* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve Tissue Notes
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
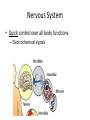
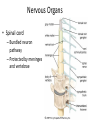
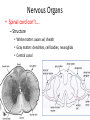
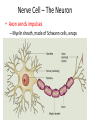
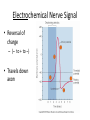
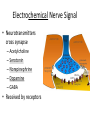
WARM UP “The secret of action is to begin.” 1. What does this mean to you? 2. How can you apply this to Biology II? Nerve Tissue Levels of Organization • Organism –Organ System »Organ • Tissue • Cell • Organelle • Molecule – Atom… • Each level depends on many cooperating structures at the levels below Nervous System • Quick control over all body functions – Electrochemical signals Nervous Organs • Brain – 100 billion neurons forming connections Nervous Organs • Spinal cord – Bundled neuron pathway – Protected by meninges and vertebrae Nervous Organs • Spinal cord con’t…. – Structure • White matter: axons w/ sheath • Gray matter: dendrites, cell bodies, neuroglials • Central canal Nerve Tissue • Made of connected neurons and neuroglial cells – Control over responses – Transmit electrical and chemical signals Nerve Cell – The Neuron • Dendrites receive info • Cell body, with trigger zone at end • Axon sends impulses Nerve Cell – The Neuron • Axon sends impulses – Myelin sheath, made of Schwann cells, wraps around axons and speeds up signals Electrochemical Nerve Signal • Reversal of charge – (– to + to –) • Travels down axon Electrochemical Nerve Signal • Controlled by ion flow – Sodium+ pumped in – Potassium+ pumped out Electrochemical Nerve Signal • Neurotransmitters cross synapse – Acetylcholine – Serotonin – Norepinephrine – Dopamine – GABA • Received by receptors WRAP UP • Which part of a neuron is most important, and why? WARM UP • Explain why nerve signals are described as “electrochemical.” WRAP UP • List the 3 parts of a neuron and describe the function of each.
























![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)



