Chapter 17. Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea
... acid cycle (generating one NADH), then take an amino group from Glu via a transamination reaction. ...
... acid cycle (generating one NADH), then take an amino group from Glu via a transamination reaction. ...
Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism
... – If ATP use decreases, the concentration of ATP increases. The ATP binds to phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase, slowing down their activity, and thus slowing the glycolysis pathway. – When ATP concentrations are low, ADP and AMP concentrations are high, which activates the phosphofructokinase, ...
... – If ATP use decreases, the concentration of ATP increases. The ATP binds to phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase, slowing down their activity, and thus slowing the glycolysis pathway. – When ATP concentrations are low, ADP and AMP concentrations are high, which activates the phosphofructokinase, ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... c) Pyruvate: which can be used in synthesis of amino acid alanine. 4. Aerobic glycolysis provides the mitochondria with pyruvate, which gives acetyl CoA Krebs' cycle. ...
... c) Pyruvate: which can be used in synthesis of amino acid alanine. 4. Aerobic glycolysis provides the mitochondria with pyruvate, which gives acetyl CoA Krebs' cycle. ...
Ubiquinone
... • This lysyl-tRNA mutation is also one of the causes of adult-onset (type II) diabetes. ...
... • This lysyl-tRNA mutation is also one of the causes of adult-onset (type II) diabetes. ...
Introduction: Dietary carbohydrates digestion give mainly
... Fructose is more rapidly metabolized than glucose and galactose, since the glucokinase (GK) and phosphofructokinase ( PFK) metabolic bottlenecks, are not encountered in fructose metabolism. However, excess fructose in the diet depletes Pi in the liver. The production of fructose 1 phosphate will be ...
... Fructose is more rapidly metabolized than glucose and galactose, since the glucokinase (GK) and phosphofructokinase ( PFK) metabolic bottlenecks, are not encountered in fructose metabolism. However, excess fructose in the diet depletes Pi in the liver. The production of fructose 1 phosphate will be ...
Pyruvate Kinase - Wiley Online Library
... Kinetic studies of the pyruvate kinases of rat and human tissues have led t o the identification of three classes of isoenzymes with qualitative differences in regulatory properties. Class L, the major component in liver extracts and a minor component of kidney extracts, shows markedly sigmoidal kin ...
... Kinetic studies of the pyruvate kinases of rat and human tissues have led t o the identification of three classes of isoenzymes with qualitative differences in regulatory properties. Class L, the major component in liver extracts and a minor component of kidney extracts, shows markedly sigmoidal kin ...
Energy Metabolism Review
... Lactic Acid Fermentation o The product of Lactic Acid fermentation, lactic acid o This is the "burn" felt when undergoing strenuous activity ...
... Lactic Acid Fermentation o The product of Lactic Acid fermentation, lactic acid o This is the "burn" felt when undergoing strenuous activity ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism in hypercapnia changes in G-6-P and F-6-P, and highly significant decreases in 3-PG and pyruvate. The data obtained at shorter exposure periods demonstrate that there was a transient decrease in glycogen concentration, that the concentrations of G-6-P and F-6- ...
... Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism in hypercapnia changes in G-6-P and F-6-P, and highly significant decreases in 3-PG and pyruvate. The data obtained at shorter exposure periods demonstrate that there was a transient decrease in glycogen concentration, that the concentrations of G-6-P and F-6- ...
finalcarbohydrat met..
... c) Pyruvate: which can be used in synthesis of amino acid alanine. 4. Aerobic glycolysis provides the mitochondria with pyruvate, which gives acetyl CoA Krebs' cycle. ...
... c) Pyruvate: which can be used in synthesis of amino acid alanine. 4. Aerobic glycolysis provides the mitochondria with pyruvate, which gives acetyl CoA Krebs' cycle. ...
pdf of article - ACG Publications
... metabolites. This fact is not surprising, since amino acids are soluble in polar solvents; therefore, the use of water associated with high temperatures enables their extraction. Alanine was clearly the major compound in both extracts, accounting for more than 83% of the total of amino acids (Table ...
... metabolites. This fact is not surprising, since amino acids are soluble in polar solvents; therefore, the use of water associated with high temperatures enables their extraction. Alanine was clearly the major compound in both extracts, accounting for more than 83% of the total of amino acids (Table ...
Fatty Acid and Glucose Sensors in Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
... effects for the cell2; thus DNL is the preferred mechanism to stock excess energy within the body. When DNL is overactivated in the liver because of hyperinsulinemia, it promotes hepatic fat accumulation leading to NAFLD, and hypertriglyceridemia. Adipose tissue function is thus an important factor ...
... effects for the cell2; thus DNL is the preferred mechanism to stock excess energy within the body. When DNL is overactivated in the liver because of hyperinsulinemia, it promotes hepatic fat accumulation leading to NAFLD, and hypertriglyceridemia. Adipose tissue function is thus an important factor ...
Amino Acids and Simple Proteins
... glycogen synthesis and degradation. Anaerobic metabolism: glycolysis, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Aerobic metabolism: pentose phosphate pathway of glucose oxidation; oxidative decarboxylation. of pyruvate, the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation, The respiratory chain of electrons ...
