Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency presenting as acute hypercapnic respiratory failure CASE STUDY
... whereas adult-onset disease is usually restricted to muscles. For disorders of fatty acid metabolism, carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) II deficiency is the most common defect, as well as being the most common metabolic cause of recurrent rhabdomyolysis. The clinical features in the patient were ...
... whereas adult-onset disease is usually restricted to muscles. For disorders of fatty acid metabolism, carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) II deficiency is the most common defect, as well as being the most common metabolic cause of recurrent rhabdomyolysis. The clinical features in the patient were ...
acid
... containing mitochondria. Both pyruvate molecules are oxidized to two acetylCoA molecules. Entry of Pyruvate into Mitochondria In mitochondria, pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation and remaining two carbon fragment is converted to acetyl-CoA. The reaction is irreversible and multi-step proces ...
... containing mitochondria. Both pyruvate molecules are oxidized to two acetylCoA molecules. Entry of Pyruvate into Mitochondria In mitochondria, pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation and remaining two carbon fragment is converted to acetyl-CoA. The reaction is irreversible and multi-step proces ...
Tutorial 3 (Ans Scheme) ERT 317, Sem 1 2015/2016
... The enzyme triose phosphate dehydrogenase serves two functions in this step. First the enzyme transfers a hydrogen (H-) from glyceraldehyde phosphate to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to form NADH. Next triose phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate (P) from the cytoso ...
... The enzyme triose phosphate dehydrogenase serves two functions in this step. First the enzyme transfers a hydrogen (H-) from glyceraldehyde phosphate to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to form NADH. Next triose phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate (P) from the cytoso ...
檔案下載
... – If a component of the citric acid cycle is taken out for biosynthesis, it must be replaced 中間產物被利用來合成其他 分子,之後這些中間產物就必須被補充 • [Oxaloacetate] maintained at a level sufficient to allow acetylCoA to enter the cycle ...
... – If a component of the citric acid cycle is taken out for biosynthesis, it must be replaced 中間產物被利用來合成其他 分子,之後這些中間產物就必須被補充 • [Oxaloacetate] maintained at a level sufficient to allow acetylCoA to enter the cycle ...
Regulation of Elovl and fatty acid metabolism
... 2.3. Elongation of very long chain fatty acids Fatty acids taken up from the diet as well as a significant amount of the fatty acids produced by FAS, undergo further elongation into long chain fatty acids (LCFA > C18) and very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA > C20). As early as in the nineteen sixtie ...
... 2.3. Elongation of very long chain fatty acids Fatty acids taken up from the diet as well as a significant amount of the fatty acids produced by FAS, undergo further elongation into long chain fatty acids (LCFA > C18) and very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA > C20). As early as in the nineteen sixtie ...
PDF - MD Body and Med spa
... When beta-oxidation outstrips carbohydrate breakdown (e.g. during starvation and uncontrolled diabetes) ketone bodies are produced by liver mitochondria. This is because the large amount of acetyl CoA produced by beta oxidation overloads the citric acid cycle (limited carbohydrate means that citric ...
... When beta-oxidation outstrips carbohydrate breakdown (e.g. during starvation and uncontrolled diabetes) ketone bodies are produced by liver mitochondria. This is because the large amount of acetyl CoA produced by beta oxidation overloads the citric acid cycle (limited carbohydrate means that citric ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... are the basis of boxidation of fatty acids. Reduction of the b-keto group is followed by dehydration to form a double bond. Reduction of the double bond yields a fatty acyl-CoA that is elongated by two carbons. Note that the reducing coenzyme for the second step is NADH, whereas the reductant for th ...
... are the basis of boxidation of fatty acids. Reduction of the b-keto group is followed by dehydration to form a double bond. Reduction of the double bond yields a fatty acyl-CoA that is elongated by two carbons. Note that the reducing coenzyme for the second step is NADH, whereas the reductant for th ...
