* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review 1 - misshoughton.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
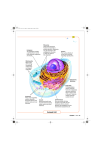
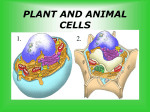
Cell Theory: Lets Review Biology! Scientists: Robert Hooke, (1663) 1. All life forms are made from one or more cells. 2. Cells only arise from pre-existing cells. 3. The cell is the smallest form of life. Definition Example Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism Cell Parts and Their Functions: Cells contain smaller parts called organelles. Organelles have special functions that maintain all the life processes of the cell. intake of nutrients response to stimuli movement exchange of gases growth waste removal Cell Parts and Function _______________________________ — the outer boundary of the cell that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Found in both plant and animal cells. _______________________________ — the fluid within the cell that contains organelles and aids in moving things around in the cell. It is inside the cell membrane surrounding the nucleus. The cytoplasm is made up of about two-thirds water. ______________________________ — One of the larger organelles found in all cells. The nucleus is usually the shape of a sphere and contains the cell's genetic material. It is the control center of the cell. It is found floating in the cytoplasm. ______________________________ —- DNA looks like a twisted extension ladder. It is found in the nucleus and controls everything inside the cell. __________________ — produces energy to power the cell's activities. It changes the energy stored in food compounds into ATP. It is a kidney-bean-shaped organelle floating around the cytoplasm. ____________________________________ — a network of membranes that stores, separates, and transports substances within the cell. It is like a ribbon floating throughout the cytoplasm. ____________________________________ — makes lipids, processes carbohydrates and modifies toxic chemicals in the cell. ____________________________________ — contains ribosomes on its surface and makes proteins to be secreted by the cell, makes new cell membranes. _______________________ — tiny ball-like structures at the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins are formed in the ribosomes. ____________________________________ — flat pancake-like sacs where protein molecules are sorted, changed, packaged and distributed throughout the cell. __________________________ — small spheres floating around the cytoplasm that contain digestive enzymes to help break down bacteria and viruses within the cell. ________________________ — a sac that absorbs water, stores proteins, ions and waste products. Vacuoles are large in plant cells and small in animal cells. They provide support for plant cells. _________________________ — the tough, rigid outer covering that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells. It protects plant cells and helps the plant keep its shape. _________________________ — green oval-shaped structures, plants make sugars through photosynthesis here. Cell Parts and Function-answers Cell Membrane — the outer boundary of the cell that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Found in both plant and animal cells. Cytoplasm — the fluid within the cell that contains organelles and aids in moving things around in the cell. It is inside the cell membrane surrounding the nucleus. The cytoplasm is made up of about twothirds water. Nucleus — One of the larger organelles found in all cells. The nucleus is usually the shape of a sphere and contains the cell's genetic material. It is the control center of the cell. It is found floating in the cytoplasm. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) —- DNA looks like a twisted extension ladder. It is found in the nucleus and controls everything inside the cell. Mitochondria — produces energy to power the cell's activities. It changes the energy stored in food compounds into ATP. It is a kidney-bean-shaped organelle floating around the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum — a network of membranes that stores, separates, and transports substances within the cell. It is like a ribbon floating throughout the cytoplasm. