Chapter 26 - Palm Beach State College
... fatty acids • Resulting free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol enter adipocytes to be made into triglycerides for storage • Chylomicron remnant—the remainder of a chylomicron after the triglycerides have been extracted and degraded by liver ...
... fatty acids • Resulting free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol enter adipocytes to be made into triglycerides for storage • Chylomicron remnant—the remainder of a chylomicron after the triglycerides have been extracted and degraded by liver ...
Glycerolipids and Glycerophospholipids
... Diagnostics: the L/S Ratio • Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is produced by type II alveolar epithelial cells in the fetal lung. During gestation it is found in the amniotic fluid. PC ...
... Diagnostics: the L/S Ratio • Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is produced by type II alveolar epithelial cells in the fetal lung. During gestation it is found in the amniotic fluid. PC ...
Chapter 26
... • Secreted by enteroendocrine cells of ileum and colon • Sense that food has arrived in the stomach • Secrete PYY long before chyme reaches the ileum in amounts proportionate to calories consumed • Primary effect is to signal satiety and terminate eating • Signal that ends a meal ...
... • Secreted by enteroendocrine cells of ileum and colon • Sense that food has arrived in the stomach • Secrete PYY long before chyme reaches the ileum in amounts proportionate to calories consumed • Primary effect is to signal satiety and terminate eating • Signal that ends a meal ...
Glycolysis
... • Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. • The free energyreleased in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP & NADH. • Glycolysis is a definite sequence of ten reactions involving ten intermediate compounds. • The interm ...
... • Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. • The free energyreleased in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP & NADH. • Glycolysis is a definite sequence of ten reactions involving ten intermediate compounds. • The interm ...
Document
... 3-D shape and recognizes and binds only the specific substrate of a reaction • often – reaction with only one substrate • sometimes – reaction with group of similar substrates • eg. aspartase ...
... 3-D shape and recognizes and binds only the specific substrate of a reaction • often – reaction with only one substrate • sometimes – reaction with group of similar substrates • eg. aspartase ...
Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism
... mole of glucose that is converted to pyruvate. • Other sugars are also digested in glycolysis: – Fructose enters glycolysis as dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. – Galactose is isomerized to form glucose-6phosphate. ...
... mole of glucose that is converted to pyruvate. • Other sugars are also digested in glycolysis: – Fructose enters glycolysis as dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. – Galactose is isomerized to form glucose-6phosphate. ...
pptx
... So what would happen if we gave a patient a large dose of aspirin or Coxib to reduce inflammation/pain in these tissues? ...
... So what would happen if we gave a patient a large dose of aspirin or Coxib to reduce inflammation/pain in these tissues? ...
KINE 3350 TEST 2 2008
... C. cellular uptake of carbohydrates. 41. Which of the following hormones is believed to exert a "permissive" effect on the mobilization of glucose from liver and FFA from adipose tissue? A. epinephrine B. T3 and T4 C. insulin D. glucagon 42. The changes in the plasma concentration of most of the hor ...
... C. cellular uptake of carbohydrates. 41. Which of the following hormones is believed to exert a "permissive" effect on the mobilization of glucose from liver and FFA from adipose tissue? A. epinephrine B. T3 and T4 C. insulin D. glucagon 42. The changes in the plasma concentration of most of the hor ...
03-232 Biochemistry ... Name:________________________ or the back of the preceding page. In questions... Instructions:
... 12. (12 pts) Please do one of the following two choices related to the conversion of captured energy to ATP. Feel free to use a diagram in your answer. Choice A: Briefly describe the second to last step in the conversion of the energy in the bagel to ATP, i.e. electron transport. Be sure to indicate ...
... 12. (12 pts) Please do one of the following two choices related to the conversion of captured energy to ATP. Feel free to use a diagram in your answer. Choice A: Briefly describe the second to last step in the conversion of the energy in the bagel to ATP, i.e. electron transport. Be sure to indicate ...