Requirements - Department of Medical Biochemistry, Semmelweis
... (carbohydrates, metabolic integration) (iii) block#C 30 multiple choice type test questions (lipids, amino acids, nucleotides, porphyrins). Correct answer for a biochemistry problem may result in max 1-3 points. The correct solution for a multiple choice type question results in 1 point. Futher poin ...
... (carbohydrates, metabolic integration) (iii) block#C 30 multiple choice type test questions (lipids, amino acids, nucleotides, porphyrins). Correct answer for a biochemistry problem may result in max 1-3 points. The correct solution for a multiple choice type question results in 1 point. Futher poin ...
Ch18.doc
... by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP and 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP. So for one lactate: (3+1+1)(2.5 ATP) + 1.5 ATP + 1 ATP = 15 ATP. From alanine, it is the transaminase reaction, then pyruvate ...
... by pyruvate dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP and 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP. So for one lactate: (3+1+1)(2.5 ATP) + 1.5 ATP + 1 ATP = 15 ATP. From alanine, it is the transaminase reaction, then pyruvate ...
Document
... • Occurs in mitochondrial matrix • Is the biochemical hub of the cell, oxidizing carbon fuels, usually in the form of acetyl CoA, interconversion of carbohydrates, lipids, and some amino acids, as well as serving as a source of precursors for biosynthesis • For the citric acid cycle, the goal is to ...
... • Occurs in mitochondrial matrix • Is the biochemical hub of the cell, oxidizing carbon fuels, usually in the form of acetyl CoA, interconversion of carbohydrates, lipids, and some amino acids, as well as serving as a source of precursors for biosynthesis • For the citric acid cycle, the goal is to ...
28 - Weebly
... the liver, and released to the blood or converted to glycogen or fat. • Most fats enter the lymph as chylomicrons, which are broken down to glycerol and fatty acids to enable them to pass into capillaries. • Adipose cells, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, and the liver use triglycerides to synthes ...
... the liver, and released to the blood or converted to glycogen or fat. • Most fats enter the lymph as chylomicrons, which are broken down to glycerol and fatty acids to enable them to pass into capillaries. • Adipose cells, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, and the liver use triglycerides to synthes ...
Functions of the liver Assessment and interpretation of liver function
... • Normal pregnancy, bone growth and bone diseases do not affect 5' NT • In pts with HBD, changes in ALP are usually followed by similar ...
... • Normal pregnancy, bone growth and bone diseases do not affect 5' NT • In pts with HBD, changes in ALP are usually followed by similar ...
Hans Adolf Krebs (2)
... It was assumed that the formation of citrate from oxaloacetate occurred as a result of the oxaloacetate condensing with a substance derived from a carbohydrate, such as pyruvate or acetate (Ref. 3 Krebs, 1953) ...
... It was assumed that the formation of citrate from oxaloacetate occurred as a result of the oxaloacetate condensing with a substance derived from a carbohydrate, such as pyruvate or acetate (Ref. 3 Krebs, 1953) ...
Note Set 11 1 GLYCOLYSIS (also known as: EMBDEN
... precursor inositol, pentose phosphate pathway (NADPH, ribose) and more… G6-P is the precursor for synthesis of glycogen and is also used in pentose phosphate pathway to form NADPH •thus the HEX step is not the committed step because product of the reaction goes other places…committed means it only g ...
... precursor inositol, pentose phosphate pathway (NADPH, ribose) and more… G6-P is the precursor for synthesis of glycogen and is also used in pentose phosphate pathway to form NADPH •thus the HEX step is not the committed step because product of the reaction goes other places…committed means it only g ...
Lecture 27
... Degradation of amino acids converts the to TCA cycle intermediates or precursors to be metabolized to CO2, H2O, or for use in gluconeogenesis. Aminoacids are glucogenic, ketogenic or both. Glucogenic amino acids-carbon skeletons are broken down to pyruvate, -ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, fumarate, o ...
... Degradation of amino acids converts the to TCA cycle intermediates or precursors to be metabolized to CO2, H2O, or for use in gluconeogenesis. Aminoacids are glucogenic, ketogenic or both. Glucogenic amino acids-carbon skeletons are broken down to pyruvate, -ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, fumarate, o ...
