Assembly of Centuries • The Senate (300 powerful patricians who served for life) ...
Ancient Rome - Английский язык в школе
... The imperial city of Rome was the largest urban center of its time, with a population of about one million people Life in ancient empire revolved around this city, located on seven hills. The city had a vast number of monumental structures like the Coliseum, the Forum of Trajan and the Pantheon ...
... The imperial city of Rome was the largest urban center of its time, with a population of about one million people Life in ancient empire revolved around this city, located on seven hills. The city had a vast number of monumental structures like the Coliseum, the Forum of Trajan and the Pantheon ...
The Roman Republic
... Directions: Read Ch. 12 Section, Section 1 and Section 2 (pp. 364-375) and answer the following questions. Whatever you do not finish in class is homework. You will need to use your online textbook to complete this assignment at home. ...
... Directions: Read Ch. 12 Section, Section 1 and Section 2 (pp. 364-375) and answer the following questions. Whatever you do not finish in class is homework. You will need to use your online textbook to complete this assignment at home. ...
EARLY ROME AND REPUBLIC REVIEW SHEET
... government to? How does this new form of government work? How is it similar to our government? What are the branches of Rome’s Republic? What is the function of each branch? What changes were made to Rome’s new government? Why were these changes made? What does this teach us? What is life like for p ...
... government to? How does this new form of government work? How is it similar to our government? What are the branches of Rome’s Republic? What is the function of each branch? What changes were made to Rome’s new government? Why were these changes made? What does this teach us? What is life like for p ...
Chapter 14 Sections 1 and 2 Student
... • Elections of tribunes and recording of laws were the first steps towards a democratic government. • By 250 B.C. no one could be sold into slavery because of debt and plebeians could hold office. ...
... • Elections of tribunes and recording of laws were the first steps towards a democratic government. • By 250 B.C. no one could be sold into slavery because of debt and plebeians could hold office. ...
Rise of Rome Began with the City`s founding set by legend in 753
... In 509 BC, the Romans established a republic, a government of representatives chosen to act for the people at large. North America and France founded the republics modeled after the Roman republic. From 509-250 BC, two struggles propelled the Roman history. o Externally: the Romans set out to conque ...
... In 509 BC, the Romans established a republic, a government of representatives chosen to act for the people at large. North America and France founded the republics modeled after the Roman republic. From 509-250 BC, two struggles propelled the Roman history. o Externally: the Romans set out to conque ...
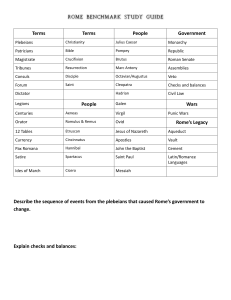
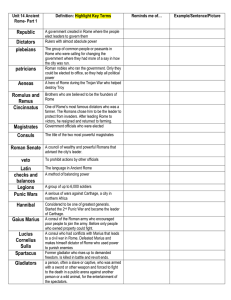
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... What were the similarities and differences in the rights of the patricians and plebeians? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Who was Rome’s most important legislative body? ________________ ...
... What were the similarities and differences in the rights of the patricians and plebeians? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Who was Rome’s most important legislative body? ________________ ...
Chapter 7: Ancient Rome Notes
... Chapter 7: Ancient Rome Notes 1. Roman Republic and Beginnings: - founded by twin brothers Romulus and Remus - settled on seven hills, along banks of Tiber river (easy to defend, fertile soil) - Republic- Most powerful was senate, made up of patricians, - Plebians (ordinary citizens, wanted respect ...
... Chapter 7: Ancient Rome Notes 1. Roman Republic and Beginnings: - founded by twin brothers Romulus and Remus - settled on seven hills, along banks of Tiber river (easy to defend, fertile soil) - Republic- Most powerful was senate, made up of patricians, - Plebians (ordinary citizens, wanted respect ...
Rome`s Beginnings
... The Birth of the Republic • Republic - Roman type of government, was set up after the Tarquin defeat – In a Republic the citizens VOTE for their elected leaders • Romans fought Latin cities and Etruscan cities for over 200 years • By 267 BC had taken the Greek colonies and most of Italy • In early ...
... The Birth of the Republic • Republic - Roman type of government, was set up after the Tarquin defeat – In a Republic the citizens VOTE for their elected leaders • Romans fought Latin cities and Etruscan cities for over 200 years • By 267 BC had taken the Greek colonies and most of Italy • In early ...
valentina+religion!!!!!!!!!!!!! - ps1286-1
... Best Known Features: The Ancient Romans were well known for their architectural ability. They constructed great buildings such as the Collesseum, auquaducts, and the Pantheon.The first architects were priests who wanted a location so they could say ?whatever happens is a sign from the gods.? The Rom ...
... Best Known Features: The Ancient Romans were well known for their architectural ability. They constructed great buildings such as the Collesseum, auquaducts, and the Pantheon.The first architects were priests who wanted a location so they could say ?whatever happens is a sign from the gods.? The Rom ...