* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution and Classification Unit Vocabulary
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
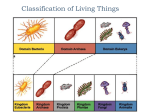
Evolution and Classification Vocabulary Charles Darwin British naturalist who observed the diversity of life on his five-year maritime journey (1850’s) on the Beagle where he formulated his theory of evolution by means of natural selection. Natural Selection Evolutionary mechanism where the members of a population that rare most suited (adapted) to their environment will most likely survive and reproduce. Jean Lamarck French biologist who proposed that evolution occurred because animals had an “inner need” to change and that acquired characteristics were passed to offspring. His theory of use and disuse was true, but the passing of acquired characteristics to offspring was not supported by evolutionary evidence. Evidence for Evolution Fossils Homologies Vestigial Structures Molecular Comparisons (Example: DNA) Similar Embryonic Development Adaptations Characteristics that increase the chance that an organism will survive and reproduce in a certain environment. Homologies Structural similarities that indicate a common evolutionary ancestry Useful in classification Examples: bird wing, whale flipper, human arm Vestigial Structures Structures with no apparent function but whose presence may indicate a common evolutionary origin with organisms having similar functional structures. Adaptive Radiation The evolution of many species from a common ancestor introduced into an environment that has a diversity of conditions. Also called divergent evolution. Examples: Darwin’s finches, marsupials in Australia Taxonomy The science of the classification of organisms. Also called systematic Carl Linnaeus Swedish biologist (1700’s) who devised “binomial nomenclature”, the scientific naming system that is still used today. Binomial Nomenclature The naming system (devised by Linnaeus) where every organism is assigned a two word Latin name. The first word is the genus name. The second word is a descriptive modifier. Example: honey bee – Apis mellifera Homo sapiens The genus and species that all human beings belong to. The scientific name of human beings. Phylogeny The evolutionary relationship among a group of organisms. Pattern of descent. Classification The seven levels to which all living things are organized. o Kingdom o Phylum o Class o Order o Family o Genus o Species Kingdoms Five kingdoms into which all living things are organized. o Monera o protista o Fungi o Plantae o Animalia Monera Composed of prokaryotic cells. Three major types include o Archaebacteria o Bacteria o Cyanobacteria (formerly called Blue-green algae) Protista Composed of eukaryotic cells. Three major groups include o Protozoa o Algae o Slime molds Animalia Composed of eukaryotic organisms. Nine phyla include o Porifera o Cnidaria (Coelenterates) o Platyhelminthes o Nematoda o Annelida o Mollusca o Arthropoda o Echinodermata o Chordata Plantae Composed of eukaryotic organism. Four phyla include o Nonvascular plants: Bryophyta – mosses, liverworts o Vascular seedless plants: Pterophyta – ferns o Vascular seed plants: Gymnosperms, coniferophyta, conifers o Flowering plants: Anthophyta, angiosperms