Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and
... analyse bisulphite-treated DNA. Reduced representation bisulphite sequencing is an approach in which DNA is cleaved by methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes before bisulphite treatment. The most comprehensive coverage at single-base level is obtained by shotgun sequencing of bisulphite-treated D ...
... analyse bisulphite-treated DNA. Reduced representation bisulphite sequencing is an approach in which DNA is cleaved by methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes before bisulphite treatment. The most comprehensive coverage at single-base level is obtained by shotgun sequencing of bisulphite-treated D ...
Genetic and biochemical identification of the
... Taq DNA polymerase (Transgen). PCR products were purified using an agarose gel DNA fragment recovery kit (TIANGEN). Cloning of PCR fragments was performed with the pEASY-T1 cloning vector systems (Transgen). Various plasmids (Table 1) for genetic disruption and complementation in C. glutamicum and f ...
... Taq DNA polymerase (Transgen). PCR products were purified using an agarose gel DNA fragment recovery kit (TIANGEN). Cloning of PCR fragments was performed with the pEASY-T1 cloning vector systems (Transgen). Various plasmids (Table 1) for genetic disruption and complementation in C. glutamicum and f ...
CHROMOTHRIPSIS FROM DNA DAMAGE IN MICRONUCLEI The
... disorders called chromothripsis. Chromothripsis is characterized by extensive genomic rearrangements and an oscillating pattern of DNA copy number levels, all curiously restricted to one or a few chromosomes. The mechanism for chromothripsis is unknown, but we previously proposed that it could occur ...
... disorders called chromothripsis. Chromothripsis is characterized by extensive genomic rearrangements and an oscillating pattern of DNA copy number levels, all curiously restricted to one or a few chromosomes. The mechanism for chromothripsis is unknown, but we previously proposed that it could occur ...
An assessment of factors affecting the likelihood
... that competent bacteria are exposed to plant transgenes to the same extent as to other plant DNA. Although positive results have been obtained in vitro, the ability of bacteria to take up plant DNA that is naturally released in situ e.g. in soil or in planta, has not been shown. Information on the ...
... that competent bacteria are exposed to plant transgenes to the same extent as to other plant DNA. Although positive results have been obtained in vitro, the ability of bacteria to take up plant DNA that is naturally released in situ e.g. in soil or in planta, has not been shown. Information on the ...
Full-Text PDF
... A potential limitation of this library is that the TMR moiety is too bulky and hydrophobic, which may cause non-specific binding or aggregation of the binders. Thus, we envisioned that conjugation of a water-soluble and small drug-like molecule, instead of TMR, to a peptide library would increase th ...
... A potential limitation of this library is that the TMR moiety is too bulky and hydrophobic, which may cause non-specific binding or aggregation of the binders. Thus, we envisioned that conjugation of a water-soluble and small drug-like molecule, instead of TMR, to a peptide library would increase th ...
Complete Characterization of the 3 Mouse Hereditary Hemochromatosis HFE Gene and
... hereditary hemochromatosis in most patients. Expression analysis by Northern blot indicated that the gene was approximately 4.1 kb in length. However, the cDNA reported was only 2716 bp. These results implied that at least 1.4 kb of the mRNA remained to be identified. In the present study, we detect ...
... hereditary hemochromatosis in most patients. Expression analysis by Northern blot indicated that the gene was approximately 4.1 kb in length. However, the cDNA reported was only 2716 bp. These results implied that at least 1.4 kb of the mRNA remained to be identified. In the present study, we detect ...
Towards Programmable Molecular Machines
... of the walker is powered by enzymatic activity. Since these enzymes occur naturally in biological cells, they in turn can draw energy from well known bio-chemical processes (such as the ADP-ATP cycle) and do not require the development of new techniques. Most excitingly, the basic steps are very alg ...
... of the walker is powered by enzymatic activity. Since these enzymes occur naturally in biological cells, they in turn can draw energy from well known bio-chemical processes (such as the ADP-ATP cycle) and do not require the development of new techniques. Most excitingly, the basic steps are very alg ...
No more than 14: the end of the amphioxus Hox cluster
... Since Edward Lewis discovery of the Bithorax complex of Drosophila [1], the Hox gene cluster has captivated the imagination of developmental and evolutionary biologists. Hox genes are a subclass of homeobox transcription factors deeply involved in the regulation of body patterning in metazoans [2]. ...
... Since Edward Lewis discovery of the Bithorax complex of Drosophila [1], the Hox gene cluster has captivated the imagination of developmental and evolutionary biologists. Hox genes are a subclass of homeobox transcription factors deeply involved in the regulation of body patterning in metazoans [2]. ...
Clinical-Genomics-Atlanta-Shabo-September-2004
... classCode*: <= PRS id: SET [0..*] (use this attribute to hold pedigree ID)
...
... classCode*: <= PRS id: SET
Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in human
... such an analysis from the TSC data because the sequence reads are not available. Instead, we define SNP density as the total number of SNPs normalized to the total number of bases in any given genomic feature. This kind of analysis is useful for looking at the TSC data, as our aim was to glean infor ...
... such an analysis from the TSC data because the sequence reads are not available. Instead, we define SNP density as the total number of SNPs normalized to the total number of bases in any given genomic feature. This kind of analysis is useful for looking at the TSC data, as our aim was to glean infor ...
Deletion of a conserved noncoding sequence in Plzf intron leads to
... Lx mutation in SHR.Lx rat manifests in homozygotes as hindlimb preaxial polydactyly. It was previously mapped to a chromosome 8 segment containing the Plzf gene. Plzf (promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein) influences limb development as a direct repressor of posterior HoxD genes. However, the Pl ...
