Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Casal, with inserts of 8-10 kb at BamHI restriction site, was amplified by transforming competent E. coli HB101 cells with a representative aliquot of the genomic library and growth of transformants in selective medium (LB with 50 mg/ml ampiciline). Genomic library screening was performed by transfo ...
... Casal, with inserts of 8-10 kb at BamHI restriction site, was amplified by transforming competent E. coli HB101 cells with a representative aliquot of the genomic library and growth of transformants in selective medium (LB with 50 mg/ml ampiciline). Genomic library screening was performed by transfo ...
Molecular events during translocation and proofreading extracted
... ble for power management of both translocation and processive active site switching. Once this oscillation is established, each leaving pyrophosphate (PPi) bound to the fingers in the closed conformation replenishes energy to maintain the oscillation. With each push from a newly cleaved PPi resultin ...
... ble for power management of both translocation and processive active site switching. Once this oscillation is established, each leaving pyrophosphate (PPi) bound to the fingers in the closed conformation replenishes energy to maintain the oscillation. With each push from a newly cleaved PPi resultin ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... When present in the germinal lineage, chromosomal abnormalities can be segregated in gametes and transmitted to the offspring, while in other cases they can hamper meiosis up to the arrest of gametogenesis, or may give rise to unbalanced gametes (13,14,15,16,17,18,19). Most diagnosed CCRs are three- ...
... When present in the germinal lineage, chromosomal abnormalities can be segregated in gametes and transmitted to the offspring, while in other cases they can hamper meiosis up to the arrest of gametogenesis, or may give rise to unbalanced gametes (13,14,15,16,17,18,19). Most diagnosed CCRs are three- ...
Control of DNA excision efficiency in Paramecium
... micronuclei undergo meiosis, whereas the macronuclei degenerate. The fusion of two gametic nuclei produces a zygotic nucleus. This nucleus divides twice and the daughter nuclei then differentiate into a micronucleus or a macronucleus. In the second case, the whole genome is processed through chromos ...
... micronuclei undergo meiosis, whereas the macronuclei degenerate. The fusion of two gametic nuclei produces a zygotic nucleus. This nucleus divides twice and the daughter nuclei then differentiate into a micronucleus or a macronucleus. In the second case, the whole genome is processed through chromos ...
evidence against micronuclear mutations as the sole
... teristic of autogamy, and by the recurrence of autogamy in sublines a t intervals too short for another normal interval. Furthermore the fission rate, the appearance a t autogamy, and the fate of the exautogamous animals indicated that the line was well aged. Fission rate in the daily isolation cult ...
... teristic of autogamy, and by the recurrence of autogamy in sublines a t intervals too short for another normal interval. Furthermore the fission rate, the appearance a t autogamy, and the fate of the exautogamous animals indicated that the line was well aged. Fission rate in the daily isolation cult ...
Gene Detection Systems Catalog
... Our mission is to be one of the most reliable suppliers of reagents and reagent systems used in genetic research technology applications worldwide. Gene Link, Inc. is privately held biotechnology company incorporated in the State of New York dedicated to fundamental and applied research on genetic/b ...
... Our mission is to be one of the most reliable suppliers of reagents and reagent systems used in genetic research technology applications worldwide. Gene Link, Inc. is privately held biotechnology company incorporated in the State of New York dedicated to fundamental and applied research on genetic/b ...
Exam 2 Answer Key Spring 1996 Mcbio 316 - page 1
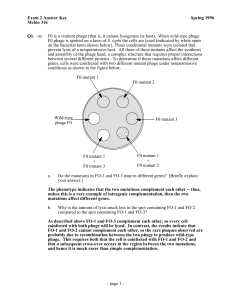
... As described above FO-1 and FO-3 complement each other, so every cell coinfected with both phage will be lysed. In contrast, the results indcate that FO-1 and FO-2 cannot complement each other, so the rare plaques observed are probably due to recombination between the two phage to produce wild-type ...
... As described above FO-1 and FO-3 complement each other, so every cell coinfected with both phage will be lysed. In contrast, the results indcate that FO-1 and FO-2 cannot complement each other, so the rare plaques observed are probably due to recombination between the two phage to produce wild-type ...
Charge Transport in DNA - Insights from
... DNA molecules between the electrodes were breaking. The fundamental features of CT in DNA have been described as well. First, the exponential dependence of CT efficiency on the length of the DNA oligomers. Second, the role of experimental setup that is both crucial and challenging to characterize. In ...
... DNA molecules between the electrodes were breaking. The fundamental features of CT in DNA have been described as well. First, the exponential dependence of CT efficiency on the length of the DNA oligomers. Second, the role of experimental setup that is both crucial and challenging to characterize. In ...
Codon usage bias from tRNA`s point of view
... species. Surprisingly, despite the wide G+C variation of bacterial genomes these anticodons are the same in most genomes. This suggests an optimization of the translation machinery to use a small subset of optimal codons and anticodons in fast-growing bacteria and in highly expressed genes. As a res ...
... species. Surprisingly, despite the wide G+C variation of bacterial genomes these anticodons are the same in most genomes. This suggests an optimization of the translation machinery to use a small subset of optimal codons and anticodons in fast-growing bacteria and in highly expressed genes. As a res ...
