Biotechnology Need To Know List
... How breeders maintain the desired traits of an organism Why polyploidy instantly produces a new plant species How to recognize a diagram of DNA cut by a restriction enzyme What DNA analysis by gel electrophoresis allows researchers to do The technique used to make many copies of a gene What genetic ...
... How breeders maintain the desired traits of an organism Why polyploidy instantly produces a new plant species How to recognize a diagram of DNA cut by a restriction enzyme What DNA analysis by gel electrophoresis allows researchers to do The technique used to make many copies of a gene What genetic ...
The E. coli genome. - life.illinois.edu.
... Whole genome shotgun sequencing strategy 1. Randomly shear genomic DNA into small pieces, size-fractionate on a gel (e.g. only 2-3kb or 9-11kb pieces), and clone in a plasmid. 2. Sequence each randomly picked plasmid clone insert from each end using flanking primers that anneal to the plasmid vecto ...
... Whole genome shotgun sequencing strategy 1. Randomly shear genomic DNA into small pieces, size-fractionate on a gel (e.g. only 2-3kb or 9-11kb pieces), and clone in a plasmid. 2. Sequence each randomly picked plasmid clone insert from each end using flanking primers that anneal to the plasmid vecto ...
Powerpoint - University of British Columbia
... isolation (Conversion to cDNA) • Require cloning of cDNAs • Require many different tissues = good coverage of genomic information • Usually sequence from 5’ or 3’ end (known as pair end or mate end sequencing) • Will require more $$ to sequence both ends • Usually less than 60% of genes coverage • W ...
... isolation (Conversion to cDNA) • Require cloning of cDNAs • Require many different tissues = good coverage of genomic information • Usually sequence from 5’ or 3’ end (known as pair end or mate end sequencing) • Will require more $$ to sequence both ends • Usually less than 60% of genes coverage • W ...
ICSB3: DRPM Measures
... 8:30-9:15 am 6-Nov-2008 Forum on Science and Biothreats FAZD Lansdowne, VA ...
... 8:30-9:15 am 6-Nov-2008 Forum on Science and Biothreats FAZD Lansdowne, VA ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Gene ...
... WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Gene ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics Test Review
... pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
... pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 7. Meristem culture is used to eliminate virus in tissue culture 8. Barbara McClintok discovered jumping genes 9. Particle gun bombardment technique cannot be used for gene transfer in plants 10. Haploid set of chromosome (n) of an organism is termed as genome ...
... 7. Meristem culture is used to eliminate virus in tissue culture 8. Barbara McClintok discovered jumping genes 9. Particle gun bombardment technique cannot be used for gene transfer in plants 10. Haploid set of chromosome (n) of an organism is termed as genome ...
SBI 3CI Diagnostic Quiz October 10, 2014 – Microbiology Name
... 2 members of the same species don’t always produce fertile offspring Vaccines are considered a form of passive immunity. Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been spliced open and strands of DNA added in. ...
... 2 members of the same species don’t always produce fertile offspring Vaccines are considered a form of passive immunity. Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been spliced open and strands of DNA added in. ...
No Slide Title
... sequence was a technological breakthrough more than a scientific breakthrough Nonetheless, it is a tremendous advance and provides short cuts to gene identification ...
... sequence was a technological breakthrough more than a scientific breakthrough Nonetheless, it is a tremendous advance and provides short cuts to gene identification ...
Genetic Markers
... Finding genes in the candidate region • In the old days, or if your organism’s genome has not been sequenced, you had to do a lot of DNA cloning and analysis in the lab • Now you just look in the database! ...
... Finding genes in the candidate region • In the old days, or if your organism’s genome has not been sequenced, you had to do a lot of DNA cloning and analysis in the lab • Now you just look in the database! ...
Bill Nye - Genetics (worksheet)
... 5) What did irradiating (exposing them to x-rays) do to the genes of the bread mold? 6) The Beadle and Tatum breakthrough was the “one gene, one _______________” hypothesis. ...
