* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Net Start Class
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
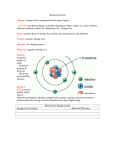
Name: Chemistry Grade Level____________ st Period :2011-2012___ 1 Semester Review Sheet KEY 1. Define ‘extensive properties’ and give 3 examples a. Definition - a property that depends on how much matter is being considered. b. Ex. 1 Size c. Ex. 2 Mass d. Ex. 3 Volume 2. Define ‘intensive properties and give 3 examples. a. Definition - a property that does not depend on how much matter is being considered. b. Ex. 1 Density c. Ex. 2 Temperature d. Ex. 3 Freezing Point 3. Define ‘valance electron’ and tell how many valance electrons each of the following elements have. a. Definition – electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. These are the electrons involved in chemical reactions. b. Silicon 4 c. Chlorine 7 d. Magnesium 2 e. Krypton 8 4. How do you calculate density and explain, using the term ‘density’, why one substance would float in another substance. Density is calculated by dividing the mass by the volume D = M/V When two substances are combined and one floats on the other it is because the liquid on top is LESS dense than the liquid on bottom. Liquid A B C D Volume 7.5 ml 100 ml 250 ml 0.5 ml Mass 10 g 100 g 200 g 0.75 g Density 1.3 g/ml 1 g/ml 0.8 g/ml 1.5 g/ml 5. How would the above liquids arrange themselves, from top to bottom, if places in a graduated cylinder? C, B, A, D 6. Define viscosity and tell which of the following liquids would have the greatest viscosity. a. Definition - a property related to the resistance of a fluid to flow b. Oil, water, maple syrup – Maple Syrup 7. Define, and give an example of each a. Suspension - a heterogeneous mixture that contains fine solid or liquid particles in a fluid that will separate spontaneously. b. Colloid – a mixture containing particles larger than solute molecules but small enough to remain suspended without settling out. c. Solution - a homogeneous mixture that consists of a solvent and at least one solute. 8. What process would best be used to separate out a salt, sand, and iron filling mixture? Remove iron fillings with a magnet; add water to the remaining salt and sand mixture; pour the mixture through filter paper to remove the sand; evaporate the water to leave the salt 9. If you had a beaker, an electronic scale and water, what process would you use to find the mass of the water? Get the mass of the beaker; add the water to the beaker and get the mass of the water and the beaker; subtract the mass of the beaker to get the mass of the water. 10. What is the general trend in atomic radius (size) and tell which of the given elements would be the biggest and the smallest. Barium, Iron, Silicon, Fluorine a. General trend – Increase from Top to bottom; decreases from the left to right b. Biggest radius – Ba c. Smallest radius – F 11. If a photon of light has an energy of 6.27 x 10-32 J, what is it’s frequency? Frequency = speed of light / wavelength Energy = Plank’s constant time frequency Speed of light = 3 x 108 m/s Plank’s constant = 6.62 x 10 -34 Joules/sec E=h*f = 6.27 x 10 -32 J / 6.62 x 10 -34 J/sec = 94.7 Hz f=E/h 12. What happens to the bonds during an endothermic reaction and how does that reaction feel to the touch? Energy is absorbed so bonds are broken; feels cold to the touch 13. What happens to the bonds during an exothermic reaction and how does that reaction feel to the touch? Energy is released as bonds are formed; feels hot to the touch 14. Identify the element, based on its electron configuration a. b. c. d. 1s2 2s2 2p5 F 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1 Al 1s1 H 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 Mg 15. Identify the following on the heating curve diagram: solid, liquid, gas, melting, boiling, melting point, boiling point. Boiling Point Boiling Melting Point Gas Liquid Melting Solid 16. Sketch a graph of each of the following experimental scenarios. a. Rate of reaction increases with increased temperature b. Rate of reaction decreases with increased temperature. c. Rate of reaction increases, than slows down, with increase in temperature. Rate of Reaction A B Temperature C 17. During which of the following scenarios would the ideal gas law break down? a. High temp and high pressure b. High temp and low pressure c. Low temp and high pressure d. Low temp and low pressure 18. If a gas is help at a constant temperature and is under an initial pressure of 1.75 atm what would the final pressure be if the volume of the gas increased from 15 L to 25 L? Show all work and include units in your final answer. Boyle’s Law V1P1 = V2P2 V1 = 15L P1 = 1.75 atm V2 = 25L P2 = ? V1P1 = V2P2 1.75atm * 15L / 25L = P2 1.05atm = P2 19. Identify each of the following compounds. a. H2O water b. CO2 carbon dioxide c. NaCl sodium chloride 20. The partial chemical equation represents the formation of PbCl2. What is the missing reactant? ________ + 4 HCl PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2 H2O PbO 21. What would happen to a crystal of a solute if it were added to each of the following types of solutions? a. Saturated: The crystal would fall to the bottom b. Unsaturated:The crystal would dissolve c. Supersaturated: