2 Biochemistry
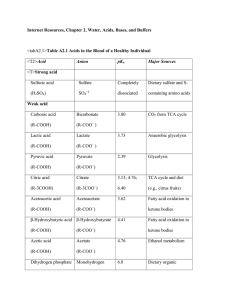
... • pH scale- 1 (acid), 7 (water), 14 (base or alkaline) • Acids- digestion HCl in stomach, Acetic Acid, & Carbonic Acid are produced in the body • Bases- Bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) is abundant in the blood, Ammonia (NH3) common waste product of protein breakdown ...
... • pH scale- 1 (acid), 7 (water), 14 (base or alkaline) • Acids- digestion HCl in stomach, Acetic Acid, & Carbonic Acid are produced in the body • Bases- Bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) is abundant in the blood, Ammonia (NH3) common waste product of protein breakdown ...
Organic Compounds
... double bonds back to single bonds, which lowers the melting temperature, giving solid margarine. • Fats store about twice as much energy per weight as carbohydrates like starch. ...
... double bonds back to single bonds, which lowers the melting temperature, giving solid margarine. • Fats store about twice as much energy per weight as carbohydrates like starch. ...
Macromolecule
... AP Biology Notes Macromolecule Biological macromolecules: Organic molecules that weigh more than 100,000 Dalton's. (1 Dalton 1.66 x 10 26 g) Four main macromolecules: These macromolecules are constructed of smaller units called polymers. These polymers are subdivided into their basic units ...
... AP Biology Notes Macromolecule Biological macromolecules: Organic molecules that weigh more than 100,000 Dalton's. (1 Dalton 1.66 x 10 26 g) Four main macromolecules: These macromolecules are constructed of smaller units called polymers. These polymers are subdivided into their basic units ...
Organic Compounds
... storage in animals and insulation; solid at room temperature) phospholipids (make up cell membranes) ...
... storage in animals and insulation; solid at room temperature) phospholipids (make up cell membranes) ...
Biology Nutrition and Digestion Revision
... • Extra: Protein is made from amino acids. Protein is also used to make enzymes (chemicals that speed up reactions in your body) Fats • Used as a store of energy and also as a layer of insulation. • Fats are found in dairy products (milk, cheese, butter) and fried food. • Too much fat in your diet c ...
... • Extra: Protein is made from amino acids. Protein is also used to make enzymes (chemicals that speed up reactions in your body) Fats • Used as a store of energy and also as a layer of insulation. • Fats are found in dairy products (milk, cheese, butter) and fried food. • Too much fat in your diet c ...
Middle-Term Test Paper on Biochemistry
... D. glycerol kinase E. Hormone-sensitive triglyceride lipase 16) The enzyme which can present both in the pathway of glycolysis or gluconeogenesis is A. Hexokinase B. Pyruvate kinase C. Pyruvate carboxylase D. Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase E. Phosphoglycerate kinase 17) All the narrations on the synthes ...
... D. glycerol kinase E. Hormone-sensitive triglyceride lipase 16) The enzyme which can present both in the pathway of glycolysis or gluconeogenesis is A. Hexokinase B. Pyruvate kinase C. Pyruvate carboxylase D. Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase E. Phosphoglycerate kinase 17) All the narrations on the synthes ...
File - Hope Christian College Parent and Student Portal
... steps, controlled by enzymes to release ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria and uses the oxygen we breathe in and is called AEROBIC RESPIRATION This allows energy to be used for movement contraction of muscles, nerve transmission of messages, transport, warmth, growth, cell division and mov ...
... steps, controlled by enzymes to release ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria and uses the oxygen we breathe in and is called AEROBIC RESPIRATION This allows energy to be used for movement contraction of muscles, nerve transmission of messages, transport, warmth, growth, cell division and mov ...
02-3 Carbon Compounds
... • Mostly contain C and H atoms. • Secondary functions of lipids are as structural components (the major building block in cell membranes) and as "messengers" (hormones) that play roles in communications within and between cells. ...
... • Mostly contain C and H atoms. • Secondary functions of lipids are as structural components (the major building block in cell membranes) and as "messengers" (hormones) that play roles in communications within and between cells. ...
MACRONUTRIENT FOUNDATIONS
... • Protein plays a big role in keeping the body functioning properly, and a healthy, nourished body is one that can perform at the highest levels. • In our bodies, protein makes up tissues (including muscle), enzymes (which help facilitate reactions in the body, e.g., metabolism of food into usable e ...
... • Protein plays a big role in keeping the body functioning properly, and a healthy, nourished body is one that can perform at the highest levels. • In our bodies, protein makes up tissues (including muscle), enzymes (which help facilitate reactions in the body, e.g., metabolism of food into usable e ...
Biomolecules
... Made of C,H,O,N Functions: Build body structures, control chemical reactions, do cellular work Example: meat/muscle, hair, nails, enzymes, peanut butter, milk Monomer: amino acid ...