... glycogen synthesis and degradation. Anaerobic metabolism: glycolysis, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Aerobic metabolism: pentose phosphate pathway of glucose oxidation; oxidative decarboxylation. of pyruvate, the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Biological oxidation, The respiratory chain of electrons ...
Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids
... Lipid absorption by formation of mixed micelles intestinal diseases à incomplete digestion and absorption of fat & protein à steatorrhea & Re-‐synthesis of TAGs, cholesteryl ester and PLs inside appeara ...
... Lipid absorption by formation of mixed micelles intestinal diseases à incomplete digestion and absorption of fat & protein à steatorrhea & Re-‐synthesis of TAGs, cholesteryl ester and PLs inside appeara ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... Acetate is subsequently transferred to a cysteine thiol of the Condensing Enzyme domain. ...
... Acetate is subsequently transferred to a cysteine thiol of the Condensing Enzyme domain. ...
ppt file/carnitine
... Never nowhere fatty acids can enter to mitochondria to be oxidized, therefore: a) always everywhere glucose (and amino acids) are degraded to yield energy, glucose is consumed very fast, causing between meals life threatening hypoglycemia, coma b) in liver, muscle etc. PDHC is not inhibited by acety ...
... Never nowhere fatty acids can enter to mitochondria to be oxidized, therefore: a) always everywhere glucose (and amino acids) are degraded to yield energy, glucose is consumed very fast, causing between meals life threatening hypoglycemia, coma b) in liver, muscle etc. PDHC is not inhibited by acety ...
Isoforms of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
... evolution and are well conserved between eubacteria, unicellular eukaryotes, plants and animals. The importance of malonyl-CoA in cell metabolism is most directly reflected by the fact that ACC expression is essential for normal growth of bacteria, yeast and isolated animal cells in culture. For exa ...
... evolution and are well conserved between eubacteria, unicellular eukaryotes, plants and animals. The importance of malonyl-CoA in cell metabolism is most directly reflected by the fact that ACC expression is essential for normal growth of bacteria, yeast and isolated animal cells in culture. For exa ...
LIPID METABOLISM BIOSYNTHESIS or DE NOVO SYNTHESIS OF
... The majority of the fatty acids required supplied through our diet. Fatty acids are synthesised whenever there is a caloric excess in the our diet. The excess carbohydrate and protein obtained through diet can be converted to fatty acids which are stored as triacylglycerol. ...
... The majority of the fatty acids required supplied through our diet. Fatty acids are synthesised whenever there is a caloric excess in the our diet. The excess carbohydrate and protein obtained through diet can be converted to fatty acids which are stored as triacylglycerol. ...
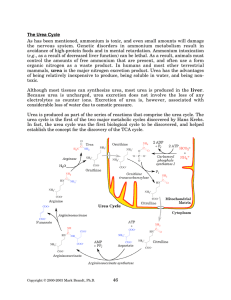
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... a source outside the cell (either from protein breakdown or from a dietary source). A second method is to synthesize ornithine directly. Ornithine synthesis normally begins with glutamate, although proline can also act as a source of ornithine synthesis. One pathway for the conversion of glutamate t ...
... a source outside the cell (either from protein breakdown or from a dietary source). A second method is to synthesize ornithine directly. Ornithine synthesis normally begins with glutamate, although proline can also act as a source of ornithine synthesis. One pathway for the conversion of glutamate t ...
05 Farm Animal Metabolism 05
... milk. Although a normal part of animal growth or milk synthesis, fat synthesis decreases the efficiency of conversion of feed nutrients into lean meat or low-fat milk products that consumers desire. Furthermore, metabolism of lipids in the liver is an integral component of animal production and is a ...
... milk. Although a normal part of animal growth or milk synthesis, fat synthesis decreases the efficiency of conversion of feed nutrients into lean meat or low-fat milk products that consumers desire. Furthermore, metabolism of lipids in the liver is an integral component of animal production and is a ...
Clinical Biochemistry
... can be quickly mobilized to meet a sudden need for glucose, but one that is less compact and more immediately available as an energy reserve than triglycerides (lipids). In the liver hepatocytes, glycogen can compose up to eight percent (100–120 g in an adult) of the fresh weight soon after a meal.[ ...
... can be quickly mobilized to meet a sudden need for glucose, but one that is less compact and more immediately available as an energy reserve than triglycerides (lipids). In the liver hepatocytes, glycogen can compose up to eight percent (100–120 g in an adult) of the fresh weight soon after a meal.[ ...
LFT- GIT
... 1- Check certain enzymes & proteins levels in blood that if are higher or lower than normal can indicate liver problems (diagnosis) 2- Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis 3- Monitor the progression of a liver disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis & determine how well a treatment i ...
... 1- Check certain enzymes & proteins levels in blood that if are higher or lower than normal can indicate liver problems (diagnosis) 2- Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis 3- Monitor the progression of a liver disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis & determine how well a treatment i ...
Metabolism
... Enzymes work by bending their substrates in such a way that the bonds to be broken are stressed and the substrate molecule resembles the transition state. This makes them more amenable to reaction with other molecules. Enzymes function by lowering the barriers that block a particular reaction. Put ...
... Enzymes work by bending their substrates in such a way that the bonds to be broken are stressed and the substrate molecule resembles the transition state. This makes them more amenable to reaction with other molecules. Enzymes function by lowering the barriers that block a particular reaction. Put ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.