OSI Model Layers
... commands, data compression sets standards for different systems to provide seamless communication from multiple protocol stacks not always implemented in a network protocol establishes, maintains and ends sessions across the network responsible for name recognition (identification) so only the desig ...
... commands, data compression sets standards for different systems to provide seamless communication from multiple protocol stacks not always implemented in a network protocol establishes, maintains and ends sessions across the network responsible for name recognition (identification) so only the desig ...
Topologies for Power Efficient Wireless Sensor Networks
... SPIN (Sensor Protocols for Information via Negotiation): ...
... SPIN (Sensor Protocols for Information via Negotiation): ...
Ethernet - Inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... • Carrier Sense: wait till medium is idle before sending frame. • Multiple Access: multiple computers use the same shared media. Each uses same access algorithm. • Collision Detection: Listen to medium – detect if another station’s signal interferes – back off and try again later. ...
... • Carrier Sense: wait till medium is idle before sending frame. • Multiple Access: multiple computers use the same shared media. Each uses same access algorithm. • Collision Detection: Listen to medium – detect if another station’s signal interferes – back off and try again later. ...
Document
... • Cost of electronics/software: 35% ~ 40% in premium cars (for hybrid it is even higher!) • How can we ensure timely and reliable communication via the “wires”? [http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/feb09/7649] EECS 149, UC Berkeley: 3 ...
... • Cost of electronics/software: 35% ~ 40% in premium cars (for hybrid it is even higher!) • How can we ensure timely and reliable communication via the “wires”? [http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/feb09/7649] EECS 149, UC Berkeley: 3 ...
Slide 1
... The web services metaphor, roles and responsibilities are as important to an effort like this as the technology. Immaturity in Web Services Standards and Tools but they are improving rapidly. Many current reporting processes are “semiautomated”, moving these to fully automated requires addressin ...
... The web services metaphor, roles and responsibilities are as important to an effort like this as the technology. Immaturity in Web Services Standards and Tools but they are improving rapidly. Many current reporting processes are “semiautomated”, moving these to fully automated requires addressin ...
ns2-ch15 16
... MobileNode object is a split object. The C++ class MobileNode is derived from parent class Node. (ref ch5) ...
... MobileNode object is a split object. The C++ class MobileNode is derived from parent class Node. (ref ch5) ...
An Ultra-Low Power Asynchronous-Logic In-Situ Self
... each node is connected to one (or sometimes several) sensors ...
... each node is connected to one (or sometimes several) sensors ...
Network types Point-to-Point (Direct) Connection
... • If cable fails, the entire network will shut down • Earlier Ethernet commonly implement a bus topology ...
... • If cable fails, the entire network will shut down • Earlier Ethernet commonly implement a bus topology ...
Wireless LAN and IEEE 802.11
... backoff counter. When backoff counter reaches zero, the node transmits the packet. Since the probability that two nodes will choose the same back off factor is small, collision between packets are minimized. Collision detection cannot be used because when a node is transmitting it cannot hear any ot ...
... backoff counter. When backoff counter reaches zero, the node transmits the packet. Since the probability that two nodes will choose the same back off factor is small, collision between packets are minimized. Collision detection cannot be used because when a node is transmitting it cannot hear any ot ...
(3) 2013 test
... 2. (10) In our neural network example with the veterans data, our first attempt at fitting a model using all of the features (inputs) failed to converge. What did we do to remedy that situation? Explain briefly. We preceded the neural network with a logistic regression using stepwise to select a mod ...
... 2. (10) In our neural network example with the veterans data, our first attempt at fitting a model using all of the features (inputs) failed to converge. What did we do to remedy that situation? Explain briefly. We preceded the neural network with a logistic regression using stepwise to select a mod ...
CS 455: Computer Networks and Data Communication Sample Final Examination Points: 125
... b. An application produces output in terms of 2-Mbyte bursts. Each burst has a 20 milliseconds duration, and bursts occur at a constant interval of 500 milliseconds (i.e., 2 in a second). The application lasts for 2 seconds. It is connected to an 8-Mbps network through a token bucket. Suppose the to ...
... b. An application produces output in terms of 2-Mbyte bursts. Each burst has a 20 milliseconds duration, and bursts occur at a constant interval of 500 milliseconds (i.e., 2 in a second). The application lasts for 2 seconds. It is connected to an 8-Mbps network through a token bucket. Suppose the to ...
2 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... Union) • ISO (International Organization for Standardization) • W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) ...and many others ...
... Union) • ISO (International Organization for Standardization) • W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) ...and many others ...
802.11 frame - Department of Computer and Information Science
... Hidden node problem A, B hear each other B, C hear each other A, C can not hear each other means A, C unaware of their interference at B ...
... Hidden node problem A, B hear each other B, C hear each other A, C can not hear each other means A, C unaware of their interference at B ...
1-Introduction :
... For Network layer packets to be transported from source host to destination host, they must traverse different physical networks. These physical networks can consist of different types of physical media such as copper wires, microwaves, optical fibers, and satellite links. Network layer packets do n ...
... For Network layer packets to be transported from source host to destination host, they must traverse different physical networks. These physical networks can consist of different types of physical media such as copper wires, microwaves, optical fibers, and satellite links. Network layer packets do n ...
Ch. 5 The Data Communications Interface
... • The efficiency E = # of inf. bits/ total # of bits. • Example: ASCII code, odd parity, 2 stop bits. – # of inf. bits= 7 – Total =1 start + 7 data + 1 parity + 2 stop = 11 – Efficiency = 7/11= .64 or 64%. ...
... • The efficiency E = # of inf. bits/ total # of bits. • Example: ASCII code, odd parity, 2 stop bits. – # of inf. bits= 7 – Total =1 start + 7 data + 1 parity + 2 stop = 11 – Efficiency = 7/11= .64 or 64%. ...
ppt - ICS
... The node that owns P splits its zone and sets the new node as a neighbor. Periodically update messages are exchanged between nodes located closed to the "neighborhood". Node insertion is a local process and affects only O(dimensions) existing nodes. ...
... The node that owns P splits its zone and sets the new node as a neighbor. Periodically update messages are exchanged between nodes located closed to the "neighborhood". Node insertion is a local process and affects only O(dimensions) existing nodes. ...
PowerPoint Slides
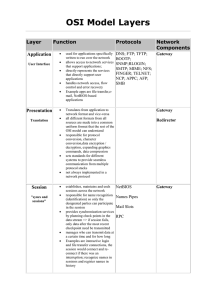
... Layer 7, the application layer, the highest layer of the model, defines the way applications (client or server) interact with the network. Layer 6, the presentation layer, includes protocols that are part of the operating system, and defines how information is formatted for display or printing and ...
... Layer 7, the application layer, the highest layer of the model, defines the way applications (client or server) interact with the network. Layer 6, the presentation layer, includes protocols that are part of the operating system, and defines how information is formatted for display or printing and ...
1.7M PowerPoint Presentation
... To make serious safety gains, it is necessary to communicate with the vehicle ...
... To make serious safety gains, it is necessary to communicate with the vehicle ...