... Lx mutation in SHR.Lx rat manifests in homozygotes as hindlimb preaxial polydactyly. It was previously mapped to a chromosome 8 segment containing the Plzf gene. Plzf (promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein) influences limb development as a direct repressor of posterior HoxD genes. However, the Pl ...
Myriad--Ambry -- Final Version of Ambry Preliminary Injunction
... Chromosomes in a human cell are made up of two complementary strands of DNA molecules—one strand is on one side of the double helix and the second strand is on the other side. For any given gene, only one molecule strand (the “template strand”) is actually transcribed into mRNA and ultimately used t ...
... Chromosomes in a human cell are made up of two complementary strands of DNA molecules—one strand is on one side of the double helix and the second strand is on the other side. For any given gene, only one molecule strand (the “template strand”) is actually transcribed into mRNA and ultimately used t ...
The msh2 Gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe Is
... msh2 locus. The open box represents the msh21 coding region; dark grey boxes indicate the two introns. The his31 marker (light grey box) was inserted into the MluI and StyI restriction sites of pRU23 as shown to give rise to plasmid pRU24. The resulting msh2::his31 HindIII fragment was transformed i ...
... msh2 locus. The open box represents the msh21 coding region; dark grey boxes indicate the two introns. The his31 marker (light grey box) was inserted into the MluI and StyI restriction sites of pRU23 as shown to give rise to plasmid pRU24. The resulting msh2::his31 HindIII fragment was transformed i ...
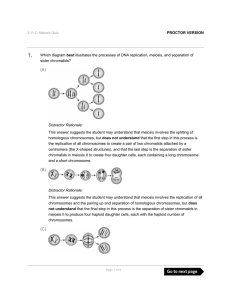
(A) (B) (C)
... (C) Markers on other chromosomes in the body would be less useful for determining paternity, because autosomal genetic markers are very difficult to identify compared to those that are sex-linked, since there are so many more autosomal chromosomes than sex chromosomes. Distractor Rationale: This ans ...
... (C) Markers on other chromosomes in the body would be less useful for determining paternity, because autosomal genetic markers are very difficult to identify compared to those that are sex-linked, since there are so many more autosomal chromosomes than sex chromosomes. Distractor Rationale: This ans ...
Characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana Mutant pcb2 which
... The growth rate of the pcb2 mutant was severely reduced compared with the wild-type. The thylakoid membranes of the pcb2 chloroplasts were arranged in a disorderly fashion and did not develop distinct grana stacks; extensive adhesion of two to a few thylakoid membranes was observed instead (Fig. 2). ...
... The growth rate of the pcb2 mutant was severely reduced compared with the wild-type. The thylakoid membranes of the pcb2 chloroplasts were arranged in a disorderly fashion and did not develop distinct grana stacks; extensive adhesion of two to a few thylakoid membranes was observed instead (Fig. 2). ...
Supplemental Tables
... also posted at the AAA site, were also used in this analysis. The FlyBase inferred cytological map locations were assigned to all of the orthologs called in the four species. These associations were then ordered and sorted according to their scaffold assignments and molecular coordinates for each sp ...
... also posted at the AAA site, were also used in this analysis. The FlyBase inferred cytological map locations were assigned to all of the orthologs called in the four species. These associations were then ordered and sorted according to their scaffold assignments and molecular coordinates for each sp ...
Multiple domain structure in a chitinase gene (chic)
... Fig. 1. Restriction map and various subcloned DNA fragments of the insert fragment of pEMJ7. The solid horizontal lines below the restriction map indicate the fragments used in this study to localize the gene and/or for sequencing analysis. The bold line indicates the smallest restriction fragment c ...
... Fig. 1. Restriction map and various subcloned DNA fragments of the insert fragment of pEMJ7. The solid horizontal lines below the restriction map indicate the fragments used in this study to localize the gene and/or for sequencing analysis. The bold line indicates the smallest restriction fragment c ...
Towards an accurate identification of mosaic genes and
... can be used (6). The tree rooting is necessary because it allows us to take into account the evolutionary time-constraints that should be satisfied when inferring HGTs. These time constraints, which include the same lineage HGTs as well as some criss-crossing transfers, are imposed by the necessity f ...
... can be used (6). The tree rooting is necessary because it allows us to take into account the evolutionary time-constraints that should be satisfied when inferring HGTs. These time constraints, which include the same lineage HGTs as well as some criss-crossing transfers, are imposed by the necessity f ...
Centromere Locations and Associated Chromosome
... the centromere (CEN) regions of A. thaliana, using at least two genes from the short and long arms of each chromosome. In our map, genes from all 10 A. thaliana chromosome arms are also tightly linked in A. lyrata. Genes from the regions on the two sides of CEN5 have distant map localizations in A. ...
... the centromere (CEN) regions of A. thaliana, using at least two genes from the short and long arms of each chromosome. In our map, genes from all 10 A. thaliana chromosome arms are also tightly linked in A. lyrata. Genes from the regions on the two sides of CEN5 have distant map localizations in A. ...
Unit 30C Cell Division, Genetics, and Molecular
... All life depends on the ability to grow and reproduce. Both these processes involve cell division. Organisms that reproduce asexually produce offspring that are identical to the parents. Sexually reproducing organisms exchange genetic information, so that the offspring have a unique combination of t ...
... All life depends on the ability to grow and reproduce. Both these processes involve cell division. Organisms that reproduce asexually produce offspring that are identical to the parents. Sexually reproducing organisms exchange genetic information, so that the offspring have a unique combination of t ...
DNA
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acids: Biological molecules (RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce ...
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acids: Biological molecules (RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.