* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
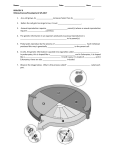
Cell Cycle UNIT Study Guide Cell Division 1. Cells divide to produce new cells. 2. Cells divide to pass on genetic material (unicellular reproduction). 3. Cells divide in order for an organism to grow and develop (multi-cellular organism). 4. Cells divide at different rates depending on their function. Cell Division (Size) 1. When cells become too large, they divide. 2. Information overload- limited amount of DNA. 3. Movement of materials- a larger cell has to move more materials farther (less efficient). 4. Know and explain the surface area to volume ratio and how it relates to cell division. 5. A larger cell has a harder time maintaining homeostasis. Cell Cycle 1. Know that all living cells go through a cell cycle. 2. Know the cell cycle vocabulary. Also be able to name and tell the differences between all of the types of DNA (chromatin, chromatid, chromosome). 3. Know that the reproduction of body (somatic) cells is asexual and produces two identical daughter cells. 4. Know the phases of the cell cycle, and know what is happening in each phase. Mitosis 1. Know that mitosis is nucleus division. 2. List all the steps. 3. Clearly define what is happening in each step. 4. Know the order of the steps, and be able to identify steps from pictures. 5. Know why each step is happening. Cell Cycle UNIT Study Guide Cell Division 1. Cells divide to produce new cells. 2. Cells divide to pass on genetic material (unicellular reproduction). 3. Cells divide in order for an organism to grow and develop (multi-cellular organism). 4. Cells divide at different rates depending on their function. Cell Division (Size) 1. When cells become too large, they divide. 2. Information overload- limited amount of DNA. 3. Movement of materials- a larger cell has to move more materials farther (less efficient). 4. Know and explain the surface area to volume ratio and how it relates to cell division. 5. A larger cell has a harder time maintaining homeostasis. Cell Cycle 1. Know that all living cells go through a cell cycle. 2. Know the cell cycle vocabulary. Also be able to name and tell the differences between all of the types of DNA (chromatin, chromatid, chromosome). 3. Know that the reproduction of body (somatic) cells is asexual and produces two identical daughter cells. 4. Know the phases of the cell cycle, and know what is happening in each phase. Mitosis 1. Know that mitosis is nucleus division. 2. List all the steps. 3. Clearly define what is happening in each step. 4. Know the order of the steps, and be able to identify steps from pictures. 5. Know why each step is happening.