Section II Study Guide I. Vocabulary: Be able to define these terms
... Vocabulary: Be able to define these terms. legion: a group of 6, 000 soldiers Etruscans: a people that played a major role in shaping Roman civilization Aeneas: the Trojan hero of the epic the Aeneid republic: a form of government in which its citizens vote for its leader Apennines: the mountain ran ...
... Vocabulary: Be able to define these terms. legion: a group of 6, 000 soldiers Etruscans: a people that played a major role in shaping Roman civilization Aeneas: the Trojan hero of the epic the Aeneid republic: a form of government in which its citizens vote for its leader Apennines: the mountain ran ...
The Romans - Time Detectives - Bungay Primary School History Club
... city called Rome which is situated in Italy. Rome was the greatest city of its time and at one point it had nearly one million people living in it. ...
... city called Rome which is situated in Italy. Rome was the greatest city of its time and at one point it had nearly one million people living in it. ...
The Civil War
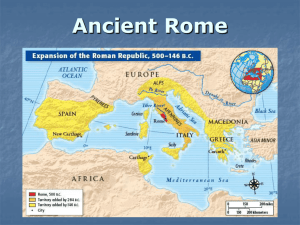
... warfare, and it is a testament to the tenacity of the Romans. • After the battle of Corinth (146 BC) the whole of the Greek peninsula becomes Roman territory • In the same year the Romans destroy Carthage, and thus they complete the subjugation of their two ancient rivals for the supremacy of the Me ...
... warfare, and it is a testament to the tenacity of the Romans. • After the battle of Corinth (146 BC) the whole of the Greek peninsula becomes Roman territory • In the same year the Romans destroy Carthage, and thus they complete the subjugation of their two ancient rivals for the supremacy of the Me ...
Rome Vocabulary
... who tried to make himself dictator of Rome. He was killed by members of the Roman Senate on March 15, 44 BC. ...
... who tried to make himself dictator of Rome. He was killed by members of the Roman Senate on March 15, 44 BC. ...
Name
... 1. Describe the myth young Romans learned about the founding of their state. It describes Rome’s location where the seven hills rise above the Tiber River 2. What was a major difference between the patricians and the plebeians during the earliest days of the Roman Republic? Could not hold office or ...
... 1. Describe the myth young Romans learned about the founding of their state. It describes Rome’s location where the seven hills rise above the Tiber River 2. What was a major difference between the patricians and the plebeians during the earliest days of the Roman Republic? Could not hold office or ...
Ancient Rome
... Gov’t in Ancient Rome • In 509 B.C., the Roman nobility overthrew the king (Tarquin the Proud), and what had been a monarchy became a republic. – Republic: a government in which the people elect their representatives. ...
... Gov’t in Ancient Rome • In 509 B.C., the Roman nobility overthrew the king (Tarquin the Proud), and what had been a monarchy became a republic. – Republic: a government in which the people elect their representatives. ...
Name Class Date Rome`s location on the Italian peninsula, centrally
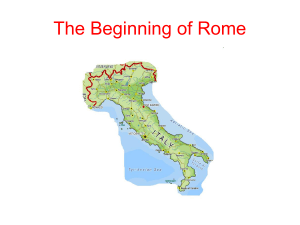
... Mediterranean Sea, benefited the Romans as they expanded. In addition, Italy had wide, fertile plains, which supported a growing population. Rome began on seven hills near the Tiber River. Romans shared the Italian peninsula with Greek colonists and the Etruscans—a people who ruled most of central I ...
... Mediterranean Sea, benefited the Romans as they expanded. In addition, Italy had wide, fertile plains, which supported a growing population. Rome began on seven hills near the Tiber River. Romans shared the Italian peninsula with Greek colonists and the Etruscans—a people who ruled most of central I ...
History Unit 3: Chapter 11
... The story of the twin brothers is a myth, but the city became the center of a great empire. C. Ruled first by kings, Rome was later governed by the Senate. D. Republican Rome was ruled by representatives of the Roman elite. E. Early Rome was divided into to classes: patricians and plebeians. F. The ...
... The story of the twin brothers is a myth, but the city became the center of a great empire. C. Ruled first by kings, Rome was later governed by the Senate. D. Republican Rome was ruled by representatives of the Roman elite. E. Early Rome was divided into to classes: patricians and plebeians. F. The ...
The basic unit of the ancient roman army, made up of 5,000 soldiers
... all people rather than use a king like the Etruscans? ...
... all people rather than use a king like the Etruscans? ...
Ancient Rome Review 1. Who are the Etruscans? What did the
... disadvantages to this landscape? 5. What are the Punic Wars? Who are the Romans fighting (Group of people are called…) 6. Describe the achievements of Hannibal? 7. Describe the structure of Roman politics during the Republic and the Empire. Ex. Senators, Consuls, Assemblies etc. 8. What are some of ...
... disadvantages to this landscape? 5. What are the Punic Wars? Who are the Romans fighting (Group of people are called…) 6. Describe the achievements of Hannibal? 7. Describe the structure of Roman politics during the Republic and the Empire. Ex. Senators, Consuls, Assemblies etc. 8. What are some of ...
Chp 8, Sec 1 The Beginning of Rome Powerpoint
... alphabet, and the toga. • Etruscan kings ruled Rome and the Latins for over 100 years ...
... alphabet, and the toga. • Etruscan kings ruled Rome and the Latins for over 100 years ...
The Roman Republic - English Worksheets Land
... The Roman Republic Students learn about the history of the Roman Empire. Studying ancient Rome is important because much of the culture of Europe and the United States was greatly influenced by the culture of Ancient Rome. When the Roman Empire was at it highest point in history, the Roman Emperor w ...
... The Roman Republic Students learn about the history of the Roman Empire. Studying ancient Rome is important because much of the culture of Europe and the United States was greatly influenced by the culture of Ancient Rome. When the Roman Empire was at it highest point in history, the Roman Emperor w ...
Roman world takes shape
... • Patricians: members of land-holding upper class • 2 Consuls nominated to supervise business of gov’t and command armies • In the event of war senate might choose a dictator ...
... • Patricians: members of land-holding upper class • 2 Consuls nominated to supervise business of gov’t and command armies • In the event of war senate might choose a dictator ...
Chapter 9 Roman Test
... The rule of Augustus Caesar marked the end ofDisciples = Roman leaders feared the spread of Christianity because- ...
... The rule of Augustus Caesar marked the end ofDisciples = Roman leaders feared the spread of Christianity because- ...
The Rise of the Roman Republic
... tools and weapons • 800 BC Distinct groups occupied the Italian peninsula- Umbrians, the Sabines, the Samnites, the Etruscans and the Latins ...
... tools and weapons • 800 BC Distinct groups occupied the Italian peninsula- Umbrians, the Sabines, the Samnites, the Etruscans and the Latins ...
Document
... Which group of lower-class people were granted full citizenship in Rome? The Ancient Roman Senate consisted of: Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus made what important social reform in Rome? The _____, accessed through the Gate of Death, was where dead bodies and bodies were dragged to be stripped of their ...
... Which group of lower-class people were granted full citizenship in Rome? The Ancient Roman Senate consisted of: Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus made what important social reform in Rome? The _____, accessed through the Gate of Death, was where dead bodies and bodies were dragged to be stripped of their ...