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum — makes lipids, processes carbohydrates and modifies toxic chemicals in the cell. Rough endoplasmic reticulum — contains ribosomes on its surface and makes proteins to be secreted by the cell, makes new cell membranes. Ribosomes — tiny ball-like structures at the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. Proteins are formed in the ribosomes. Golgi apparatus — flat pancake-like sacs where protein molecules are sorted, changed, packaged and distributed throughout the cell. Lysosome — small spheres floating around the cytoplasm that contain digestive enzymes to help break down bacteria and viruses within the cell. Vacuole — a sac that absorbs water, stores proteins, ions and waste products. Vacuoles are large in plant cells and small in animal cells. They provide support for plant cells. Cell wall — the tough, rigid outer covering that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells. It protects plant cells and helps the plant keep its shape. Chloroplast — green oval-shaped structures, plants make sugars through photosynthesis here. Label the Cells Label the following diagrams and place them in the correct order. Mouth Esophagus Liver Gall Bladder Large Intestine Appendix Anus Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Organ Systems Use your text p. 96 to fill in the chart. In animals: Organ System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Digestive System Respiratory System Circulatory System Nervous System Endocrine System Excretory System Reproductive System Lymphatic System Organs Involved Basic Function Organ Systems In animals: Organ System Organs Involved skin, hair, nails, glands Integumentary System bones, cartilage Skeletal System Muscular System Digestive System Respiratory System skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, tendons, ligaments mouth, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, gall bladder, liver, intestines, rectum nose, mouth, trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, diaphragm heart, blood vessels, blood Circulatory System brain, nerves, spinal cord Nervous System Endocrine System Excretory System Reproductive System Lymphatic System glands (pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenals), pancreas, ovaries (females), testes (males) skin, kidney, bladder, ureter, urethra female: ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina, uterus male: testes, epididymis, vas deferens, penis, urethra white blood cells, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, lymph vessels Basic Function Covers and protects body Glands help control body temperature Supports body Allows movement Protects the body Works with skeletal system to provide movement Moves materials within body Ingestion Digestion Absorption of nutrients Elimination of solid wastes Exchange of gases Transportation of materials (such as oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and wastes) within body Controls body functions Coordinates responses and activities Controls growth and development Controls metabolism Elimination of wastes Reproduction Protects body from disease Circulates fluid called lymph Absorbs and transports fats Structure Mouth Esophagus Liver Stomach Gall Bladder Pancreas Small Intestine Large Intestine Epiglottis Larynx Trachea Alveoli Diaphragm Red Blood Cell Leaf Root Stem Xylem Phloem Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Cardiac Muscle Function(s) Structure Function(s) Mouth - chew food, inject saliva (breaks down carbohydrates) Esophagus - muscular tube that actively moves food from mouth to stomach through peristalsis Liver - bile production, metabolizes toxins, protein synthesis Stomach - Acidic environment that breaks down food through muscular contractions Gall Bladder - stores bile (fat breakdown) Pancreas - enzyme production (ex. Insulin) Small Intestine - Nutrient absorption Large Intestine - Water absorption Epiglottis - muscular flap that covers trachea during swallowing Larynx - vocal chords Trachea - (wind pipe) rigid tube connecting nasal cavity and lungs Alveoli - Small sacs in lungs that passively diffuse oxygen to red blood cells and remove carbon dioxide Diaphragm - muscle that expands lungs by contracting Red Blood Cell - cell that binds to oxygen and transports it around the body Leaf - plant organ for photosynthesis and gas exchange flower (type of leaf used for reproduction) Root - plant organ for support, water/nutrient absorption and sugar storage Stem - plant organ for support Xylem - vascular tissue in plants used for water transport Phloem - vascular tissue in plants used for sugar transport Skeletal Muscle - muscle tissue attached to bone structure, used for locomotion (voluntary contraction) Smooth Muscle - organ muscle tissue used in digestion (involuntary contraction) Cardiac Muscle - muscle tissue of the heart Don’t Forget to Study … The Cell Life Cycle: Interphase (G1, S, G2), Mitosis (P.M.A.T.) The 4 types of animal tissue: Epithelial, Connective, Muscular (skeletal, smooth, cardiac), and Nervous The 4 types of plant tissue: Epidermal, Ground, Vascular, and Meristematic 1. What are the three functions of the roots? 2. Describe the major job of the leaf and explain how two tissues in the leaf work together to accomplish this job. 3. Describe two functions of a stem, and explain how the tissues in the stem work together to accomplish one of the stem functions. 4. What is the major function of a flower? Cell Specialization Medical Imaging Technology – X-Ray, Ultrasound, CT Scan, MRI Viruses – Structure, Replication, Immunity Cool Website – Digestive and Circulatory Systems www.medtropolis.com/vbody.asp