The crystal would cause the soultuion to crystallize 22. Identify what type of reaction is represented by each of the following chemical equations. a. b. c. d. 8 Fe + S8 8 FeS Synthesis Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Single displacement (replacement) NaCl + AgNO3 NaNO3 + AgCl Double displacement (replacement) 2Fe2O3 4Fe + 3O2 Decomposistion 23. Based on Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, what did he conclude about each of the following? a. Charge on the center of the atom The charge was positive b. Size of the center of the atom (compared to the whole atom) The center was extremely small c. Majority of the space in the atom Most of the atom was empty space d. Density of the center of the atom (compared to the whole atom) The center of the atom was extremely dense 24. What type of chemical reaction is taking place in the above diagram? decomposition - hydrolysisi ( the DECOMPOSITION was water) 25. List and describe the penetrating power of the 3 things emitted during nuclear decay. a. Alpha radiation: very low penetrating, blocked by paper, very harmful b. Beta radiation: medium penetrating, blocked by wood, medium harmful c. Gamma radiation: high penetrating, blocked by lead, low harmful 26. Write the alpha decay of Uranium – 238. 238 U 92 4 He + 2 234 Th 90 27. Write the beta decay of Carbon – 14. 14 C 6 0 e + -1 14 N 7 28. If both variable increase, what type of relationship is it? Sketch a graph of this relationship. A directly proportional relationship 29. If one variable increases while the other variable decreases, what type of relationship is it? Sketch a graph of this relationship. An inversely proportional relationship y x 30. In which state of matter does a molecule move the least? The most? Solids move the least; gases move the most 31. What do elements in the same group on the Periodic Table all have in common? Elements in the same group on the P.T. all have the same number of valence electrons. They also have similar chemical properties. 32. Name an element that would have similar physical and/or chemical properties to the following elements. Any of the following a. b. c. d. Magnesium (Be, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra) Potassium (H, Li, Na, Rb, Cs, Fr) Argon (He, Ne, Kr, Xe, Rn) Bromine (F, Cl, I, At) 33. Calculate the average atomic mass of the following element with the given information. Relative Abundance 37.5% 42.9% 19.6% Mass (amu) 75 80 77 (0.375 * 75) + (0.429 * 80) + (0.196 * 77) = 77.537 34. Write the short hand electron configuration for each of the following elements. a. Silicon [Ne] 3s23p2 b. Iron [Ar] 4s23d6 c. Bromine [Ar]4s23d104p5 d. Strontium [Kr]5s2 35. What is one of the main differences between the modern periodic table and the one created by Mendeleev? Mendeleev organized the P.T. by atomic mass. The modern table is arranged by atomic number. 36. Describe the shape and volume of: a. Solid – fixed shape and fixed volume b. Liquid - takes the shape of the container; fixed volume c. Gas - takes the shape of the container; fills the entire volume of the container 37. How is the flame test useful in determining the identity of an element? Different elements give off distinct wavelengths of light in their emission spectrum. Therefore, the identity of an element can be determined by analyzing the color of the flame. 38. Identify the following as either ionic or covalent bonds a. NaCl - Ionic b. SO2 - Covalent c. NaF - Ionic d. BaO - Ionic e. H2O - Covalent f. KCl - Ionic g. NH3 - Covalent h. HCl - Covalent 39. List characteristics of each of the following a. Ionic compounds i. .High Melting Points ii. .Conducts electricity in the molten state iii. .Normally Crystalline Solids at 25oC iv. Solution conducts electricity when dissolved b. Covalent compounds i. .Low Melting Points ii. .Does not conduct electricity iii. .Normally liquids or amorphous solids at 25oC iv. .Does not conduct electricity when dissolved. 40. Draw the proper orbital diagram for each of the following elements. a. Example: Oxygen – 8 electrons ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ 3p b. Magnesium - __12__ electrons ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ 3p c. Neon - __10_ electrons ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ 3p d. Carbon - _6_ electrons ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ 3p e. Beryllium- _4__ electrons ____ 1s ____ 2s ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 2p ____ 3s ____ 3p 41. Metals have the property of malleability. What is it about the electrons in metals that gives it this ability to bend, but not break? The electrons are shared in a “sea of electrons”. 42. When exposed to heat, which of the following will expand more, metal or glass? Why? Metal, they are conductors of heat (not insulators like glass) 43. Stars are light years away, but astronomers know what elements they are composed of. How are they able to determine the composition of the stars with the light they receive? The wavelengths found in the emission spectra of stars indicate which elements are present. 44. What is the relationship between wavelength and energy according to the following diagram? Energy decreases As wavelength Increases. Energy increases As wavelength Decreases.