
inflectional
... Present participles are formed by the suffixation of verbs with the –ing suffix. This suffix does not cause any major changes to the verb. It does not change the stress or pronunciation in any way. To achieve this, some alterations in spelling have to ...
... Present participles are formed by the suffixation of verbs with the –ing suffix. This suffix does not cause any major changes to the verb. It does not change the stress or pronunciation in any way. To achieve this, some alterations in spelling have to ...
Year 4 - Crossley Fields
... Adverbial: A phrase that acts like an adverb is known as an adverbial. A fronted adverbial is one that comes at the start of a sentence. Fronted adverbial: A fronted adverbial is an adverbial that comes at the start of a sentence. Pronoun: A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun or noun phrase ...
... Adverbial: A phrase that acts like an adverb is known as an adverbial. A fronted adverbial is one that comes at the start of a sentence. Fronted adverbial: A fronted adverbial is an adverbial that comes at the start of a sentence. Pronoun: A pronoun is a word that stands in for a noun or noun phrase ...
Parts of Speech
... How can you make an adjective into an adverb? __________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Change the adjectives “definite” and “deep” into adverbs: ____________ ...
... How can you make an adjective into an adverb? __________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Change the adjectives “definite” and “deep” into adverbs: ____________ ...
parts of speech
... ADJECTIVE: An adjective is a word that describes, or tells about, a noun. Examples: pretty, old, green, plentiful, twelve, this, that, these, those, a, an, the In Sentences: The old brown dog wagged his short tail. I am very happy today. VERB: A verb is a word that tells an action or state of being. ...
... ADJECTIVE: An adjective is a word that describes, or tells about, a noun. Examples: pretty, old, green, plentiful, twelve, this, that, these, those, a, an, the In Sentences: The old brown dog wagged his short tail. I am very happy today. VERB: A verb is a word that tells an action or state of being. ...
nouns - Bastian10
... Refers to persons, places, or things in a more general way than a noun does. ...
... Refers to persons, places, or things in a more general way than a noun does. ...
PARTS OF SPEECH ADJECTIVE: Describes a noun or pronoun
... the action of the verb is directed; cannot be present without a direct object; will precede the direct object in the sentence. MODIFIER: A descriptive word, usually an adjective or adverb or any phrase or clause functioning as an adjective or adverb. OBJECT OF A VERBAL: A noun that receives the acti ...
... the action of the verb is directed; cannot be present without a direct object; will precede the direct object in the sentence. MODIFIER: A descriptive word, usually an adjective or adverb or any phrase or clause functioning as an adjective or adverb. OBJECT OF A VERBAL: A noun that receives the acti ...
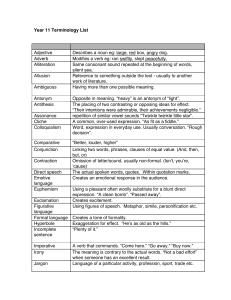
Year 11 Terminology List
... Modifies a verb eg: ran swiftly, slept peacefully. Same consonant sound repeated at the beginning of words, silent sea. Reference to something outside the text - usually to another work of literature. Having more than one possible meaning. Opposite in meaning. “heavy” is an antonym of “light”. The p ...
... Modifies a verb eg: ran swiftly, slept peacefully. Same consonant sound repeated at the beginning of words, silent sea. Reference to something outside the text - usually to another work of literature. Having more than one possible meaning. Opposite in meaning. “heavy” is an antonym of “light”. The p ...
Grammar – A unit
... Conjunction – a word that joins two words or two groups of words Coordinating conjunctions join equals – they are: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions join unequals –something of lesser importance to something of greater importance: if, as, since, when, because, etc. . . . C ...
... Conjunction – a word that joins two words or two groups of words Coordinating conjunctions join equals – they are: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions join unequals –something of lesser importance to something of greater importance: if, as, since, when, because, etc. . . . C ...
Editor In Chief
... Nouns ending in –s are plural Verbs ending in –s are singular (most of the time); not ending in –s are plural Exception: verbs used with “I” or “You” • I go, you go; however, he goes, she goes, it goes, they go, and we go ...
... Nouns ending in –s are plural Verbs ending in –s are singular (most of the time); not ending in –s are plural Exception: verbs used with “I” or “You” • I go, you go; however, he goes, she goes, it goes, they go, and we go ...
PRONOUN REVIEW
... The copy that I read was from the library The people who live there are on vacation Demonstrative This, that, these, those This is the one I want. This seems to be my lucky day. Indefinite All, another, any, anybody, anyone, both, each, other, either, everybody, everyone, few, many, most, neither, n ...
... The copy that I read was from the library The people who live there are on vacation Demonstrative This, that, these, those This is the one I want. This seems to be my lucky day. Indefinite All, another, any, anybody, anyone, both, each, other, either, everybody, everyone, few, many, most, neither, n ...
Stay and write 2015 y1 [ ppt 5MB ]
... words’ because they name people, places and ‘things’; this is often true, but it doesn’t help to distinguish nouns from other word classes. For example, prepositions can name places and verbs can name ‘things’ such as actions. Nouns may be classified as common (e.g. boy, day) or proper (e.g. Ivan, W ...
... words’ because they name people, places and ‘things’; this is often true, but it doesn’t help to distinguish nouns from other word classes. For example, prepositions can name places and verbs can name ‘things’ such as actions. Nouns may be classified as common (e.g. boy, day) or proper (e.g. Ivan, W ...
