Paradigm Shifts in Biomedical Research
... Cell Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
... Cell Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
Human Genome Project
... completion of a “working draft” DNA sequence (90%) of the human genome By 2003 ...
... completion of a “working draft” DNA sequence (90%) of the human genome By 2003 ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells that carries the DNA. Each human has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one of each parent. Gene: A gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that contains the “instructions” of how, when and where our bodies function. These instructi ...
... Chromosome: A compact, threadlike organization in the nucleus of human cells that carries the DNA. Each human has two sets of 23 chromosomes, one of each parent. Gene: A gene is a segment of the DNA molecule that contains the “instructions” of how, when and where our bodies function. These instructi ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
... 1. A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. 2. A karyotype shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. 3. Two of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because ...
Human Genome Project
... Most of the actual human genome sequencing was done on BAC clones, which are less prone to rearrangement than YAC clones. BACs are about 100-200 kbp long. Large clones are generally sequenced by shotgun sequencing: The large cloned DNA is randomly broken up into a series of small fragments ( less th ...
... Most of the actual human genome sequencing was done on BAC clones, which are less prone to rearrangement than YAC clones. BACs are about 100-200 kbp long. Large clones are generally sequenced by shotgun sequencing: The large cloned DNA is randomly broken up into a series of small fragments ( less th ...
2nd problem set
... a) ______________ : a sequence that immediately precedes a gene and indicates the start of transcription. b) ______________ : a protein that synthesizes a new strand of DNA. c) ______________: a molecule which can terminate a growing DNA strand. 7. Which one of the following molecules is NOT found i ...
... a) ______________ : a sequence that immediately precedes a gene and indicates the start of transcription. b) ______________ : a protein that synthesizes a new strand of DNA. c) ______________: a molecule which can terminate a growing DNA strand. 7. Which one of the following molecules is NOT found i ...
Cloning vectors share four common properties
... Many cloning vectors contain a multiple cloning site or polylinker: a DNA segment with several unique sites for restriction endo- nucleases located next to each other Restriction sites of the polylinker are not present anywhere else in the plasmid. Cutting plasmids with one of the restriction enzyme ...
... Many cloning vectors contain a multiple cloning site or polylinker: a DNA segment with several unique sites for restriction endo- nucleases located next to each other Restriction sites of the polylinker are not present anywhere else in the plasmid. Cutting plasmids with one of the restriction enzyme ...
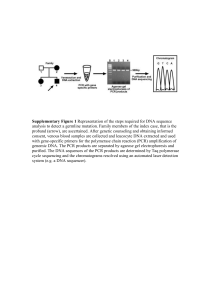
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Genetic Engineering - Effingham County Schools
... .. Genetic Modification Make changes in DNA code by Insert or delete specific genes Use modern molecular biology techniques. ...
... .. Genetic Modification Make changes in DNA code by Insert or delete specific genes Use modern molecular biology techniques. ...
DNA Technology
... Long answer, no with a but • Environment has a major effect on gene expression • The HGP detected 20,000 to 35,000 genes but we have over a million distinct proteins….what gives? ...
... Long answer, no with a but • Environment has a major effect on gene expression • The HGP detected 20,000 to 35,000 genes but we have over a million distinct proteins….what gives? ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... modified plants and animals (GMOs) for a variety of reasons. including increased nutrition and pest resistance 2. Transgenic-an organism that has genes from more than one species due to genetic modification C. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Process used to separate different DNA segments 2. Restriction enzy ...
... modified plants and animals (GMOs) for a variety of reasons. including increased nutrition and pest resistance 2. Transgenic-an organism that has genes from more than one species due to genetic modification C. Gel Electrophoresis 1. Process used to separate different DNA segments 2. Restriction enzy ...
DNA TECHNOLOGY
... 5. Transgenic animals help scientists study human diseases & treatments. Ranchers & dairy farmers can clone - create genetically identical copies - of productive, healthy animals to increase yields. ...
... 5. Transgenic animals help scientists study human diseases & treatments. Ranchers & dairy farmers can clone - create genetically identical copies - of productive, healthy animals to increase yields. ...
Advances in Genetics
... • The process of selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation is called selective breeding • The corn we use today is a great example! • 2 techniques • Inbreeding • hybridization ...
... • The process of selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation is called selective breeding • The corn we use today is a great example! • 2 techniques • Inbreeding • hybridization ...
4/17
... – One-nucleotide difference in sequence of two organisms – Discovered by sequencing – Example: Between any two humans, on average one SNP every 1,000 base pairs ...
... – One-nucleotide difference in sequence of two organisms – Discovered by sequencing – Example: Between any two humans, on average one SNP every 1,000 base pairs ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.