word
... Genetic and epigenetic regulators of the germ line Specification of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in mammals occurs according to the 'stem cell model' in which pluripotent stem cells give rise to both the PGCs and somatic cells in response to signaling molecules. Expression of a transcriptional repre ...
... Genetic and epigenetic regulators of the germ line Specification of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in mammals occurs according to the 'stem cell model' in which pluripotent stem cells give rise to both the PGCs and somatic cells in response to signaling molecules. Expression of a transcriptional repre ...
10.1 - My Haiku
... between pairs of alleles long before the details of meiosis were known. Where Mendel states that pairs of alleles of a gene separate independently during gamete production, we can now attribute this to random orientation of chromosomes during metaphase I. Mendel made this deduction when working with ...
... between pairs of alleles long before the details of meiosis were known. Where Mendel states that pairs of alleles of a gene separate independently during gamete production, we can now attribute this to random orientation of chromosomes during metaphase I. Mendel made this deduction when working with ...
biofundamentals - virtual laboratories
... Latin meaning, anew. Rather each organism, including us, is the product of continuous evolutionary processes that have been in play since the origin of life (~3.5 billion years ago). While a particular individual does not evolve, populations do - evolution is simply a description of how populations ...
... Latin meaning, anew. Rather each organism, including us, is the product of continuous evolutionary processes that have been in play since the origin of life (~3.5 billion years ago). While a particular individual does not evolve, populations do - evolution is simply a description of how populations ...
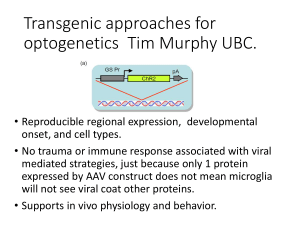
Transgenic approaches for optogenetics Tim Murphy UBC.
... Cre recombinase is a tyrosine recombinase enzyme derived from the P1 Bacteriophage. The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I like mechanism to carry out site specific recombination events. The enzyme (38kDa) is a member of the integrase family of site specific recombinase and it is known to catalyse the si ...
... Cre recombinase is a tyrosine recombinase enzyme derived from the P1 Bacteriophage. The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I like mechanism to carry out site specific recombination events. The enzyme (38kDa) is a member of the integrase family of site specific recombinase and it is known to catalyse the si ...
SVPaper050711
... Classification of SVs and their size characteristics are summarized in Figure 3. SVs are most often due to retrotransposons (LINEs (25%), LTRs (14%) and SINEs (15%)), followed by variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) (15%) and pseudogenes (2%). Other mechanisms, not involving retrotransposons, acco ...
... Classification of SVs and their size characteristics are summarized in Figure 3. SVs are most often due to retrotransposons (LINEs (25%), LTRs (14%) and SINEs (15%)), followed by variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) (15%) and pseudogenes (2%). Other mechanisms, not involving retrotransposons, acco ...
by Vanessa Di Gioacchino A thesis submitted to the Department of Biology
... Mental illness encompasses a wide variety of disorders that affect diverse subsets of the population. Despite their prevalence, the underlying causes of many of these illnesses are still poorly understood. For example, schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the population (Carpenter and Buchanan, ...
... Mental illness encompasses a wide variety of disorders that affect diverse subsets of the population. Despite their prevalence, the underlying causes of many of these illnesses are still poorly understood. For example, schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the population (Carpenter and Buchanan, ...
Genome-wide scan of bipolar disorder in 65 pedigrees: supportive evidence for linkage at 8q24, 18q22, 4q32, 2p12, and 13q12.
... The analyzed family sample consisted of 573 interviewed and genotyped subjects ascertained through 65 BPI probands. Among the 508 relatives, 64 were diagnosed with BPI, 97 with BPII, 69 with RUP, and seven with SAM. The mean age of onset for the BPI subjects (including probands) was 21.6711.9 years, ...
... The analyzed family sample consisted of 573 interviewed and genotyped subjects ascertained through 65 BPI probands. Among the 508 relatives, 64 were diagnosed with BPI, 97 with BPII, 69 with RUP, and seven with SAM. The mean age of onset for the BPI subjects (including probands) was 21.6711.9 years, ...
Plant Molecular Biology
... Abbreviations: Cmr, chloramphenicol; n'f, rifampicin; Spr, speetinomycin; str, streptomycin, Te r, tetraeyclin; Sym, Symbiosis. ...
... Abbreviations: Cmr, chloramphenicol; n'f, rifampicin; Spr, speetinomycin; str, streptomycin, Te r, tetraeyclin; Sym, Symbiosis. ...
The universal reagent for genome tailoring
... expression. In spite of the above difficulties, the number of satisfying Cre recombinase transgenic lines is growing, as this issue of Genesis also illustrates. To take advantage of the precise recombination mediated by the Cre enzyme, target loxP sites have to be introduced into the genome of the c ...
