CHAPTER 17 Variation in Chromosomal Number and Structure
... d. Strains heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation must pair a set of normal chromosomes (N) with a set of translocated ones (T). i. Result is a cross-like configuration in meiotic prophase I of four associated chromosomes, each partially homologous to two others in the group (Figure 17.12). ii ...
... d. Strains heterozygous for a reciprocal translocation must pair a set of normal chromosomes (N) with a set of translocated ones (T). i. Result is a cross-like configuration in meiotic prophase I of four associated chromosomes, each partially homologous to two others in the group (Figure 17.12). ii ...
Test Info Sheet
... 4. Prenatal diagnosis for known familial mutation(s) in at-risk pregnancies Methods: Using genomic DNA, coding exons and flanking splice junctions of the genes on this panel are enriched using a proprietary targeted capture method developed by GeneDx. The products are sequenced on an Illumina instru ...
... 4. Prenatal diagnosis for known familial mutation(s) in at-risk pregnancies Methods: Using genomic DNA, coding exons and flanking splice junctions of the genes on this panel are enriched using a proprietary targeted capture method developed by GeneDx. The products are sequenced on an Illumina instru ...
D. melanogaster - GEP Community Server
... Simulate restriction digests of 21 genomes DNA fragments range from 21-33 bp in size Calculate distance between two genomes based on number of shared fragments Seetharam AS and Stuart GW. Whole genome phylogeny for 21 Drosophila species using predicted 2b-RAD fragments. PeerJ. 2013 Dec 23;1:e226. ...
... Simulate restriction digests of 21 genomes DNA fragments range from 21-33 bp in size Calculate distance between two genomes based on number of shared fragments Seetharam AS and Stuart GW. Whole genome phylogeny for 21 Drosophila species using predicted 2b-RAD fragments. PeerJ. 2013 Dec 23;1:e226. ...
PDF
... of the flow cell is essential for single molecule studies. This is achieved by combining together an unmodified DNA with derivatized DNA handles. Such handles can be prepared in a variety of ways. Perhaps the easiest way involves PCR using modified dNTPs. For the generation of a DNA tether, modified ...
... of the flow cell is essential for single molecule studies. This is achieved by combining together an unmodified DNA with derivatized DNA handles. Such handles can be prepared in a variety of ways. Perhaps the easiest way involves PCR using modified dNTPs. For the generation of a DNA tether, modified ...
Diploidy and the selective advantage for sexual reproduction in
... are formally distinct phenomena, they can often be associated with one another, as is the case with the models being considered here (Bull and Wilke 2008). However, for sexual reproduction in the multi-chromosomed genome, the error catastrophe does not occur as long as κl > 0 for each l. This result ...
... are formally distinct phenomena, they can often be associated with one another, as is the case with the models being considered here (Bull and Wilke 2008). However, for sexual reproduction in the multi-chromosomed genome, the error catastrophe does not occur as long as κl > 0 for each l. This result ...
lncRNA in
... • Find protein coding evidence, if none then label lncRNA – Requires accurate full length transcript sequence – Assumes we know all proteins – In phylogenomic approaches need enough interspecies multiple sequence alignments ...
... • Find protein coding evidence, if none then label lncRNA – Requires accurate full length transcript sequence – Assumes we know all proteins – In phylogenomic approaches need enough interspecies multiple sequence alignments ...
Integration of the Classical and Molecular Linkage Maps of Tomato
... the species L. esculentum and mapped using intraspecific crosses. As the number of DNA polymorphisms detectable between genotypes of L. esculentum is very 1990; VAN DER BEEKet low (MILLERand TANKSLEY al. 1992), construction of an integrated mapof an entire chromosome is only attainable through linka ...
... the species L. esculentum and mapped using intraspecific crosses. As the number of DNA polymorphisms detectable between genotypes of L. esculentum is very 1990; VAN DER BEEKet low (MILLERand TANKSLEY al. 1992), construction of an integrated mapof an entire chromosome is only attainable through linka ...
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism of hsp70
... them were purchased from commercial North American sources (Taconic Farms, Inc., Germantown, N.Y., and Charles River, Wilmington, Mass.), and the third was obtained from the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague (but originated from OLAC, England). The normotensive animals were Brown-Norway BN.lx ...