A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea. Persons: teacher, Beyonce
... This that these those An interrogative pronoun introduces a question. Interrogative Pronouns What Which Who Whom Whose An indefinite pronoun refers to a person, a place, a thing, or an idea that may or may not be specifically named. ...
... This that these those An interrogative pronoun introduces a question. Interrogative Pronouns What Which Who Whom Whose An indefinite pronoun refers to a person, a place, a thing, or an idea that may or may not be specifically named. ...
Grammar Review
... a word usually preceding (coming before) a noun or pronoun and expressing a relation to another word or element in the clause, as in “the man on the platform” and “she arrived after dinner.” ...
... a word usually preceding (coming before) a noun or pronoun and expressing a relation to another word or element in the clause, as in “the man on the platform” and “she arrived after dinner.” ...
HPC U3 TE193 GRMR Mini Present Perfect Tense
... Ex.) I have experienced peer mediation first hand in another school. This sentence shows an action occurred in the past and may still be continuing. The present perfect tense uses the helping verb “has” or “have” followed by the past participle of the verb. See HP handbook pg. 450-451 for a list of ...
... Ex.) I have experienced peer mediation first hand in another school. This sentence shows an action occurred in the past and may still be continuing. The present perfect tense uses the helping verb “has” or “have” followed by the past participle of the verb. See HP handbook pg. 450-451 for a list of ...
Nonnegotiable Editing Check List for 2009-2010 Year
... o Capitalization rules o Beginning of sentence o Titles (and should be underlined), “short stories” o Proper Nouns o Check homophones (there, their, they’re, to, too, which, witch, weather, whether, through, threw, were, where, *are/our, etc.) o Watch apostrophes: they show possession--Mary’s dog, t ...
... o Capitalization rules o Beginning of sentence o Titles (and should be underlined), “short stories” o Proper Nouns o Check homophones (there, their, they’re, to, too, which, witch, weather, whether, through, threw, were, where, *are/our, etc.) o Watch apostrophes: they show possession--Mary’s dog, t ...
Feb. 2017 Language notes
... • Adjective: is a word that describes, or modifies, a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can tell what kind, how many, or which one. An adjective can come before the noun it modifies, or it can follow a linking verb, such as is, seems, appears, or feels. More than one adjective can describe the same noun. ...
... • Adjective: is a word that describes, or modifies, a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can tell what kind, how many, or which one. An adjective can come before the noun it modifies, or it can follow a linking verb, such as is, seems, appears, or feels. More than one adjective can describe the same noun. ...
IntrotoGrammarNounSlideShow
... in addition to gum problems. I wonder if the formulation is smart enough to know exactly which 12 teeth need to be fought in any given mouth.... ...
... in addition to gum problems. I wonder if the formulation is smart enough to know exactly which 12 teeth need to be fought in any given mouth.... ...
Latin I Final Exam Study Guide (Final Exam is 20% of Course Grade
... occurro, occurrere, occurrī, occursurus o 3rd declension adjectives ...
... occurro, occurrere, occurrī, occursurus o 3rd declension adjectives ...
parts of speech presentation
... Subject PRONOUNS: I, you, he, she, it, we, they Object PRONOUNS: me, him her, them, us ...
... Subject PRONOUNS: I, you, he, she, it, we, they Object PRONOUNS: me, him her, them, us ...
Parts of Speech - Flagstaff High School
... * How many? – three weeks, several mistakes * How much? – less noise, more dessert * Which one? – first answer, this jacket, next year * Proper adjectives, which come from proper nouns, always begin with a capital letter. ...
... * How many? – three weeks, several mistakes * How much? – less noise, more dessert * Which one? – first answer, this jacket, next year * Proper adjectives, which come from proper nouns, always begin with a capital letter. ...
English Notes
... specific people, places, or things: this, that, these, those *Indefinite pronouns refer to or replace nouns in a general way. Some indefinite pronouns are also used as adjectives: all, any, anyone, both, each, either, every, many, neither, nobody, no one, nothing, other(s), several, some, someone ...
... specific people, places, or things: this, that, these, those *Indefinite pronouns refer to or replace nouns in a general way. Some indefinite pronouns are also used as adjectives: all, any, anyone, both, each, either, every, many, neither, nobody, no one, nothing, other(s), several, some, someone ...
Mrs. Ray*s TAG Language Arts Class
... Common Nouns-name any one of a group of persons, places, things, or ideas. Proper Nouns-names a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Concrete Nouns-name a person, place, thing, or idea that can be perceived by the senses. Abstract Nouns-name an idea, feeling, quality, or ...
... Common Nouns-name any one of a group of persons, places, things, or ideas. Proper Nouns-names a particular person, place, thing, or idea. Concrete Nouns-name a person, place, thing, or idea that can be perceived by the senses. Abstract Nouns-name an idea, feeling, quality, or ...
File type: application/vnd.ms-powerpoint
... • A preposition is a word or phrase that is used before a noun or pronoun to show place, time, direction, etc.. • Commonly used prepositions: • above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, i ...
... • A preposition is a word or phrase that is used before a noun or pronoun to show place, time, direction, etc.. • Commonly used prepositions: • above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, i ...










![Stay and write 2015 y1 [ ppt 5MB ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003100526_1-72287210420a6e1d2b6a1ef8c9b96048-300x300.png)