... expression. In spite of the above difficulties, the number of satisfying Cre recombinase transgenic lines is growing, as this issue of Genesis also illustrates. To take advantage of the precise recombination mediated by the Cre enzyme, target loxP sites have to be introduced into the genome of the c ...
Selection at the Wobble Position of Codons Read by the Same tRNA
... carried out with the iterative use of the program FASTA (Pearson and Lipman 1988) set to standard parameters; a dedicated C language program was employed to conduct pairwise homology searches and to eliminate all the sequences having nucleotide sequence similarity scores with other yeast genes highe ...
... carried out with the iterative use of the program FASTA (Pearson and Lipman 1988) set to standard parameters; a dedicated C language program was employed to conduct pairwise homology searches and to eliminate all the sequences having nucleotide sequence similarity scores with other yeast genes highe ...
B/b
... Random chromatid assortment (Quadrivalents are formed): Requirements for double reduction (requires that after crossing over between the centromere and gene marker in adjacent chromosomes, these chromosomes go to the same pole at anaphase I ): ...
... Random chromatid assortment (Quadrivalents are formed): Requirements for double reduction (requires that after crossing over between the centromere and gene marker in adjacent chromosomes, these chromosomes go to the same pole at anaphase I ): ...
CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION AND LITERATURE REVIEW 1.1
... on a game farm in the Kimberley district, Northern Cape Province, South Africa, developed a similar lesion on one of its legs. This arid area of South Africa is not the natural habitat of these antelopes as they are a savanna woodland species (Smithers 1983). Electron microscopically, virus particle ...
... on a game farm in the Kimberley district, Northern Cape Province, South Africa, developed a similar lesion on one of its legs. This arid area of South Africa is not the natural habitat of these antelopes as they are a savanna woodland species (Smithers 1983). Electron microscopically, virus particle ...
Cytogenetics with special reference to domestic animals
... Conserved synteny between the human and mouse genomes. Regions from different mouse chromosomes (indicated by the colors of each mouse in B) show conserved synteny (gene order) with the indicated regions of the human genome (A). For example the genes present in the upper portion of human chromosome ...
... Conserved synteny between the human and mouse genomes. Regions from different mouse chromosomes (indicated by the colors of each mouse in B) show conserved synteny (gene order) with the indicated regions of the human genome (A). For example the genes present in the upper portion of human chromosome ...
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
... in use as a supplement of animal diet in order to improve phosphorus utilisation. Based on sequence homology, phytases (EC 3.1.3.8 for 3-phytase and EC 3.1.8.26 for 6phytase) can be divided into histidine acid phosphatases, plant purple acid phosphatases and Bacillus beta-propeller phytases. Besides ...
... in use as a supplement of animal diet in order to improve phosphorus utilisation. Based on sequence homology, phytases (EC 3.1.3.8 for 3-phytase and EC 3.1.8.26 for 6phytase) can be divided into histidine acid phosphatases, plant purple acid phosphatases and Bacillus beta-propeller phytases. Besides ...
structure and mechanism of dna polymerases
... and thumb subdomains. Kinetically, they cycle through various states corresponding to conformational transitions, which may or may not generate force. In this review, we present and discuss the kinetic, structural, and single‐molecule works that have contributed to our understanding of DNA polymeras ...
... and thumb subdomains. Kinetically, they cycle through various states corresponding to conformational transitions, which may or may not generate force. In this review, we present and discuss the kinetic, structural, and single‐molecule works that have contributed to our understanding of DNA polymeras ...
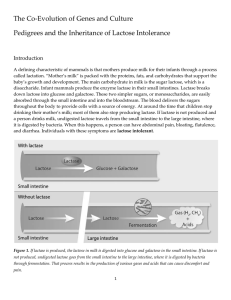
The Co-Evolution of Genes and Culture Pedigrees and the
... 2. Identify and circle all the nucleotides that differ between at least two sequences in each table. 3. Pretend that you are the researcher who discovered the variations and you are writing to a colleague describing what you found. a) How would you describe the variation(s) you found in Sequence 1? ...
... 2. Identify and circle all the nucleotides that differ between at least two sequences in each table. 3. Pretend that you are the researcher who discovered the variations and you are writing to a colleague describing what you found. a) How would you describe the variation(s) you found in Sequence 1? ...
meiosis
... Telophase II – The only difference from mitotic division is that chromosomes do not replicate before they divide at centromeres. ...
... Telophase II – The only difference from mitotic division is that chromosomes do not replicate before they divide at centromeres. ...
1 THE EVOLUTION OF LINE-1 IN VERTEBRATES Stéphane
... probably one of the genomic features that show the most variation in this group. At one end of the spectrum, mammalian genomes host an extremely large number of L1 insertions that have accumulated since the origin of mammals and account for close to 20% of their mass (Lander et al. 2001; Mouse Genom ...
... probably one of the genomic features that show the most variation in this group. At one end of the spectrum, mammalian genomes host an extremely large number of L1 insertions that have accumulated since the origin of mammals and account for close to 20% of their mass (Lander et al. 2001; Mouse Genom ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.