Parts of Speech and Parts of the Sentence
... Pronoun Antecedent The noun that the pronoun refers to “Ante” means before—the antecedent will always come before the pronoun— sometimes even a couple sentences before! EX: When the moped stalled, I gave it a swift kick. Pronoun “it” refers to the noun “moped” ...
... Pronoun Antecedent The noun that the pronoun refers to “Ante” means before—the antecedent will always come before the pronoun— sometimes even a couple sentences before! EX: When the moped stalled, I gave it a swift kick. Pronoun “it” refers to the noun “moped” ...
-ing forms in English
... I am talking to you right now. (present progressive or present continuous) I have been thinking a lot about this decision. (present perfect progressive or present perfect continuous) You were already sleeping. (past progressive or past continuous) I will be taking my friend to the airport. (future p ...
... I am talking to you right now. (present progressive or present continuous) I have been thinking a lot about this decision. (present perfect progressive or present perfect continuous) You were already sleeping. (past progressive or past continuous) I will be taking my friend to the airport. (future p ...
Subject
... Identify the Subject and Predicate in the following sentences. My parents work very hard. The students in this class are real smart. ...
... Identify the Subject and Predicate in the following sentences. My parents work very hard. The students in this class are real smart. ...
Words and their characteristics Word classes Traditional v. modern
... – suffixes: most purely lexical: change meaning of base form e.g. -ness, -ship, -able • few are purely grammatical: show how words must be used in sentences e.g. plural -s, past tense -ed ...
... – suffixes: most purely lexical: change meaning of base form e.g. -ness, -ship, -able • few are purely grammatical: show how words must be used in sentences e.g. plural -s, past tense -ed ...
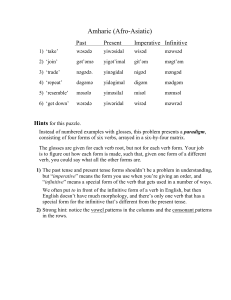
Amharic (Afro
... The glosses are given for each verb root, but not for each verb form. Your job is to figure out how each form is made, such that, given one form of a different verb, you could say what all the other forms are. 1) The past tense and present tense forms shouldn’t be a problem in understanding, but “im ...
... The glosses are given for each verb root, but not for each verb form. Your job is to figure out how each form is made, such that, given one form of a different verb, you could say what all the other forms are. 1) The past tense and present tense forms shouldn’t be a problem in understanding, but “im ...
Subject Verb Agreement and Pronoun Agreement
... These create problems: • Verbs that accompany pronouns such as all and some will be determined by whether the pronoun is referring to something that is COUNTABLE or not. ...
... These create problems: • Verbs that accompany pronouns such as all and some will be determined by whether the pronoun is referring to something that is COUNTABLE or not. ...
Parts of Speech1
... Verbs need to agree with their subjects. Bold the correct verb in parentheses for each sentence. (a) Miguel (talk, talks) all the time on his cell phone. (b) The tanker (fuel, fuels) the jet before take-off. (c) Everyone (try, tries) to work very hard during the holiday season. ...
... Verbs need to agree with their subjects. Bold the correct verb in parentheses for each sentence. (a) Miguel (talk, talks) all the time on his cell phone. (b) The tanker (fuel, fuels) the jet before take-off. (c) Everyone (try, tries) to work very hard during the holiday season. ...
The Parts of Speech
... Collective Nouns: words that name a group of a people, animals, or things. Ex. audience, flock, assortment ...
... Collective Nouns: words that name a group of a people, animals, or things. Ex. audience, flock, assortment ...
parts of speech 2
... People handle old violins carefully. Very old violins are valuable. Orchestras almost always include violins. ...
... People handle old violins carefully. Very old violins are valuable. Orchestras almost always include violins. ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... •You had better be finished before noon. •Please don’t drive over the bicycle. ...
