* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An Ultra-Low Power Asynchronous-Logic In-Situ Self
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
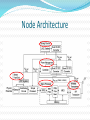
Authors: Tong Lin, Kwen-Siong Chong, Joseph S. Chang, and Bah-Hwee Gwee Journal: IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 48, no. 2, 2013 Presented by: Jim Wales Le Zheng Hany Fahmy Bin Wu Outline Wireless Sensor Network Node Architecture Proposed Idea for Low Power Design Action Items Wireless Sensor Network Spatially distributed autonomous sensors Monitor physical or environmental conditions Temperature, sound, etc. Pass their data through the network to a main location Modern networks are bi-directional, also enabling control of sensor activity Applications Battlefield surveillance Industrial process monitoring Wireless Sensor Network The WSN is built of "nodes“ a few to several hundreds or even thousands each node is connected to one (or sometimes several) sensors Each such sensor network node has typically several parts a radio transceiver a microcontroller an electronic circuit for interfacing with the sensors an energy source, usually a battery Node Architecture Proposed Idea for Low Power Design Signal processor accounts for ~50% of total power consumption ‘Sub-threshold Self-Adaptive Scaling’ (SSAVS) Circuits work in sub-threshold region Supply voltage is adjusted dynamically depending on the processing speed required by external environment Proposed Idea for Low Power Design Asynchronous logic implementation Pre-charged Static Logic (PCSL) Superior than existing asynchronous logics in energy, delay and chip area. Action Items Background knowledge Understanding WSN Common techniques for WSN lower power design Vdd scaling On/off ratio Clock gating, etc Pre-charged static logic Quasi-delay-insensitive asynchronous logic Action Items Carry out detailed analysis/simulation Evaluate the proposed idea Summarize pros/cons of the paper Potentially propose our own low power design idea Thank you Q&A