Glycolysis
... Hexokinase is inhibited by product glucose-6-phosphate: by competition at the active site by allosteric interaction at a separate enzyme site. Cells trap glucose by phosphorylating it, preventing exit on glucose carriers. Product inhibition of Hexokinase ensures that cells will not continue to a ...
... Hexokinase is inhibited by product glucose-6-phosphate: by competition at the active site by allosteric interaction at a separate enzyme site. Cells trap glucose by phosphorylating it, preventing exit on glucose carriers. Product inhibition of Hexokinase ensures that cells will not continue to a ...
Glycolysis
... Hexokinase is inhibited by product glucose-6-phosphate: by competition at the active site by allosteric interaction at a separate enzyme site. Cells trap glucose by phosphorylating it, preventing exit on glucose carriers. Product inhibition of Hexokinase ensures that cells will not continue to a ...
... Hexokinase is inhibited by product glucose-6-phosphate: by competition at the active site by allosteric interaction at a separate enzyme site. Cells trap glucose by phosphorylating it, preventing exit on glucose carriers. Product inhibition of Hexokinase ensures that cells will not continue to a ...
Syllabus for BASIC METABOLIC PRINCIPLES
... Note that some of the arrows in the pathway point in both directions, indicating that these reactions are reversible; for the reactions catalyzed by E1, E3, and E4, the direction is determined by the concentration of substrate and product for that particular reaction. In contrast, the arrow for t ...
... Note that some of the arrows in the pathway point in both directions, indicating that these reactions are reversible; for the reactions catalyzed by E1, E3, and E4, the direction is determined by the concentration of substrate and product for that particular reaction. In contrast, the arrow for t ...
The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in some
... The presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in marine bacteria has been demonstrated (Delong & Yayanos, 1986; Wirsen et al., 1987; Yazawa et al., 1988; Intriago & Floodgate, 1991), but the mechanism controlling their biosynthesis is unknown. A potential regulator such as cyclic AMP (CAMP) is ...
... The presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in marine bacteria has been demonstrated (Delong & Yayanos, 1986; Wirsen et al., 1987; Yazawa et al., 1988; Intriago & Floodgate, 1991), but the mechanism controlling their biosynthesis is unknown. A potential regulator such as cyclic AMP (CAMP) is ...
lect4
... Free ammonia is a by-product of brain metabolism The neurotransmitter GABA is inactivated by deamination glutamate + NH4+ + ATP ...
... Free ammonia is a by-product of brain metabolism The neurotransmitter GABA is inactivated by deamination glutamate + NH4+ + ATP ...
Slide 1
... cups of coffee can result in a positive drug test (urine levels greater than 12 ug/ml). 2. caffeine is a diuretic: increased water loss; greater likelihood of dehydration. 3. in large quantities can cause cardiac arrhythmia, tachycardia. Also may result in mental confusion. ...
... cups of coffee can result in a positive drug test (urine levels greater than 12 ug/ml). 2. caffeine is a diuretic: increased water loss; greater likelihood of dehydration. 3. in large quantities can cause cardiac arrhythmia, tachycardia. Also may result in mental confusion. ...
Lecture 3: Glycolysis Part 2 - University of California, Berkeley
... Mechanism. “Aldolase” name is derived from ―aldol condensation‖ reaction in organic chemistry, and involves the formation of a covalently-linked, substrate-enzyme intermediate. The epsilon amino group of lysine in the enzyme active site makes a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon, forms a pro ...
... Mechanism. “Aldolase” name is derived from ―aldol condensation‖ reaction in organic chemistry, and involves the formation of a covalently-linked, substrate-enzyme intermediate. The epsilon amino group of lysine in the enzyme active site makes a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon, forms a pro ...
Answer Key for the Supplemental Problem Set #1
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
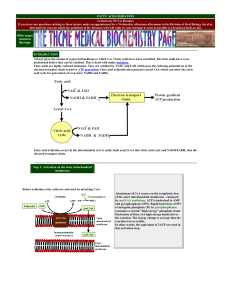
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.