... •You had better be finished before noon. •Please don’t drive over the bicycle. ...
basic terms used in english
... ADJECTIVE and VERB [I (p) am glad (aj) TO see (v) (p) you.] VERB and VERB [I (p) have been moving (v) FROM place (n) TO place (n).] In the above examples FROM and TO are prepositions. OTHER PREPOSITIONS: In, on, upon, below, before, after, under, across, along, through, about, up, since, etc. ...
... ADJECTIVE and VERB [I (p) am glad (aj) TO see (v) (p) you.] VERB and VERB [I (p) have been moving (v) FROM place (n) TO place (n).] In the above examples FROM and TO are prepositions. OTHER PREPOSITIONS: In, on, upon, below, before, after, under, across, along, through, about, up, since, etc. ...
Slide 1
... anybody, anything, anyone, each, either, everyone, everybody, everything, neither, nobody, no one, one, someone, something Plural all, both, few, most, none, some If none means “not one,” it is singular. ...
... anybody, anything, anyone, each, either, everyone, everybody, everything, neither, nobody, no one, one, someone, something Plural all, both, few, most, none, some If none means “not one,” it is singular. ...
SENTENCE PARTS AND TYPES
... An adverb modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells how, when, where, why, how often, to what extent, and how much: Yesterday a fire completely destroyed the home of a family on Hill Street. Rarely does a fire last so long. The family looked totally grungy after hauling out t ...
... An adverb modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells how, when, where, why, how often, to what extent, and how much: Yesterday a fire completely destroyed the home of a family on Hill Street. Rarely does a fire last so long. The family looked totally grungy after hauling out t ...
- West Point High School
... a noun or a pronoun and another word in the sentence. A preposition always has at least one noun or pronoun as an object. This noun or pronoun is called the object of the ...
... a noun or a pronoun and another word in the sentence. A preposition always has at least one noun or pronoun as an object. This noun or pronoun is called the object of the ...
The Word Class Book
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
The Word Class Book
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
Different words do different jobs in a sentence. The word class book
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
Grammar Lessons 49-53
... Regular verbs form past tense with d or ed Irregular verbs have no rules for forming past tense and past participles ...
... Regular verbs form past tense with d or ed Irregular verbs have no rules for forming past tense and past participles ...
File
... form to express the tense. It is the context that is used to show time. In SJE, the verbs are always enough to show the tense (e.g. ...
... form to express the tense. It is the context that is used to show time. In SJE, the verbs are always enough to show the tense (e.g. ...
Nouns • Noun phrase - builds around a simple noun (person, place
... ‘small’ words such as: must, will, may, should, could, would, shall, might, can Imperative verbs - not to be called ‘bossy’ verbs! These verbs give orders in a sentence, usually paired with an exclamation, never question sentences e.g. Stop that now! ...
... ‘small’ words such as: must, will, may, should, could, would, shall, might, can Imperative verbs - not to be called ‘bossy’ verbs! These verbs give orders in a sentence, usually paired with an exclamation, never question sentences e.g. Stop that now! ...
partsofspeech3
... The cat was on the table. The dog was under the table. These are some common prepositions: For on to up at under above toward With between in behind From upon into off ...
... The cat was on the table. The dog was under the table. These are some common prepositions: For on to up at under above toward With between in behind From upon into off ...
A Remedial English Grammar
... A verb must agree with its subject in number and person. For present tense forms most English verbs end in –s in the third person singular, but there is no –s on the third person plural. E.g. He walks ; They walk. In forms of primary auxiliary be (where different words are used), do, the singular en ...
... A verb must agree with its subject in number and person. For present tense forms most English verbs end in –s in the third person singular, but there is no –s on the third person plural. E.g. He walks ; They walk. In forms of primary auxiliary be (where different words are used), do, the singular en ...
Knowing the Difference
... – This is how I feel about increased wages. – How do you feel about that policy? ...
... – This is how I feel about increased wages. – How do you feel about that policy? ...