Advances in genetics
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
October 3, 2016 Worksheet
... 1. You leave for the bathroom and coming back, you notice that someone has taken a bite from your cookie you left on your plate. You collect the saliva from the crime scene. You carry out PCR amplification and electrophorese the DNA. You suspect your mom, dad or your little brother (suspects 1, 2, a ...
... 1. You leave for the bathroom and coming back, you notice that someone has taken a bite from your cookie you left on your plate. You collect the saliva from the crime scene. You carry out PCR amplification and electrophorese the DNA. You suspect your mom, dad or your little brother (suspects 1, 2, a ...
Insects and genetics
... 21. Name two UIUC faculty members who are involved in the honey bee genome project: a b. 22. What tool developed at UIUC being used to investigate Colony Collapse Disorder? 23. Name two insects other than Drosophila melanogaster that have been sequenced: a. b. 24. On March 1, 2005, the National Huma ...
... 21. Name two UIUC faculty members who are involved in the honey bee genome project: a b. 22. What tool developed at UIUC being used to investigate Colony Collapse Disorder? 23. Name two insects other than Drosophila melanogaster that have been sequenced: a. b. 24. On March 1, 2005, the National Huma ...
Principles and Practices of Biosafety
... not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of an organism is being established, a higher BSL will be required. Cloning of genes coding for proteins that have potential pharmacol ...
... not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of an organism is being established, a higher BSL will be required. Cloning of genes coding for proteins that have potential pharmacol ...
Fluorescent dye, SYBR Green, is incorporated into PCR reaction
... • Linkage mapping – Flanking markers identified – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
... • Linkage mapping – Flanking markers identified – 1cM, for example • Probably ~ 1 MB or more in humans • Need very many families to get closer than this in human, or very large populations ...
Genetic and Genomics: An Introduction
... the female), each gamete may not carry the exact same DNA sequence, i.e., a polymorphism (poly = many, morph = form) may occur which involves one of two or more variants of a particular DNA sequence. The most common polymorphism involves variation at a single base pair. This variation is called a si ...
... the female), each gamete may not carry the exact same DNA sequence, i.e., a polymorphism (poly = many, morph = form) may occur which involves one of two or more variants of a particular DNA sequence. The most common polymorphism involves variation at a single base pair. This variation is called a si ...
genome433
... two homologous chromosomes (for example, the homologous chromosome 1 copies that you received, one from your mother and one from your father). Most human haploid genomes differ by about 1-3 million SNPs from each other. There are a variety of mechanisms used to identify SNPs. The disadvantage of SNP ...
... two homologous chromosomes (for example, the homologous chromosome 1 copies that you received, one from your mother and one from your father). Most human haploid genomes differ by about 1-3 million SNPs from each other. There are a variety of mechanisms used to identify SNPs. The disadvantage of SNP ...
Name_____________________ Date__________ Class
... is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic material. It can be small, involving a single missing DNA base pair, or large, involving a piece of a chromosome. any of a group of enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of DNA molecules at specific sites. DNA in which one or more segments or genes ha ...
... is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic material. It can be small, involving a single missing DNA base pair, or large, involving a piece of a chromosome. any of a group of enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of DNA molecules at specific sites. DNA in which one or more segments or genes ha ...
Section 6-3
... There are three methods people have created to develop organisms with desired traits ...
... There are three methods people have created to develop organisms with desired traits ...
Lecture 32 Slides
... 5% of the human genome is found to be recently-duplicated large segments (>500bp, identity>95%). [JA Bailey, Science, 2002] The duplicated regions create mosaic structure. Some of the duplicated segments contain new genes. ...
... 5% of the human genome is found to be recently-duplicated large segments (>500bp, identity>95%). [JA Bailey, Science, 2002] The duplicated regions create mosaic structure. Some of the duplicated segments contain new genes. ...
Genomic Library cDNA Library
... The best strategy to produce fragments which are long, and overlapping is to choose an enzyme (Sau3A) which cuts very frequently in the genome – not obvious!! But only to cleave a few of these sites at random (partial cleavage) ...
... The best strategy to produce fragments which are long, and overlapping is to choose an enzyme (Sau3A) which cuts very frequently in the genome – not obvious!! But only to cleave a few of these sites at random (partial cleavage) ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
... 1. Genetic engineering- remaking genes for practical purposes 2. Recombinant DNA- DNA made from two or more different organisms 3. Restriction enzyme- enzymes that recognize short specific DNA sequences and that cut the DNA there 4. Plasmid- small, circular DNA molecules that can replicate independa ...
The Human Genome https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_genome
... Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and spermgamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNAbase pairs, while dipl ...
... Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Haploid human genomes, which are contained in germ cells (the egg and spermgamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNAbase pairs, while dipl ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
Chpt. 5 Review Questions
... • Genetic Engineering the process of transferring genes from one organism to another • Gene Therapy involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. ...
... • Genetic Engineering the process of transferring genes from one organism to another • Gene Therapy involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. ...
7th grade Ch. 5 section 2 and 3 Notes
... • Medical care and treatments can help people with some of these disorders. • Most genetic disorders do not prevent people from living active and productive lives. ...
... • Medical care and treatments can help people with some of these disorders. • Most genetic disorders do not prevent people from living active and productive lives. ...
Biotechnology - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... A gene is a sequence of ______ protein that codes for one __________. DNA codes for proteins. **Remember, not all of the ______ genes the parts that The parts that do are called ________, don’t are called _________________ non-coding regions. ...
... A gene is a sequence of ______ protein that codes for one __________. DNA codes for proteins. **Remember, not all of the ______ genes the parts that The parts that do are called ________, don’t are called _________________ non-coding regions. ...
Genetic Engineering
... sequencing the genes of many model species to provide insights into gene function. ...
... sequencing the genes of many model species to provide insights into gene function. ...
Chapter 15 - Advances in Molecular Genetics
... organism in question #11 has how many? Why does this make it a unique organism to study? 13. What is functional genomics? How does it contribute to our understanding our own genome? 14. Read the Focus On section on p. 396. How has automation sped up our ability to sequence DNA? 15. What is the role ...
... organism in question #11 has how many? Why does this make it a unique organism to study? 13. What is functional genomics? How does it contribute to our understanding our own genome? 14. Read the Focus On section on p. 396. How has automation sped up our ability to sequence DNA? 15. What is the role ...
Recombinant DNA Technologies
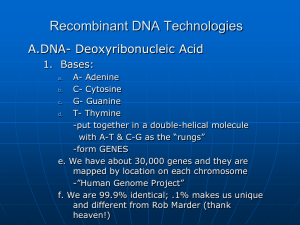
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Recombinant DNA Technology: Using the above tools, genes are combined from two or more different sources. The recombinant fragment is introduced into a cell that can express that gene. Uses: Mass production of biochemicals needed by other species Creation of new strains of living organisms Pro ...
... Recombinant DNA Technology: Using the above tools, genes are combined from two or more different sources. The recombinant fragment is introduced into a cell that can express that gene. Uses: Mass production of biochemicals needed by other species Creation of new strains of living organisms Pro ...
Genetic Engineering
... separates pieces of DNA based on size (after being cut up with restriction enzymes) Different people will have different banding patterns. Related individuals will have similar patterns. ...
... separates pieces of DNA based on size (after being cut up with restriction enzymes) Different people will have different banding patterns. Related individuals will have similar patterns. ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.