... Made of C,H,O,N Functions: Build body structures, control chemical reactions, do cellular work Example: meat/muscle, hair, nails, enzymes, peanut butter, milk Monomer: amino acid ...
shortmolecular-model-build-lab
... Fat molecules are made from fatty acids and glycerol. There are many types of fatty acid molecules called lipids. A lipid found in beef fat is C57 H110 O6 (i.e. it is very “saturated” with hydrogens)… is very hard for our digestive enzymes to break it apart. It is a long molecule that can get “stuck ...
... Fat molecules are made from fatty acids and glycerol. There are many types of fatty acid molecules called lipids. A lipid found in beef fat is C57 H110 O6 (i.e. it is very “saturated” with hydrogens)… is very hard for our digestive enzymes to break it apart. It is a long molecule that can get “stuck ...
PCGHS March Test ~ Year 2009 ~ Upper Six BIOLOGY Mark
... Photorespiration is inhibited by high [CO2] (due to Krantz anatomy). Photosynthesis is efficient. Yield is much higher. Krantz anatomy present. Two different forms of chloropast: Palisade mesophyll cell contain few small chloroplasts, many large well-developed grana but no starch ...
... Photorespiration is inhibited by high [CO2] (due to Krantz anatomy). Photosynthesis is efficient. Yield is much higher. Krantz anatomy present. Two different forms of chloropast: Palisade mesophyll cell contain few small chloroplasts, many large well-developed grana but no starch ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... 1. Scope & objective of the Course: Biochemistry has been undergoing transition, stimulated by new experimental findings and new insights. Molecular understanding of genetics, has transformed the biological sciences and has given a new direction of teaching and research. Biochemistry is the language ...
... 1. Scope & objective of the Course: Biochemistry has been undergoing transition, stimulated by new experimental findings and new insights. Molecular understanding of genetics, has transformed the biological sciences and has given a new direction of teaching and research. Biochemistry is the language ...
File
... – Liver, muscle, and fat cells – Insulin stimulates these cells to increase the rate at which they absorb glucose, convert it to glycogen, and use it in respiration • Causes decrease in concentration of glucose in blood ...
... – Liver, muscle, and fat cells – Insulin stimulates these cells to increase the rate at which they absorb glucose, convert it to glycogen, and use it in respiration • Causes decrease in concentration of glucose in blood ...
Nutrients
... present lactic acid produced from pyruvate and krebs does not occur -- referred to as anaerobic carbohydrate metabolism Hydrogen ions form a concentration gradient ...
... present lactic acid produced from pyruvate and krebs does not occur -- referred to as anaerobic carbohydrate metabolism Hydrogen ions form a concentration gradient ...
Building Blocks of Organic
... • Important because they contain a great deal of energy which is stored in the bonds • called sugar or saccharide With energy from light, plants can build sugars from carbon dioxide and water. ...
... • Important because they contain a great deal of energy which is stored in the bonds • called sugar or saccharide With energy from light, plants can build sugars from carbon dioxide and water. ...
fatty acid synthesis
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
... synthesis. Phosphorylation of ACC, for example a result of activation of PKA by stress or exercise switches on fatty acid oxidation (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC-2 resulting in decreased malonyl CoA levels) while switching off fatty acid synthesis (via phosphorylation and inhibition of ...
2.3 Biomolecules Hon
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon and hydrogen ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Sources of blood glucose
... Hormonal Control of Blood Glucose • Endocrine pancreas – Only 2% of entire pancreas, – the rest produces digestive enzymes ...
... Hormonal Control of Blood Glucose • Endocrine pancreas – Only 2% of entire pancreas, – the rest produces digestive enzymes ...
投影片 1
... 18CO2 + 9CoA-SH + 9FADH2 + 27NADH + 9GTP + 27H+ 17FADH2 + 8.5O2 + 25.5ADP + 25.5Pi 17 FAD + 25.5 ATP + 17 H2O 35NADH + 35H+ + 17.5 O2 + 87.5ADP + 87.5Pi 35NAD+ + 87.5ATP + 35H2O O CH3(CH2)16C-S-CoA + 26O2 + 122 ADP + 122Pi 18CO2 + 17H2O + 122ATP + CoA-SH one 18C fatty acid ...
... 18CO2 + 9CoA-SH + 9FADH2 + 27NADH + 9GTP + 27H+ 17FADH2 + 8.5O2 + 25.5ADP + 25.5Pi 17 FAD + 25.5 ATP + 17 H2O 35NADH + 35H+ + 17.5 O2 + 87.5ADP + 87.5Pi 35NAD+ + 87.5ATP + 35H2O O CH3(CH2)16C-S-CoA + 26O2 + 122 ADP + 122Pi 18CO2 + 17H2O + 122ATP + CoA-SH one 18C fatty acid ...
Chapter 5
... some more that fits specific substrates that are responsible for you remember The substrate binds I am a product, too. tosucrose! convert you. catalyzing reactions me? to me. I am a fructose now. I am now a product. In addition I am a glucose now. to what you know. I am a substrate. ...
... some more that fits specific substrates that are responsible for you remember The substrate binds I am a product, too. tosucrose! convert you. catalyzing reactions me? to me. I am a fructose now. I am now a product. In addition I am a glucose now. to what you know. I am a substrate. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.