... them were purchased from commercial North American sources (Taconic Farms, Inc., Germantown, N.Y., and Charles River, Wilmington, Mass.), and the third was obtained from the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague (but originated from OLAC, England). The normotensive animals were Brown-Norway BN.lx ...
SNP Analysis (GAW15 data)
... we checked the LOD scores among families with no parents genotyped (59%) versus families with at least one genotyped parent (41%) for the major regions of linkage on chromosomes 2, 4, 7, 10 and 11. LOD scores remained positive in all family groups. On chromosomes 2, 7, and 11 the LOD scores from the ...
... we checked the LOD scores among families with no parents genotyped (59%) versus families with at least one genotyped parent (41%) for the major regions of linkage on chromosomes 2, 4, 7, 10 and 11. LOD scores remained positive in all family groups. On chromosomes 2, 7, and 11 the LOD scores from the ...
A genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation in buccal - VU-DARE
... three candidate genes (DRD4, SLC6A4/SERT and MAOA) based on buccal cells indicated that changes in methylation of these genes within individuals between age 5 and 10 are mostly attributable to non-shared environmental influences and stochastic variation 31. Clearly, twin studies of candidate regions ...
... three candidate genes (DRD4, SLC6A4/SERT and MAOA) based on buccal cells indicated that changes in methylation of these genes within individuals between age 5 and 10 are mostly attributable to non-shared environmental influences and stochastic variation 31. Clearly, twin studies of candidate regions ...
Application of rpoB sequence similarity analysis, REP‐PCR and
... the rpoB tree, both phylogenetic analyses shared satisfactory bootstrap support. In terms of the 16S rRNA gene sequences of Geobacillus and Bacillus type strains and isolates, similarity values among 90% and 100% were retrieved, in agreement with Zeigler (2005) who confirmed 16S rRNA gene sequences ...
... the rpoB tree, both phylogenetic analyses shared satisfactory bootstrap support. In terms of the 16S rRNA gene sequences of Geobacillus and Bacillus type strains and isolates, similarity values among 90% and 100% were retrieved, in agreement with Zeigler (2005) who confirmed 16S rRNA gene sequences ...
Induction of XIST expression from the human active
... by northern blot analysis for two of the genes, PGK1 (Fig. 4B) and TIMP1 (data not shown). In both cases expression was similar in the active X parental line (AHA-11a) and the XIST-expressing clone AHA-A5-2b, and hybridisation was specific to the human transcript as no signal was detected for RNA fr ...
... by northern blot analysis for two of the genes, PGK1 (Fig. 4B) and TIMP1 (data not shown). In both cases expression was similar in the active X parental line (AHA-11a) and the XIST-expressing clone AHA-A5-2b, and hybridisation was specific to the human transcript as no signal was detected for RNA fr ...
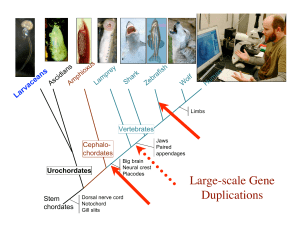
(Japan), organized by Nori Satoh
... Developmental signaling by retinoic acid (RA) is thought to be an innovation essential for the origin of the chordate body plan. The larvacean urochordate Oikopleura dioica maintains a chordate body plan throughout life, and yet its genome appears to lack genes for RA synthesis, degradation, and rec ...
... Developmental signaling by retinoic acid (RA) is thought to be an innovation essential for the origin of the chordate body plan. The larvacean urochordate Oikopleura dioica maintains a chordate body plan throughout life, and yet its genome appears to lack genes for RA synthesis, degradation, and rec ...
the Gene Ontology
... GO annotation relies on computational methods (rapid) functional literature exists for many genes/proteins prior to genome sequencing GO annotation does not rely on a completed genome sequence! ...
... GO annotation relies on computational methods (rapid) functional literature exists for many genes/proteins prior to genome sequencing GO annotation does not rely on a completed genome sequence! ...
