Chem*3560 Lecture 21: Fatty acid synthase
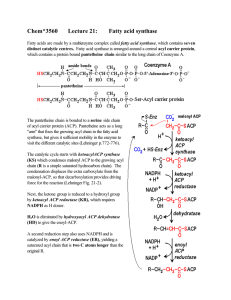
... Organization of fatty acid synthase Fatty acid synthase consists of the seven catalytic centres arranged around a central ACP. In bacteria such as E.coli, ACP is a small protein of mass 8.8 kDa. Six additional catalytic subunits are arranged around the central ACP (Lehninger p. 777 and Figs. 21-5 t ...
... Organization of fatty acid synthase Fatty acid synthase consists of the seven catalytic centres arranged around a central ACP. In bacteria such as E.coli, ACP is a small protein of mass 8.8 kDa. Six additional catalytic subunits are arranged around the central ACP (Lehninger p. 777 and Figs. 21-5 t ...
University of Groningen Interactions between carbohydrate
... Oxidizable substrates include carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Cells are also capable of synthesizing these three types of substrates. The processes of oxidation and synthesis are ingeniously regulated. This thesis focuses on the interactions between carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, particularl ...
... Oxidizable substrates include carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Cells are also capable of synthesizing these three types of substrates. The processes of oxidation and synthesis are ingeniously regulated. This thesis focuses on the interactions between carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, particularl ...
03-232 Biochemistry
... 3 H+. As γ rotates it can contact one of the three β subunits and influence their conformation (2 pts). Each has 3 potential conformations, one that has a low affinity for either ADP and ATP, one that binds ADP and Pi with high affinity, and a third one that binds ATP with high affinity such that AT ...
... 3 H+. As γ rotates it can contact one of the three β subunits and influence their conformation (2 pts). Each has 3 potential conformations, one that has a low affinity for either ADP and ATP, one that binds ADP and Pi with high affinity, and a third one that binds ATP with high affinity such that AT ...
Energy Cycle in Vertebrates - Jean
... and glycogen, mainly in adipose tissue, liver and muscle. Over 90% of total energy reserves are in the form of triacylglycerol for long-term, maintenance metabolism. The glycogen reserves are only used when ATP must be produced very quickly or when enough oxygen cannot be supplied to the cells (e.g. ...
... and glycogen, mainly in adipose tissue, liver and muscle. Over 90% of total energy reserves are in the form of triacylglycerol for long-term, maintenance metabolism. The glycogen reserves are only used when ATP must be produced very quickly or when enough oxygen cannot be supplied to the cells (e.g. ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... • The proximity of one enzyme to another increases the overall reaction rate and minimizes side reactions. • All the intermediates in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate are tightly bound to the complex and are readily transferred because of the ability of the lipoyllysine arm of E2 to call on ...
... • The proximity of one enzyme to another increases the overall reaction rate and minimizes side reactions. • All the intermediates in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate are tightly bound to the complex and are readily transferred because of the ability of the lipoyllysine arm of E2 to call on ...
Changes in cardiac metabolism: a critical step from stable angina to
... flux through PDH by NADH and acetyl-CoA, and results in more pyruvate oxidation and thus more glucose and lactate uptake. tissue, resulting in a decrease in ATP formation by oxidative phosphorylation (Fig. 4)[1,2,17]. The reduction in aerobic ATP formation stimulates glycolysis, and an increase in m ...
... flux through PDH by NADH and acetyl-CoA, and results in more pyruvate oxidation and thus more glucose and lactate uptake. tissue, resulting in a decrease in ATP formation by oxidative phosphorylation (Fig. 4)[1,2,17]. The reduction in aerobic ATP formation stimulates glycolysis, and an increase in m ...
Seminar compendium 2016/2017
... be carried out by various modes. Two important mechanisms are covalent modification and allosteric regulation. Discuss the principles for these modes! Many enzymatic reactions are energy-requiring and ATP is commonly employed to provide the necessary input of energy. Discuss the structure of ATP, wh ...
... be carried out by various modes. Two important mechanisms are covalent modification and allosteric regulation. Discuss the principles for these modes! Many enzymatic reactions are energy-requiring and ATP is commonly employed to provide the necessary input of energy. Discuss the structure of ATP, wh ...
