* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download campus-area network
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
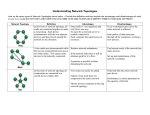
Name:Pattawee Anantawan Room: M.2/SR No.21 Vocabulary: Network Terms LANA system that links together electronic office equipment, such as computers and printers, and forms a network within an office, building, or group of buildings . MAN metropolitan-area network. Network that spans a metropolitan area. Generally, a MAN spans a larger geographic area than a LAN, but a smaller geographic area that a WAN WANA communications network that uses such devices as telephone lines, satellite dishes, or radio waves to span a larger geographic area than can be covered by a LAN. CAN.(1) Acronym for campus-area network. An interconnection of local-area networks within a limited geographical space, such as a school campus or a military base. (2) See controller area network PAN (1) In all capitals, PAN is short for Personal Area Network. Based on the electric-field transmission medium, is an IBM technology that allows individuals to exchange data with a simple touch or grasp PROTOCOLIn networking, a specification of the data structures and algorithms necessary to accomplish a particular network function FIREWALLRouter or access server, or several routers or access servers, designated as a buffer between any connected public networks and a private network. A firewall router uses access lists and other methods to ensure the security of the private network. BANDWIDTHIn analog communications, the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies available in the band. In digital communications, bandwidth is loosely used to refer to the information-carrying capacity of a network or component of a network. GATEWAY1. A device that performs a protocol translation at the SessionLayer or higher. 2. Archaic. A TCP/IP router that routes packets between different network numbers. NETWORK TOPOLOGYis the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network.[1][2] Essentially, it is the topological[3] structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network, including device location and cable installation, while logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network, regardless of its physical design. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two networks, yet their topologies may be identical. An example is a local area network (LAN): Any given node in the LAN has one or more physical links to other devices in the network; graphically mapping these links results in a geometric shape that can be used to describe the physical topology of the network. Conversely, mapping the data flow between the components determines the logical topology of the network. BUS TOPOLOGY. A bus network is a network topology in which nodes are directly connected to a common linear (or branched) half-duplex link called a bus RING TOPOLOGYA ring network is a network topology in which each node connects to exactly two other nodes, forming a single continuous pathway for signals through each node - a ring. Data travels from node to node, with each node along the way handling every packet MESH TOPOLOGYis a network topology in which each node relays data for the network TREE TOPOLOGYNetwork cabling scheme in which two or more hubs and/or data centers are connected to one another in a succession of levels to provideredundancy. Also called cascaded star topology or tree network STAR TOPOLOGYare one of the most common computer networktopologies. In its simplest form, a star network consists of one central switch, hub or computer, which acts as a conduit to transmit messages SERVERA device that is shared by several users of a network ISPInternet service provider. DIRECTORYServices that help network devices locate service providers ETHERNETa system for connecting a number of computer systems to form a local area network, with protocols to control the passing of information and to avoid simultaneous transmission by two or more systems NETWORKThe infrastructure that supports electronic data exchange. References:http://www.wildpackets.com/resources/compendiu m/glossary_of_networking_terms#N https://en.wikipedia.org