* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skeletal Muscle Activity
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
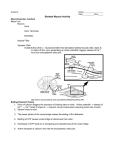
Anatomy Name___________________ Date___________Hour_____ Skeletal Muscle Activity Neuromuscular Junction Motor Unit Neuron Axon Axon Terminals Dendrites Muscle Fiber Synaptic Cleft Acetylcholine (ACh) http://www.neuroanatomy.wisc.edu/SClinic/Weakness/Nmj.JPG Sliding Filament Theory 1. Influx of calcium triggers the exposure of binding sites on actin. 2. Myosin binds to actin. 3. The power stroke of the cross bridge causes the sliding of thin filaments. 4. Binding of ATP causes cross bridge to disconnect from actin. 5. Hydrolysis of ATP leads to re-energizing and repositioning of the cross bridge. 6. Active transport of calcium ions into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Energy for Muscle Contraction Muscles require ATP for muscle contraction. Muscles contain only 4-6 seconds worth of ATP. ATP must continuously be regenerated. A lack of ATP such as in death leads to rigor mortis. Three ways ATP is generated: Direct Phosphorylation of ADP by Creatine Phosphate Aerobic Respiration (also called Oxidative Phosphorylation) Anaerobic Respiration Types of Muscle Contractions Isotonic Isometric