FLEMINGIA STROBILIFERA R.B Research Article
... levels of serum SGOT and SGPT released from liver to circulation. Among the two, GPT is a better index of liver injury, since SGPT catalyses the conversion of alanine to pyruvate and glutamate, and is released in a similar manner, thus liver GPT represents 90% of total enzy ...
... levels of serum SGOT and SGPT released from liver to circulation. Among the two, GPT is a better index of liver injury, since SGPT catalyses the conversion of alanine to pyruvate and glutamate, and is released in a similar manner, thus liver GPT represents 90% of total enzy ...
Metabolism of Lipids
... tissues, especially during times of prolonged starvation. Reconversion of ketone bodies to acetylCoA inside the mitochondria provides metabolic energy. ...
... tissues, especially during times of prolonged starvation. Reconversion of ketone bodies to acetylCoA inside the mitochondria provides metabolic energy. ...
Biochemistry II, Test One
... 2. Which of the following statements about ATP and its roles in cells are true? (2 points) A. The ATP molecule is kinetically unstable and is thus consumed within about one minute following its formation in cells. B. ATP provides free energy to a thermodynamically unfavorable reactions by group tran ...
... 2. Which of the following statements about ATP and its roles in cells are true? (2 points) A. The ATP molecule is kinetically unstable and is thus consumed within about one minute following its formation in cells. B. ATP provides free energy to a thermodynamically unfavorable reactions by group tran ...
Chapter 3
... Efficiency of Oxidative Phosphorylation • One mole of ATP has energy yield of 7.3 kcal • 32 moles of ATP are formed from one mole of glucose • Potential energy released from one mole of glucose is 686 ...
... Efficiency of Oxidative Phosphorylation • One mole of ATP has energy yield of 7.3 kcal • 32 moles of ATP are formed from one mole of glucose • Potential energy released from one mole of glucose is 686 ...
Cell Respiration
... A. Glycolysis is most likely one of the earliest of all biochemical reactions to evolve. Glycolysis uses molecular oxygen, however it occurs in anaerobic environments. B. Glycolysis is most likely one of the earliest of all biochemical reactions to evolve. Glycolysis uses no molecular oxygen. All re ...
... A. Glycolysis is most likely one of the earliest of all biochemical reactions to evolve. Glycolysis uses molecular oxygen, however it occurs in anaerobic environments. B. Glycolysis is most likely one of the earliest of all biochemical reactions to evolve. Glycolysis uses no molecular oxygen. All re ...
Plasma enzyme
... In the liver, it catalyzes the oxidation of L-lactate to pyruvate (L P) with the mediation of NAD as hydrogen acceptor. The reaction is reversible and the reaction equilibrium strongly favors the reverse reaction, namely the reduction of pyruvate to lactate (P L). The formation of NADH produces an i ...
... In the liver, it catalyzes the oxidation of L-lactate to pyruvate (L P) with the mediation of NAD as hydrogen acceptor. The reaction is reversible and the reaction equilibrium strongly favors the reverse reaction, namely the reduction of pyruvate to lactate (P L). The formation of NADH produces an i ...
- Free Documents
... production of ATP from GTP is easily determined. In the process NADH and FADH are oxidized back to NAD and FAD and these can be used again in various metabolic pathways. Electron Transport Chain . thus. is reduced to water. the Electron Transport Chain completes the process by which glucose is compl ...
... production of ATP from GTP is easily determined. In the process NADH and FADH are oxidized back to NAD and FAD and these can be used again in various metabolic pathways. Electron Transport Chain . thus. is reduced to water. the Electron Transport Chain completes the process by which glucose is compl ...
rapid determination of total lipids in mosquitoes
... suitable for the small amount of lipids found in individual mosquiroes. Chloroform-methanol is a much more efficient and widely used analytical lipid solvenr. The disadvantage is that the methanol in combination with tissul water also extracts non-lipid material such as glycerol, sugars, amino acids ...
... suitable for the small amount of lipids found in individual mosquiroes. Chloroform-methanol is a much more efficient and widely used analytical lipid solvenr. The disadvantage is that the methanol in combination with tissul water also extracts non-lipid material such as glycerol, sugars, amino acids ...
Urea cycle
... Glutamate, aspartate and some BCAAs fuel for the gut. 60% to 70% of AA present in portal vein is taken by liver conversion to glucose in the gluconeogenetic pathway. High protein diet stimulates glucagon and insulin release. Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis in the liver Insulin stimulates pro ...
... Glutamate, aspartate and some BCAAs fuel for the gut. 60% to 70% of AA present in portal vein is taken by liver conversion to glucose in the gluconeogenetic pathway. High protein diet stimulates glucagon and insulin release. Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis in the liver Insulin stimulates pro ...
Amino Acid Catabolism
... Amino acids are either used as building blocks or burned for energy (~10% of our energy needs). Catabolism of amino acids increases for use in gluconeogenesis when glucose is unavailable (e.g., starvation/diabetes) when protein content of diet exceeds need for building blocks during times of ...
... Amino acids are either used as building blocks or burned for energy (~10% of our energy needs). Catabolism of amino acids increases for use in gluconeogenesis when glucose is unavailable (e.g., starvation/diabetes) when protein content of diet exceeds need for building blocks during times of ...
L03_MitoOx
... Carnitine often sold as a ‘fat metaboliser’. Claim is that carnitine will help the transport of FA into matrix…. And that this will help burn fat. Sorry, unless you’re specifically deficient in carnitine, it ...
... Carnitine often sold as a ‘fat metaboliser’. Claim is that carnitine will help the transport of FA into matrix…. And that this will help burn fat. Sorry, unless you’re specifically deficient in carnitine, it ...
Chapter 3
... type of glycolysis. During aerobic glycolysis every triosephosphate is converted to pyruvate and one molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH. NADH is reoxidised to NAD+ by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase through the conversion of DHAP to G3P. Due to the inhibition of G3P oxidase, the G3P concentratio ...
... type of glycolysis. During aerobic glycolysis every triosephosphate is converted to pyruvate and one molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH. NADH is reoxidised to NAD+ by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase through the conversion of DHAP to G3P. Due to the inhibition of G3P oxidase, the G3P concentratio ...
Krebs Cycle - 2008 BIOCHEM 201
... • All enzymes are hydrophilic and occur in the matrix except for succinate dehydrogenase, which occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane • Citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and aketoglutarate dehydrogenase are the three ...
... • All enzymes are hydrophilic and occur in the matrix except for succinate dehydrogenase, which occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane • Citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and aketoglutarate dehydrogenase are the three ...
lipoprotein metabolism
... What are the lipids carried by CM? Where is CM formed? What is the source for lipids in CM? How does the CM release FFA? What is the fate of the FFA and Glycerol? Where is the LPL found? What are the components of Remnant CM? ...
... What are the lipids carried by CM? Where is CM formed? What is the source for lipids in CM? How does the CM release FFA? What is the fate of the FFA and Glycerol? Where is the LPL found? What are the components of Remnant CM? ...
NUTRITIONAL INTEREST OF CHEESE FAT A lot of new datas
... Ø Myristic acid and palmitic acid have not the same metabolic fate in the cell : Ø Myristic acid is rapidly b-oxidized, weakly secreted in the form of TGVLDL, but strongly elongated into palmitic acid. No accumulation ! Ø Palmitic acid is stored and secreted in the form of TG, weakly elongated into ...
... Ø Myristic acid and palmitic acid have not the same metabolic fate in the cell : Ø Myristic acid is rapidly b-oxidized, weakly secreted in the form of TGVLDL, but strongly elongated into palmitic acid. No accumulation ! Ø Palmitic acid is stored and secreted in the form of TG, weakly elongated into ...
biology 2402
... *Insulin increases the rate of glucose facilitated diffusion into most cells, except neurons and liver cells. *The rate of glucose transport into cells is greatly increased by Insulin. Immediately upon entry into cells, glucose is phosphorylated. It combines with a phosphate group, produced by the b ...
... *Insulin increases the rate of glucose facilitated diffusion into most cells, except neurons and liver cells. *The rate of glucose transport into cells is greatly increased by Insulin. Immediately upon entry into cells, glucose is phosphorylated. It combines with a phosphate group, produced by the b ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.























