Macromolecules - Nolte Science
... glycogen is released from your liver to be used in your muscles for muscular contraction and movement. ...
... glycogen is released from your liver to be used in your muscles for muscular contraction and movement. ...
Baumgard Post absorptive CHO metabolism
... – Occurs in the liver and muscle – The synthesis of a branched polysaccharide form glucose….resembles amylopectin – Liver stores are especially important as an emergency source of blood glucose ...
... – Occurs in the liver and muscle – The synthesis of a branched polysaccharide form glucose….resembles amylopectin – Liver stores are especially important as an emergency source of blood glucose ...
chapter 5 the structure & function of macromolecules
... double bonds between the carbons in the chain. (Liquids at room temp due to “kinks” in the fatty acid which prevents it from solidifying) Fat Molecules are storage for energy. ...
... double bonds between the carbons in the chain. (Liquids at room temp due to “kinks” in the fatty acid which prevents it from solidifying) Fat Molecules are storage for energy. ...
and fatty acids
... that forms citrate to start the TCA. • But the supply of oxaloacetate is too low to allow all of the acetyl CoA that is made in the increased fat and protein breakdown that accompanies these states to enter the citric acid cycle. • So this pathway becomes very limited in its function. ...
... that forms citrate to start the TCA. • But the supply of oxaloacetate is too low to allow all of the acetyl CoA that is made in the increased fat and protein breakdown that accompanies these states to enter the citric acid cycle. • So this pathway becomes very limited in its function. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... and ketoacidosis after mild fasting. Note that these two phosphatase reactions do not reverse the reciprocal kinase reactions, because ATP is not regenerated. The stoichiometry for gluconeogenesis from pyruvate is: 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2 NADH + 6 H2 O Õ glucose + 4 ADP + 2 GDP + 6 Pi + 2 NAD ...
... and ketoacidosis after mild fasting. Note that these two phosphatase reactions do not reverse the reciprocal kinase reactions, because ATP is not regenerated. The stoichiometry for gluconeogenesis from pyruvate is: 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2 NADH + 6 H2 O Õ glucose + 4 ADP + 2 GDP + 6 Pi + 2 NAD ...
BIOCHEMISTRY 2.1
... •Starting material for cellular respiration—must be converted into the form our cells can use (“ATP”) •Basic form of “fuel” in living things •Soluble and transported by body fluids to all cells, where is it METABOLIZED to release energy. ...
... •Starting material for cellular respiration—must be converted into the form our cells can use (“ATP”) •Basic form of “fuel” in living things •Soluble and transported by body fluids to all cells, where is it METABOLIZED to release energy. ...
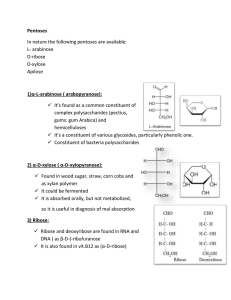
2) α-D-xylose
... Excepient in various solid dosage forms Source: Manna ash : Fraxinus ornus (F. Oleacea) ...
... Excepient in various solid dosage forms Source: Manna ash : Fraxinus ornus (F. Oleacea) ...
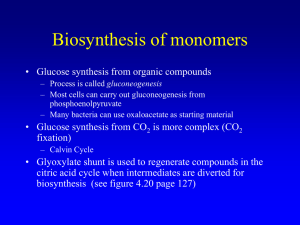
Biosynthesis of monomers
... Biosynthesis of monomers • Glucose synthesis from organic compounds – Process is called gluconeogenesis – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
... Biosynthesis of monomers • Glucose synthesis from organic compounds – Process is called gluconeogenesis – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
Medical Biochemistry: Course content 2016/2017
... Lipid synthesis, obesity. What is lipogenesis and when does this process occur? What is the significance of this process in the human body? Which enzyme systems are required for de novo synthesis of fatty acids? How is the synthesis of fatty acids carried out in the human body (structural formulas a ...
... Lipid synthesis, obesity. What is lipogenesis and when does this process occur? What is the significance of this process in the human body? Which enzyme systems are required for de novo synthesis of fatty acids? How is the synthesis of fatty acids carried out in the human body (structural formulas a ...
