* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download parts of speech
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
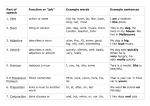
REFERENCE SHEET: Parts of Speech NOUN: A noun is the name of a person, animal, place, thing, or idea. Examples: Mohammed, cat, Phoenix College, beauty, independence In Sentences: Sedona is a beautiful city. That cloud looks like a boat. Proper nouns are usually the names of people, places, days of the week, and months and the first letter is capitalized. Examples: Phoenix, Rebecca, Mexico, Americans, January, Friday PRONOUN: A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Examples: She, we, it, they, myself, yourself, themselves, ourselves This, that, these, and those can also be pronouns when used without a noun. For example, in “this is a large city,” “this” is a pronoun because it is not used with a noun, and in “this dog is very friendly,” “this” is not a pronoun because it is used with the noun “dog.” ADJECTIVE: An adjective is a word that describes, or tells about, a noun. Examples: pretty, old, green, plentiful, twelve, this, that, these, those, a, an, the In Sentences: The old brown dog wagged his short tail. I am very happy today. VERB: A verb is a word that tells an action or state of being. They can contain more than one word. the Verbs can also have tense, which means they tell whether something happened in the present, past, or future. A verb changes its form to show its tense. Verbs also sometimes change their form depending on who or what is doing or experiencing the action or state of being told by the verb. Examples: to run, to know, to have, to write, to love, to be In Sentences: We celebrate Valentine’s Day in February. Are you happy? Did you like the movie? He has been running for an hour. ADVERB: An adverb is a word that describes, or tells about, a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs usually end in –ly, although some do not. Examples: quickly, loudly, sharply, very In Sentences: He brushed his teeth quickly. The roses were very beautiful. The angry man shouted very loudly. PREPOSITION: A preposition is a word that shows a relationship between two or more words in a sentence. Prepositions often tell the location or location in time of a thing or place. Examples: in, on, under, by, through, to In Sentences: The boy went to the store. The book fell under the table. I saw her on Tuesday. CONJUNCTION: A conjunction is a word that connects words or phrases together. Examples: and, or, but, so, for, either/or, neither/nor, whether/or In Sentences: I like Italian and Mexican food. Either you like football or you don’t. She went shopping, but didn’t buy anything. ARTICLE: Articles are similar to adjectives because they help to describe or tell a little information about a noun. An article always comes before its noun. There are three articles: “a”, “an”, and “the”. Examples: a, an, the In Sentences: The boy loved soccer. An education is a wonderful thing. © 2002 Phoenix College Learning Center By Sigrid Nord-Champie