... 5) What did irradiating (exposing them to x-rays) do to the genes of the bread mold? 6) The Beadle and Tatum breakthrough was the “one gene, one _______________” hypothesis. ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
... Short Answer On the lines provided, list the kinds of information that can be found by knowing the sequence of a DNA molecule. 4. __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________________________________________________ 6 ...
Unit 4 Part2 wksht3
... 1. Genetic engineering involves isolating, removing, and recombining genes. What is used to cut the DNA at a specific place to remove a gene? ___________________________________________ ...
... 1. Genetic engineering involves isolating, removing, and recombining genes. What is used to cut the DNA at a specific place to remove a gene? ___________________________________________ ...
Principles of genetic engineering
... Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a new genotype. Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: – inserting a foreign gene from one species into another – altering an existing gene so that its product is chan ...
... Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a new genotype. Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: – inserting a foreign gene from one species into another – altering an existing gene so that its product is chan ...
Document
... Size of Library: A gene library must contain a certain number of • recombinants for a high probability of it containing any particular sequence. This value can be calculated if the genome size and the average size of the insert in the vector are known. Genomic DNA: For making libraries, genomic DNA ...
... Size of Library: A gene library must contain a certain number of • recombinants for a high probability of it containing any particular sequence. This value can be calculated if the genome size and the average size of the insert in the vector are known. Genomic DNA: For making libraries, genomic DNA ...
+ IPTG + X-gal
... Summary of Blue/White Cloning and -Complementation 1. Cut out gene of interest with restriction enzyme 2. Cut B/W cloning vector with same restriction enzyme (MCS) a. Dephosphorylate vector to prevent self-ligation 3. Mix insert with vector and add ligase 4. Transform E. coli that is made for B ...
... Summary of Blue/White Cloning and -Complementation 1. Cut out gene of interest with restriction enzyme 2. Cut B/W cloning vector with same restriction enzyme (MCS) a. Dephosphorylate vector to prevent self-ligation 3. Mix insert with vector and add ligase 4. Transform E. coli that is made for B ...
MolecularBiology1APLab6
... • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance ...
... • Contain nonsense information • Sometimes contain useful information like antibiotic resistance ...
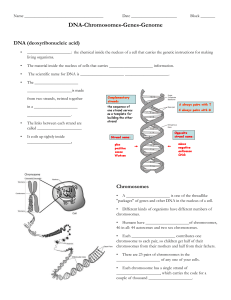
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
notes
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
Launches RNAcomplete Allowing Co-Extraction
... The co-extracted DNA produced by RNAcomplete is suitable for whole exome sequencing with PGDx’s CancerXOMETM, which captures and analyzes the coding regions of more than 20,000 genes. The CancerXOME and RNAcomplete results together provide powerful information on both gene expression and mutational ...
... The co-extracted DNA produced by RNAcomplete is suitable for whole exome sequencing with PGDx’s CancerXOMETM, which captures and analyzes the coding regions of more than 20,000 genes. The CancerXOME and RNAcomplete results together provide powerful information on both gene expression and mutational ...
Long-span, mate-pair scaffolding and other methods for
... Table 1 | Summary of Lucigen 40-kb long-span, mate-pair human genome library sequenced on Illumina platform. ...
... Table 1 | Summary of Lucigen 40-kb long-span, mate-pair human genome library sequenced on Illumina platform. ...
Molecular_Evolution
... The Genome: smaller than we once thought • The collection of all the DNA in the cell is referred to as the genome. • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
... The Genome: smaller than we once thought • The collection of all the DNA in the cell is referred to as the genome. • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
Graduate Program in Molecular Cell Biology:
... determining their own CYP2D6 genotype by RFLP-analysis. Methods applied are: Isolation of genomic DNA from blood, PCR, RE-analysis, agarose gel electrophoresis. // Following the analytical RFLP procedure, preparative DNA techniques will be used in the second part of the course: Prep. PCR for RE site ...
... determining their own CYP2D6 genotype by RFLP-analysis. Methods applied are: Isolation of genomic DNA from blood, PCR, RE-analysis, agarose gel electrophoresis. // Following the analytical RFLP procedure, preparative DNA techniques will be used in the second part of the course: Prep. PCR for RE site ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.