BioChem pg 635 to 641 ch 34 [4-20
... A. Conversion of cholesterol to Cholic Acid and Chenocholic Acid Bile salts are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol Rxns hydroxylate the steroid nucleus and cleave side chain In the first and rate-limiting reaction ...
... A. Conversion of cholesterol to Cholic Acid and Chenocholic Acid Bile salts are synthesized in the liver from cholesterol Rxns hydroxylate the steroid nucleus and cleave side chain In the first and rate-limiting reaction ...
Slide 1
... UDP-Glc synthases in protists, animals, and fungi. ADP-Glc synthase in plants. Primer of 4 to 8 Glc on a Tyr (-OH) of glycogenin. 1st Glc from UDP-Glc via Glc transferase. Remaining Glc’s tranferred by glycogenin. Amylo-(1,4 1,6)-transglycolase catalyzes the branch point. (Alpha 1-6 link) ...
... UDP-Glc synthases in protists, animals, and fungi. ADP-Glc synthase in plants. Primer of 4 to 8 Glc on a Tyr (-OH) of glycogenin. 1st Glc from UDP-Glc via Glc transferase. Remaining Glc’s tranferred by glycogenin. Amylo-(1,4 1,6)-transglycolase catalyzes the branch point. (Alpha 1-6 link) ...
03-1 Metabolism of carbohydrate
... Pathway Has a Rich History 1910s to 30s, Embden and Meyerhof (Germany), glycolysis in muscle and its extracts: in vitro reconstruction from glycogen to lactic acid; many reactions of lactic acid (muscle) and alcohol (yeast) fermentations are the same; lactic acid is reconverted to carbohydrate in ...
... Pathway Has a Rich History 1910s to 30s, Embden and Meyerhof (Germany), glycolysis in muscle and its extracts: in vitro reconstruction from glycogen to lactic acid; many reactions of lactic acid (muscle) and alcohol (yeast) fermentations are the same; lactic acid is reconverted to carbohydrate in ...
AA lecture 2 urea cycle
... H20 + fumarate + aa + NAD+ aspartate + -keto acid + NADH + H+ then aspartate + NH4+ + HCO3- + 3 ATP urea + fumarate + 2 H20 + 2 ADP + AMP + 4 Pi + H+ Four high energy phosphate bond equivalents are used for these reactions (- 4 ~P). Two NADH are produced. ...
... H20 + fumarate + aa + NAD+ aspartate + -keto acid + NADH + H+ then aspartate + NH4+ + HCO3- + 3 ATP urea + fumarate + 2 H20 + 2 ADP + AMP + 4 Pi + H+ Four high energy phosphate bond equivalents are used for these reactions (- 4 ~P). Two NADH are produced. ...
BCHEM 253 – METABOLISM IN HEALTH AND DISEASES
... change in free energy for the hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate is a −62 kJ/mol. This enzyme is strongly inhibited by fluoride in the presence of phosphate. Fluoride reacts with phosphate to form fluorophosphates (FPO 3 2-) which complexes with the Mg2+ ion located in the active site of the enzyme. ...
... change in free energy for the hydrolysis of phosphoenolpyruvate is a −62 kJ/mol. This enzyme is strongly inhibited by fluoride in the presence of phosphate. Fluoride reacts with phosphate to form fluorophosphates (FPO 3 2-) which complexes with the Mg2+ ion located in the active site of the enzyme. ...
The Energy Requirement for Growth: An A ~ ~ lication of
... transfer of hydrogen from NADH t o NADP, requires an additional ATP (1 5). The formation of 1 peptide bond will be considered t o proceed a t the expense of 5 ATP Eq. This figure is subject t o doubt. There are arguments favoring a figure of 4 (20). By applying the figure of 5, a maximum energy for ...
... transfer of hydrogen from NADH t o NADP, requires an additional ATP (1 5). The formation of 1 peptide bond will be considered t o proceed a t the expense of 5 ATP Eq. This figure is subject t o doubt. There are arguments favoring a figure of 4 (20). By applying the figure of 5, a maximum energy for ...