Article 1 Title: The pseudoautosomal regions of the U/V sex
... rho = -0.113, P = 0.598) while gene density and GC percentage increase with chromosome size (Spearman’s correlation test rho = 0.303, P = 0.151 and rho = 0.284, P = 0.178, respectively). Consequently, to analyse in detail the unusual structural features of the Ectocarpus PARs, we compared the sex ch ...
... rho = -0.113, P = 0.598) while gene density and GC percentage increase with chromosome size (Spearman’s correlation test rho = 0.303, P = 0.151 and rho = 0.284, P = 0.178, respectively). Consequently, to analyse in detail the unusual structural features of the Ectocarpus PARs, we compared the sex ch ...
A genetic linkage map for watermelon based on
... Hampshire Midget (fusarium susceptible)] x ‘New Hampshire Midget’. The map contains 155 RAPD markers, and a 700base pair sequenced characterized amplified region (SCAR) marker that corresponds to a fragment produced by the RAPD primer GTAGCACTCC. This marker was reported previously as linked (1.6 cM ...
... Hampshire Midget (fusarium susceptible)] x ‘New Hampshire Midget’. The map contains 155 RAPD markers, and a 700base pair sequenced characterized amplified region (SCAR) marker that corresponds to a fragment produced by the RAPD primer GTAGCACTCC. This marker was reported previously as linked (1.6 cM ...
Genomic and Physiological Comparisons Between Heterotrophic
... 520% homology to DNA from a reference strain (Table 1) indicates that the test strain belongs to a species that is not related to the reference strain. Test DNA having 20 to 50% homology to reference DNA indicates that the test strain belongs to a species different from, although closely related to, ...
... 520% homology to DNA from a reference strain (Table 1) indicates that the test strain belongs to a species that is not related to the reference strain. Test DNA having 20 to 50% homology to reference DNA indicates that the test strain belongs to a species different from, although closely related to, ...
Molecular function - SGD-Wiki - Saccharomyces Genome Database
... • People who understand the biology (Ph.D. biologists) are required to design the database, summarize the literature, etc. • Full-time staff positions are needed for project stability. • Our top priority is to serve the needs of the research community (yeast and other), so communication with users i ...
... • People who understand the biology (Ph.D. biologists) are required to design the database, summarize the literature, etc. • Full-time staff positions are needed for project stability. • Our top priority is to serve the needs of the research community (yeast and other), so communication with users i ...
Genomic and Physiological Comparisons Between Heterotrophic
... 520% homology to DNA from a reference strain (Table 1) indicates that the test strain belongs to a species that is not related to the reference strain. Test DNA having 20 to 50% homology to reference DNA indicates that the test strain belongs to a species different from, although closely related to, ...
... 520% homology to DNA from a reference strain (Table 1) indicates that the test strain belongs to a species that is not related to the reference strain. Test DNA having 20 to 50% homology to reference DNA indicates that the test strain belongs to a species different from, although closely related to, ...
Assessment of the mosaic structure in the
... sequencing and CGE analysis also revealed a bias of amplicons observed before (Fig. 2, lane 18) and after cloning (Fig. 2, lane 18a and 18h) which might be due to the fact that only highly abundant amplicons, present in the initial amplification derived from H. pylori HJM18MDA-DNA, were detectable b ...
... sequencing and CGE analysis also revealed a bias of amplicons observed before (Fig. 2, lane 18) and after cloning (Fig. 2, lane 18a and 18h) which might be due to the fact that only highly abundant amplicons, present in the initial amplification derived from H. pylori HJM18MDA-DNA, were detectable b ...
The KIebsieIIa pneumoniae cytochrome bd
... and nitrogen-free Davis and Mingioli medium (NFDM medium) (Cannon, 1984), supplemented when required with histidine (at 25 pgml-l) and NH,C1(15 mM). Where indicated, plates were incubated anaerobically in a Gas Pak system (Becton Dickinson). Antibiotics for E. coli and for K . pnuemoniae were added ...
... and nitrogen-free Davis and Mingioli medium (NFDM medium) (Cannon, 1984), supplemented when required with histidine (at 25 pgml-l) and NH,C1(15 mM). Where indicated, plates were incubated anaerobically in a Gas Pak system (Becton Dickinson). Antibiotics for E. coli and for K . pnuemoniae were added ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.