* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6th Study Guide D1w:ans
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Apical dendrite wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
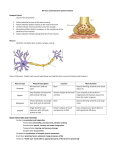
6th Science Chapter D1 Name ___________________________________ 1. What is the system that checks your body’s condition, causing hormones to be released when necessary? Endocrine System 2. A neuron is a nerve cell. 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that is sensitive to color. 7. The type of nerve cells that allows you to see, hear, and smell are sensory receptors. 8. The layer of light receptors at the back of the eye is called the retina. 9. The body’s boss is the brain. 10. The part of the neuron that collects information from other neurons is called the dendrite. 11. The system that exchanges messages with your internal organs is the nervous system. 12. The long tail-like part on the neuron is the axon. 13. Some examples of reflexes are Flinching or dodging, pulling away from something hot or sharp, sneezing, coughing 14. The part of the central nervous system that is skipped in a reflex is the brain. 15. What part of the brain controls breathing? Brain Stem 16. What is the sense organ for vision? Eyes smell? Nose hearing? Ears 17. The body gets a lot of energy from sugar or Glucose 18. What organ releases insulin? pancreas. 19. What is the part of the neuron that collects information from other neurons? dendrite 20. How is your nervous system like a two-lane highway? Information is traveling both to and from the brain just like cars are traveling to and from the city. 21. How is a message sent from one neuron to another? The dendrites receive messages from other nerve cells. Then an electrical charge forms and is sent through the cell body and axon. When it gets to the end of the axon, chemical messengers are released into the synapse and they attach to the next neuron’s dendrites. This process repeats itself.