* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network types Point-to-Point (Direct) Connection
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
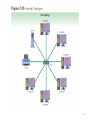
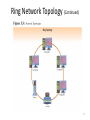
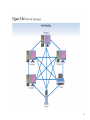
Network types Point-to-Point (Direct) Connection • Dedicated circuit boards connected by cable; • To transfer data from A to B: – A writes on its circuit board; – A’s board transfers data to B’s board; – B reads data from its board. A B Point-to-Point Connection (cont.) • Pros: – High transfer speed; – Secure connection; • Cons: – Difficult to add a new computer to a set of communicating computers. – Difficult if communication is between heterogeneous computers; – Expensive: circuit boards needed for every pair of communicating computers; • How many boards would you need to connect 5 computers via this method? Local Area Network (LAN) • A single shared medium, usually a cable, to which computers can attach. PC 1 Printer PC 2 PC n File Server Local Area Networks (cont.) • Designed and developed for communications and resource sharing in a local work environment (room, campus, building). • Because sharing occurs: – Cost decreases – Computers have to coordinate the use of the network; • Overall, LANs connect more computers than any type of network. Connecting a Computer to a LAN • Requires a network interface; • A network interface consists of: – a circuit board that plugs into the computer – A cable that connects the circuit board to the LAN; • The network interface isolates a computer from the LAN heterogeneous computers can communicate across the LAN. Network Topologies • The configurations of network components • Widely used network topologies – Bus – Star – Extended star – Ring – Mesh – Partial Mesh 6 Bus Network Topology • Most simple network topology • All devices connected to a common central cable (wire or other media ) • Inexpensive • Easily expanded • If cable fails, the entire network will shut down • Earlier Ethernet commonly implement a bus topology 7 Bus Network Topology (Continued) 8 Star Network Topology • Star topology is centered around central routing device called a switch or a hub by point-topoint links. • All network nodes connect to the hub • Easy to install and update • If hub fails, network fails • Disadvantage that it require more cabling therefore, higher cost than the bus. • Extended star 9 10 Ring Network Topology • Each node connected to two other nodes in a ring • Similar to the buss, but with the ends of the buss connected together by unidirectional transmission link to form a single closed loop. • Each station on the network connects to the network at a repeater. • Expensive and difficult to install • One example of a ring topology is Token Ring networks 11 Ring Network Topology (Continued) 12 Ring Topology (cont.) • Sending a message: – There is a special message, called token; – Exactly one token exists on the ring at any time which is passed along the ring; – To send data, a computer waits for the token to arrive, and then transmits one message; – The message is transmitted to the next computer, and then to the next, until it arrives back to the sender. – After the message is transmitted, the computer holding the token, passes the token to the next computer in the ring. • Dual-Ring – Tow rings allow data to be sent in both directions – Creates redundancy. Mesh Network Topology • Every node connected to every other node • Fast • Reliable – No hub or bus to fail – If one device goes down, it is the only node affected • Expensive – Every node must be wired to every other node • Difficult to add nodes – If there are 32 nodes in a mesh network and you wish to add a new node, how many new cables must you add? 14 • Partial Mesh – At least one derive is connected to all other devices without being fully meshed. 15 16