Detoxikace endogenních a exogenních látek
... Ammonia originates in the catabolism of amino acids that are primarily produced by the degradation of proteins – dietary as well as existing within the cell: digestive enzymes proteins released by digestion of cells sloughed-off the walls of the GIT muscle proteins hemoglobin intracellular ...
... Ammonia originates in the catabolism of amino acids that are primarily produced by the degradation of proteins – dietary as well as existing within the cell: digestive enzymes proteins released by digestion of cells sloughed-off the walls of the GIT muscle proteins hemoglobin intracellular ...
inflammatory molecules
... So what would happen if we gave a patient a large dose of aspirin or Coxib to reduce inflammation/pain in these tissues? ...
... So what would happen if we gave a patient a large dose of aspirin or Coxib to reduce inflammation/pain in these tissues? ...
14 - Ch 22 Respiration Exercise Multiple-choice questions (p. 22-35)
... hence, the overall production of pyruvate, ATP and NADH are greatly reduced (1), showing that the whole respiratory pathway was jeopardized. OR Pyruvate is the product of glycolysis. (1) As the production of pyruvate is greatly reduced after treating with drug X. (1) Glycolysis was inhibited in this ...
... hence, the overall production of pyruvate, ATP and NADH are greatly reduced (1), showing that the whole respiratory pathway was jeopardized. OR Pyruvate is the product of glycolysis. (1) As the production of pyruvate is greatly reduced after treating with drug X. (1) Glycolysis was inhibited in this ...
Ecological speciation model
... Pyruvate decarboxylase Substrate-level phosphorylation: PEP + ADP -> pyruvate + ATP 2 CO2 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP -> 3 phosphoglycerate + ATP 2 acetaldehyde H3C C O H Net ATP 2 NADH use 2 ATP make 4 ATP ...
... Pyruvate decarboxylase Substrate-level phosphorylation: PEP + ADP -> pyruvate + ATP 2 CO2 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate + ADP -> 3 phosphoglycerate + ATP 2 acetaldehyde H3C C O H Net ATP 2 NADH use 2 ATP make 4 ATP ...
Metabolic Patterns in Acetic Acid Bacteria
... Evidence is presented that the distinction, already made on nutritional grounds, between lactaphilic and glycophilic strains of acetic acid bacteria may be traced back to the metabolic level. Thus, the capacity of cell extracts to effect reversible transamination from glutamate to aspartate was well ...
... Evidence is presented that the distinction, already made on nutritional grounds, between lactaphilic and glycophilic strains of acetic acid bacteria may be traced back to the metabolic level. Thus, the capacity of cell extracts to effect reversible transamination from glutamate to aspartate was well ...
12.3 The Citric Acid Cycle Oxidizes AcetylCoA
... CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, which may lead to a resupply or net decrease in cycle intermediates ...
... CoA to CO2 by NAD+ and Q • The cycle itself is not a pathway for a net degradation of any cycle intermediates • Cycle intermediates can be shared with other pathways, which may lead to a resupply or net decrease in cycle intermediates ...
Slide 1
... expression of phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. Glucagon, which rises during starvation, inhibits the expression of these enzymes and stimulates the production of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and fructose 1,6bisphosphatase. Transcriptional control in eukaryotes is much slower than allost ...
... expression of phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. Glucagon, which rises during starvation, inhibits the expression of these enzymes and stimulates the production of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and fructose 1,6bisphosphatase. Transcriptional control in eukaryotes is much slower than allost ...
Chapter 5 (part 4) Enzyme Regulation
... Allosteric modulators bind to site other than the active site and allosteric enzymes have 4o structure Fructose-6-P + ATP -----> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP ...
... Allosteric modulators bind to site other than the active site and allosteric enzymes have 4o structure Fructose-6-P + ATP -----> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP ...
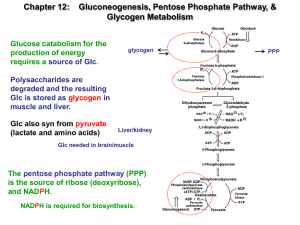
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.