Network on Chip - Architectures and Design Methodology
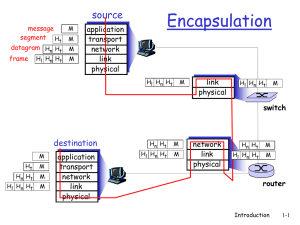
... The Network-on-Chip The seven layer OSI stack for communication ! Application System Transport Network Data link Physical ...
... The Network-on-Chip The seven layer OSI stack for communication ! Application System Transport Network Data link Physical ...
Chapter 14: Local Area Network Technology
... Can be used for bus and ring as well as star Concentration point can be wiring closet or hub (an active node that accepts frames and ...
... Can be used for bus and ring as well as star Concentration point can be wiring closet or hub (an active node that accepts frames and ...
download
... Can be used for bus and ring as well as star Concentration point can be wiring closet or hub (an active node that accepts frames and ...
... Can be used for bus and ring as well as star Concentration point can be wiring closet or hub (an active node that accepts frames and ...
dc9798.PDF
... Discuss the format of an IEEE 802.3 frame. Also estimate the minimum and maximum times to transmit an IEEE 802.3 frame. ...
... Discuss the format of an IEEE 802.3 frame. Also estimate the minimum and maximum times to transmit an IEEE 802.3 frame. ...
An Integrated approach to developing sensor network solutions
... – Provides sleep modes awakened by interrupts from internal timers or sensors – Supports selective rewriting of internal flash ROM – TR 1001 RF transceiver • Baseband transmission with either amplitude shift keying or on-off keying • Provides half duplex bit level access to physical radio medium ...
... – Provides sleep modes awakened by interrupts from internal timers or sensors – Supports selective rewriting of internal flash ROM – TR 1001 RF transceiver • Baseband transmission with either amplitude shift keying or on-off keying • Provides half duplex bit level access to physical radio medium ...
slides - Fei Hu
... Think: why put the following functions in Data Link Layer? • (most important) channel access: channel access if shared medium • Framing, – encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer – ‘physical addresses’ used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
... Think: why put the following functions in Data Link Layer? • (most important) channel access: channel access if shared medium • Framing, – encapsulate datagram into frame, adding header, trailer – ‘physical addresses’ used in frame headers to identify source, dest • different from IP address! ...
Computer Systems and Networks
... Overall size of the network Distance between the most remote nodes Speed requirements Network traffic Total number of stations ...
... Overall size of the network Distance between the most remote nodes Speed requirements Network traffic Total number of stations ...
ppt - UCL Computer Science
... Link Multiplexing • Link may be shared by multiple network protocols (e.g., IP and AppleTalk on same Ethernet) • Sender must specify protocol ID in frame • Receiver uses protocol ID to look up code responsible for processing received frame • Many protocols at many layers are multiplexed in this way ...
... Link Multiplexing • Link may be shared by multiple network protocols (e.g., IP and AppleTalk on same Ethernet) • Sender must specify protocol ID in frame • Receiver uses protocol ID to look up code responsible for processing received frame • Many protocols at many layers are multiplexed in this way ...
PPT Version
... The destination/src address field is either 16 bits or 64 bits in length, according to the value specified in the destination addressing mode subfield of the frame control field, and specifies the address of the intended recipient of the frame. A 16 bit value of 0 x ffff in this field shall represen ...
... The destination/src address field is either 16 bits or 64 bits in length, according to the value specified in the destination addressing mode subfield of the frame control field, and specifies the address of the intended recipient of the frame. A 16 bit value of 0 x ffff in this field shall represen ...
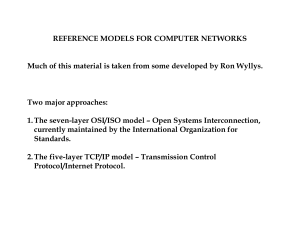
Reference Models - UT School of Information
... TCP/IP 1. Physical layer – not really part of this model, since TCP and IP deal with software; usually thought to refer to all hardware beneath the network layer. 2. Network or data link layer – defined by whatever the Internet Protocol will run over, e.g., a token-ring network. 3. Internet or netw ...