File
... Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic information. Examples: There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. ...
... Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic information. Examples: There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. ...
Introduction to the Digestive System Notes
... • Liver: The center of metabolic activity in the body provides bile salts to the small intestine, which are critical for digestion and absorption of fats. • Pancreas: provides a potent mixture of digestive enzymes to the small intestine which are critical for digestion of fats, carbohydrates and pro ...
... • Liver: The center of metabolic activity in the body provides bile salts to the small intestine, which are critical for digestion and absorption of fats. • Pancreas: provides a potent mixture of digestive enzymes to the small intestine which are critical for digestion of fats, carbohydrates and pro ...
File - Mrs Jones A
... Rest is changed to glycogen or fat During fasting/starvation /prolonged exercise: Protein is then hydrolysed (split with water) to amino acids which can be respired Some can be converted to pyruvate, or acetate and then is carried to Krebs cycle Some can enter Krebs directly Number of hydrogen atoms ...
... Rest is changed to glycogen or fat During fasting/starvation /prolonged exercise: Protein is then hydrolysed (split with water) to amino acids which can be respired Some can be converted to pyruvate, or acetate and then is carried to Krebs cycle Some can enter Krebs directly Number of hydrogen atoms ...
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-A New Target in the Fight against Obesity
... exercising will have an impact on healthy life. Eating junk food can prevent your body from absorbing vitamins and nutrients. ...
... exercising will have an impact on healthy life. Eating junk food can prevent your body from absorbing vitamins and nutrients. ...
Biomolecules
... accumulates in the liver - Highly branched GlucoseGlycogenglucosebloodstream • Starch – plant energy storage - Helical - Easily digested by animals through hydrolysis ...
... accumulates in the liver - Highly branched GlucoseGlycogenglucosebloodstream • Starch – plant energy storage - Helical - Easily digested by animals through hydrolysis ...
Metabolism and Energetics
... – Lipids broken down into pieces that can be converted into pyruvate – Triglycerides are split into glycerol and fatty acids • Glycerol enters glycolytic pathways • Fatty acids enter the mitochondrion via carnitine translocase (rate limiting factor) ...
... – Lipids broken down into pieces that can be converted into pyruvate – Triglycerides are split into glycerol and fatty acids • Glycerol enters glycolytic pathways • Fatty acids enter the mitochondrion via carnitine translocase (rate limiting factor) ...
Metabolism Chp 7
... 2. Convert it into energy via the TCA (aka Krebs, Citric Acid) cycle and ETC II. From lipids (Fig 7-11) • Glycerol (3C) is easily converted into pyruvate (3C) So, it can be used for energy via the steps mentioned above OR Say you need some glucose. Pyruvate can become glucose, right? As you may reca ...
... 2. Convert it into energy via the TCA (aka Krebs, Citric Acid) cycle and ETC II. From lipids (Fig 7-11) • Glycerol (3C) is easily converted into pyruvate (3C) So, it can be used for energy via the steps mentioned above OR Say you need some glucose. Pyruvate can become glucose, right? As you may reca ...
Organic Molecule
... • 20 different Amino Acids use to make all of life’s proteins. • How can there be so many different proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids? • Amino acids are connected by peptide bonds (protein aka polypeptide) ...
... • 20 different Amino Acids use to make all of life’s proteins. • How can there be so many different proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids? • Amino acids are connected by peptide bonds (protein aka polypeptide) ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... metabolic roles in addition to oxidation. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, transamination, synthesis of heme and fatty acids. • Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose from noncarbohydrate sources, such as lactate, glucogenic amino acids, glycerol, and propionate. It provides glucose to the ...
... metabolic roles in addition to oxidation. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, transamination, synthesis of heme and fatty acids. • Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose from noncarbohydrate sources, such as lactate, glucogenic amino acids, glycerol, and propionate. It provides glucose to the ...
Macromolecules
... steel rod of the same diameter, yet it is much more elastic, so scientists hope to use it for products as diverse as bulletproof vests and artificial joints. ...
... steel rod of the same diameter, yet it is much more elastic, so scientists hope to use it for products as diverse as bulletproof vests and artificial joints. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.