Monday, November 17, 2014 Agenda: Cell Organelle Analogy
... • Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes by half. • In Meiosis the cell divides twice : Meiosis I and Meiosis 2. The DNA copies once ...
... • Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes by half. • In Meiosis the cell divides twice : Meiosis I and Meiosis 2. The DNA copies once ...
Molecular Biology and Applied Genetics
... (transcription). You have already been exposed to the concept of the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology, i.e. that the connection between genotype and phenotype is DNA (genotype) to RNA to enzyme to cell chemistry to phenotype. James Watson and Francis Crick received the 1953 Nobel Prize for their d ...
... (transcription). You have already been exposed to the concept of the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology, i.e. that the connection between genotype and phenotype is DNA (genotype) to RNA to enzyme to cell chemistry to phenotype. James Watson and Francis Crick received the 1953 Nobel Prize for their d ...
How imprinting is relevant to human disease - Development
... the phenotypic features. However, if one takes the concept of genomic imprinting seriously, the parent of origin may be critical and the offspring may only survive or only manifest particular features depending on the parental origin of the abnormal chromosome. In our experience, for instance, the d ...
... the phenotypic features. However, if one takes the concept of genomic imprinting seriously, the parent of origin may be critical and the offspring may only survive or only manifest particular features depending on the parental origin of the abnormal chromosome. In our experience, for instance, the d ...
Detection of chromosome 2 and chromosome 7 within X-ray
... lagging chromosomes induced by spindle poisons is micronucleation, which occurs after mitosis during nuclear membrane formation. The cytokinesis block method using cytochalasin B allows detection of cells which have undergone division, as binucleated cells, and micronuclei occurring in such cells ca ...
... lagging chromosomes induced by spindle poisons is micronucleation, which occurs after mitosis during nuclear membrane formation. The cytokinesis block method using cytochalasin B allows detection of cells which have undergone division, as binucleated cells, and micronuclei occurring in such cells ca ...
Meiosis - Myersbiology
... • Intimate contact provides route for infection by parasites (AIDS, syphillis, etc.) • Genetic costs: in sex, we pass on only half of genes to offspring. • Males are an expensive luxury - in most species they contribute little to rearing offspring. ...
... • Intimate contact provides route for infection by parasites (AIDS, syphillis, etc.) • Genetic costs: in sex, we pass on only half of genes to offspring. • Males are an expensive luxury - in most species they contribute little to rearing offspring. ...
Substrate Specificity of Human Kallikreins 1 and 6
... The human tissue kallikrein (KLK) family contains 15 secreted serine proteases that are expressed in a wide range of tissues and have been implicated in different physiological functions and disease states. Of these, KLK1 has been shown to be involved in the regulation of multiple physiological proc ...
... The human tissue kallikrein (KLK) family contains 15 secreted serine proteases that are expressed in a wide range of tissues and have been implicated in different physiological functions and disease states. Of these, KLK1 has been shown to be involved in the regulation of multiple physiological proc ...
PDF
... H3K27me3 distribution over its targets is not uniform, but can be grouped into several different clusters that correlate with different levels of repression. Furthermore, we demonstrate that H3K27me3 has a preferential chromosomal localization toward telomeric and subtelomeric regions. For the first ...
... H3K27me3 distribution over its targets is not uniform, but can be grouped into several different clusters that correlate with different levels of repression. Furthermore, we demonstrate that H3K27me3 has a preferential chromosomal localization toward telomeric and subtelomeric regions. For the first ...
As a PDF file
... example, metabolic engineering of the pyruvate metabolism of LAB has resulted in efficient production of diacetyl and L-alanine. In addition, important advances have been made in the metabolic engineering of more complex biosynthetic pathways leading to products such as exopolysaccharides and vitami ...
... example, metabolic engineering of the pyruvate metabolism of LAB has resulted in efficient production of diacetyl and L-alanine. In addition, important advances have been made in the metabolic engineering of more complex biosynthetic pathways leading to products such as exopolysaccharides and vitami ...
Nucleosides, Nucleotides,Nucleic Acids
... Oswald Avery discovered (1945) that a substance which caused a change in the genetically transmitted characteristics of a bacterium was DNA. Scientists revised their opinion of the function of DNA and began to suspect it was the major functional component of genes. ...
... Oswald Avery discovered (1945) that a substance which caused a change in the genetically transmitted characteristics of a bacterium was DNA. Scientists revised their opinion of the function of DNA and began to suspect it was the major functional component of genes. ...
NIH Public Access
... Supplementary Figure S1. The genome consists of a single circular 2,628,784 bp chromosome that has a GC content of 56 % (Supplementary Figure S1). Base pair one of the chromosome was assigned within the putative origin of replication. The genome contains 51 tRNAs, 3 rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S), and 38 ...
... Supplementary Figure S1. The genome consists of a single circular 2,628,784 bp chromosome that has a GC content of 56 % (Supplementary Figure S1). Base pair one of the chromosome was assigned within the putative origin of replication. The genome contains 51 tRNAs, 3 rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S), and 38 ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.