... TCP/IP 1. Physical layer – not really part of this model, since TCP and IP deal with software; usually thought to refer to all hardware beneath the network layer. 2. Network or data link layer – defined by whatever the Internet Protocol will run over, e.g., a token-ring network. 3. Internet or netw ...
Data Transmission
... Ties up large areas of network Message packets remain in correct order Message can be more easily intercepted as it stays on the same route ...
... Ties up large areas of network Message packets remain in correct order Message can be more easily intercepted as it stays on the same route ...
The Data Link Layer
... Only one frame at a time can be in transit. 1. Source transmits frame 2. Destination receives frame and replies with acknowledgement (if it is correct, otherwise send NAK.) 3.Source waits for ACK before sending next frame 4.Destination can stop flow by not send ACK 5.Source can retransmit if got a N ...
... Only one frame at a time can be in transit. 1. Source transmits frame 2. Destination receives frame and replies with acknowledgement (if it is correct, otherwise send NAK.) 3.Source waits for ACK before sending next frame 4.Destination can stop flow by not send ACK 5.Source can retransmit if got a N ...
Graph Theory and Voltage Stability Analysis In Radial Distribution
... A graph-based method is reported in this paper to identify nodes that are on the verge of voltage collapse of radial distribution networks. The voltage stability index is derived from the bi-quadratic equation which is generally used for the voltage calculation of distribution load flow algorithms. ...
... A graph-based method is reported in this paper to identify nodes that are on the verge of voltage collapse of radial distribution networks. The voltage stability index is derived from the bi-quadratic equation which is generally used for the voltage calculation of distribution load flow algorithms. ...
Review of Researches in Controller Area Networks Evolution and
... This paper provides a comprehensive overview of CAN, its architecture, protocols, standards and some of its implementation in various industries. In Section 2, the CAN basics such as message format, message identifiers and bit-wise arbitration are explained. The following few sections will introduce ...
... This paper provides a comprehensive overview of CAN, its architecture, protocols, standards and some of its implementation in various industries. In Section 2, the CAN basics such as message format, message identifiers and bit-wise arbitration are explained. The following few sections will introduce ...
No Slide Title
... The data field has only 8 bytes You must specify for each data frame how many data bytes follow Remote frames are not necessary to use CAN ...
... The data field has only 8 bytes You must specify for each data frame how many data bytes follow Remote frames are not necessary to use CAN ...
3-Physical+logical toplogy
... – Usually coaxial cables – One communication channel shared between nodes/workstations • Shared cable capacity • Data is sent via the bus by broadcast and each node responsible to accept the data frame when it detects its MAC address as destination address in the frame • Other nodes ignore data ...
... – Usually coaxial cables – One communication channel shared between nodes/workstations • Shared cable capacity • Data is sent via the bus by broadcast and each node responsible to accept the data frame when it detects its MAC address as destination address in the frame • Other nodes ignore data ...
Looking deeper into ARQ “frames”
... Need to ensure that all stations are aware of the collision => transmit a “jam signal” (32 or 48 arbitrary bits) after detecting the collision to ensure that other nodes also detect it and back off. => non-zero abort time. Copyright © May-17, Tim MoorsFigure from Kurose and Ross ...
... Need to ensure that all stations are aware of the collision => transmit a “jam signal” (32 or 48 arbitrary bits) after detecting the collision to ensure that other nodes also detect it and back off. => non-zero abort time. Copyright © May-17, Tim MoorsFigure from Kurose and Ross ...
Advantages of CAN and LIN in Networked Embedded Systems
... Up to 3 CAN interfaces with 32 mailboxes each Time-triggered CAN support All board specific APIs and drivers available in included CD Extensive third-party middleware support available Sample projects and ...
... Up to 3 CAN interfaces with 32 mailboxes each Time-triggered CAN support All board specific APIs and drivers available in included CD Extensive third-party middleware support available Sample projects and ...
Embedded Electronics
... CANBUS or CAN bus – Controller Area Network bus An automotive serial bus system developed to satisfy the following requirements: ...
... CANBUS or CAN bus – Controller Area Network bus An automotive serial bus system developed to satisfy the following requirements: ...