* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Pool
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
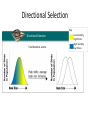
Friday 4/18 Wed. 2/13 – 16.1 LT: 1. Explain what a gene pool is 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed ET: • Outline sections 16.1 and 16.2 • Highlight headings and underline new vocabulary words (the bolded ones) • These must be quality outlines if you want to receive full credit Friday 4/18 – Genes and Variation _______________________________________________________ Daily Objective: By the end of today I should be able to… • Explain what a gene pool is • Identify that main sources of inheritable variation in a population Entrance Activity: What are the 2 important factors that Darwin was unable to explain? (17.1) Why was he unable to explain them? Gene Pool: The combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population Relative Frequency: The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool • Pg. 483 – How many alleles for black fur are there vs. alleles for white fur? What are the 2 main sources of genetic variation? 1. Mutations: Any change in a sequence of DNA Q: how do mutations occur? radiation, environment, replication of DNA 2. Gene Shuffling: Your 23 pairs of chromosomes can produce 8.4 million different combinations of genes! Q: how do chromosomes get arranged so differently? Independent assortment and crossover The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends on how many genes control the trait. • Single-Gene Traits: Controlled by a single gene that has 2 alleles Ex. Widows peak pg. 395 • Polygenic traits: Controlled by 2 or more genes, each with 2 or more alleles Ex. Height • Polygenic traits produce a bell-shaped curve when graphed – “normal distribution.” • Create a data table to record the height of each individual in the room • Create a graph using frequency and height, just like the one on pg. 396 Friday, February 15th, 2013 _______________________________________________________ Daily Objective: By the end of today I should be able to… • Explain genetic drift • Describe the conditions necessary for genetic equilibrium to be maintained. Entrance Activity: What are the 3 ways that natural selection can affect the distributions of phenotypes Natural Selection on… Directional Selection • When nature selects individuals at one end of the bell curve as the fittest Directional Selection Key Directional Selection Food becomes scarce. Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Stabilizing Selection • When nature selects individuals in the middle of the curve as more fit and the bell narrows Stabilizing Selection Key Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Birth Weight Selection against both extremes keep curve narrow and in same place. Disruptive Selection • When nature selects individuals at opposites ends of the curve as more fit. Genetic Drift • In small populations, individuals with a specific trait may leave more desendents, just by chance. • When allele frequency is altered by the migration of a small population it is called the – “founder effect” Evolution vs. Genetic Equilibrium 5 conditions can disturb equilibrium and cause evolution to occur… Genetic Equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg principle: Allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. 5 conditions that must be constant for equilibrium … If conditions are not met, the population will evolve. REVIEW!!! What is genetic drift? A population’s gene pool has to be kept together and separate from the gene pools of other populations No selective pressures!! Thursday. 2/23 – 16.3 LT: • Identify conditions necessary for a new species to evolve • Describe the process of speciation Speciation • The formation of new species based on a significant change in allele frequency As new species evolve, populations become reproductively isolated from each other Behavioral Isolation • 2 populations are capable of interbreeding but have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behaviors • Ex: Eastern Meadowlark and Western Meadowlark Geographic Isolation • Two populations are separated by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains or bodies of water. • Ex: Abert squirrel and Kaibab squirrel Temporal Isolation • 2 or more species reproduce at different times • Ex: different frog species live and breed in the same pond, but they reproduce at different times of the year. BioEd Online Common water frog Rana esculenta Speciation in Darwin’s Finches • Read and summarize steps 1-6 on pg. 408 • Compare your steps to fig. 16-17 pg. 410 Analyzing Data: complete the activity on pg. 408 “How Are These Fish Related” Answer #1-4 in NB Tuesday 2/28/2012 LT: Last day to review for exam! *Test Tomorrow