* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
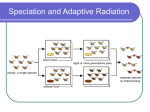
Warm up 1. Modern technology could be used to clone animals (like you favorite dog). Cloned animals would resemble the original pets because: 2. How is the process of gene therapy used to treat cystic fibrosis? 3. Describe the procedure represented in the diagram below using these terms? Restriction enzyme Recombinant DNA Plasmid Vector Who committed the crime and why? Explain the process What is similar about these two processes? Mechanisms of Evolution How did all life on Earth come from a few cells? Speciation Mechanisms of Evolution Individuals DO NOT evolve, populations do. The population is the smallest unit of evolution because acquired traits in an individual cannot be passed on (inherited by offspring). Mechanisms of Evolution However, different traits already present in a population can be “selected”, changing the population Mechanisms of Evolution Evolution occurs when the gene pool (all of the genes of a population) changes. A change in genotype may lead to a change in phenotype. Evolution acts on the phenotype. Mechanisms of Evolution Mutations are random changes in DNA and may lead to a new phenotype. Mutations provide the raw material for evolution - diversity. For example, a mutation causing white fur in Arctic foxes may lead to better camouflage in winter. Fill It In … Mutations --> ______________ in __________ --> change in ______________ Mechanisms of Evolution The environment also plays a key role in evolution. Environmental changes are natures “selection forces” that act upon the phenotype ranges caused by genes. There are three basic patters by which natural selection occurs: Patterns of natural selection: Stabilizing selection favors the “average” phenotype in a population. Patterns of natural selection: Directional selection favors the ONE of the extreme ends of the “typical” distribution Patterns of natural selection: Disruptive selection favors the BOTH of the extreme ends of the “typical” distribution Fill It In … Three types of Natural Selection: 1. 2. 3. Speciation Speciation is the development of a new species. A species is defined as a group of organisms that can produce fertile offspring. Speciation Species- a group of individuals that breed and produce fertile offspring What a about a Liger? A Mule? Speciation Speciation occurs when a population is separated, usually due to a geographical barrier, and natural selection changes the population so much the two groups could no longer interbreed. Therefore, geographic isolation leads to reproductive isolation. What is Speciation Speciation: is a lineage- splitting even that produces one or more new species formation of new species Speciation Causes of Speciation As new species evolve, populations become reproductively isolated from each other Reproductive isolation- occurrence in which the members of two populations cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring Populations have separate gene pools Causes of Speciation Behavioral Isolation- occurs when two populations are capable of interbreeding but have differences in courtship rituals or other reproductive strategies that involve behavior Bird songs Temporal Isolation- two or more species reproduce at different times Orchid pollen release Fill It In … Geographic isolation is related to speciation because … Genetic Drift By Chance- Certain individuals might leave more offspring (alleles that others) Over Time- an allele can become more and more common founder effect- a situation in which allele frequencies change as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population Rate of Evolution Timeframes of evolution differ based on the environment and the population. The fossil record provides evidence for two rates of speciation: Rate of Evolution Gradualism describes speciation that occurs over a long period of time due to the accumulation of small changes. Rate of Evolution Punctuated equilibrium describes speciation that occurs in rapid bursts that may be separated by 1000’s of years of stability. The primary stimulus is environmental change Rate of Evolution Fill It In … Venn Diagram: (Gradualism vs. Punctuated Equilibrium) Causes of Speciation Selective Pressure: Directional Selection Stabilizing Selection Disruptive Selection Adaptive Radiation Individuals will diversify rapidly to fit a NICHE in the environment Usually due to change in the environment New Resources= new niches to fill Characterized by caring for young in pouches. Evolved/ Branched from common ancestor about 160 million years ago Check Yourself! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Why can’t individuals evolve? What provides the raw material for evolution? What are the three types of natural selection? What is speciation? What conditions lead to reproductive isolation? Name the two time frames for speciation. Check Yourself! 1. Why can’t individuals evolve? AQUIRED TRAITS IN AN INDIVIDUAL CANNOT BE PASSED ON TO OFFSPRING Check Yourself! 2. What provides the raw material for evolution? MUTATIONS Check Yourself! 3. What are the three types of natural selection? STABILIZING SELECTION DIRECTIONAL SELECTION DISRUPTIVE SELECTION Check Yourself! 4. What is speciation? THE DEVELOPMENT OF A NEW SPECIES Check Yourself! 5. What conditions lead to reproductive isolation? GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION Check Yourself! 6. Name the two time frames for speciation. GRADUALISM PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM