* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Destruction of Syria's chemical weapons wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ceramic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
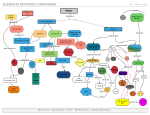
Name ______________________________________________________________ Date ________ Period ____ EOG Review- Chemistry 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. 8.P.1.1 Classify matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on how the atoms are packed together in arrangements. 8.P.1.2 Explain how the physical properties of elements and their reactivity have been used to produce the current model of the Periodic Table of elements. 8.P.1.3 Compare physical changes such as size, shape and state to chemical changes that are the result of a chemical reaction to include changes in temperature, color, formation of a gas or precipitate. 8.P.1.4 Explain how the idea of atoms and a balanced chemical equation support the law of conservation of mass. 1. Atoms are made of _________________ (+), _________________ (neutral), and ___________________ (-). 2. ______________________ and ____________________ are in the nucleus of the atom and when added together they give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly and constantly around the outside of the nucleus in the ____________ __________. 4. The number of __________________ can change which forms _________________ ( + or -). 5. Atoms of the same element will ALWAYS have the same number of ________________ or atomic ______________. 6. We call atoms of the same elements with different numbers of neutrons _____________________. 7. Elements are classified as ________________________, __________________________, or ___________________. 8. Metals are on the ________________ and __________________ of the periodic table. They tend to be: a. malleable: b. conductive: c. usually a ___________________ at room temperature 9. Metalloids are found along the ____________________ on the periodic table. 10. Non- Metals are found on the _______________________ side of the periodic table. They tend to be poor conductors. Many are _________________________ at room temperature. 11. Label A through D: A. B. C. D. 19 16 K S Potassium 39.098 Sulfur 32.066 12. How many protons does Potassium have? 13. How many electrons does Sulfur have? 14. How many neutrons does Potassium have? 15. How many electrons would Potassium (+1) have? 16. How many protons would Sulfur (-1) have? C12H6O6 17. How many oxygen atoms are in the molecule above? 18. How many carbon atoms are in the molecule above? 19. How is the periodic table organized? 20. The rows in the periodic table are called ____________________. They are organized by ______________________________________. 21. The columns in the periodic table are called ______________________. They are grouped by ____________________________________________________________. 22. Most of the elements on the periodic table are __________________. 23. Matter is anything that takes up ____________ and has ____________. All matter is made of ___________. 24. Some elements are turned into electrical wires. Which properties (from above) must they have to be used in this way? Explain why. 25. ___________ can be found by dividing the mass of an object by its volume. 26. What is solubility? 27. Identify the following atoms: A. _________________ PURE SUBSTANCES: B. ______________ C. _____________________ _________________are pure substances that cannot be changed into simpler substances. Elements are composed of _________________ kind of atom. __________________________ are pure substances that are composed of __________________________types of elements that are chemically combined. Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements through _______________________ MIXTURES Mixtures are ________________________ combinations of two or more different substances that retain their own individual properties and are combined physically (mixed together). Mixtures can be separated by physical means (_________________, _________________, _______________) Characteristic properties can be used to identify different materials and to separate a mixture into its components. Mixtures may be heterogeneous or homogeneous. In a ______________________________ mixture, which is not uniform throughout, the component substances can be visibly distinguished. Tossed salad, granite, and iced tea are examples of heterogeneous mixtures. In a ____________________________mixture, which is uniform throughout, the substances are evenly mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. Air, steel, clear salt-water are examples of homogeneous mixtures. STATES OF MATTER- Explain each state in the lines below What causes a change in state? Which phase is most dense? Which phase is least dense? ________________ ________________ ________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: __________________________ properties can be observed and measured without changing the kind of matter being studied. Physical properties include: shape, density, solubility, odor, _______________ point, ____________ point, and color _____________________ properties can be recognized only when substances react or do not react chemically with one another, that is, when they undergo a change in composition.. Chemical properties include: acidity, basicity, combustibility, and ___________________. Chemical and Physical properties can be used to ____________________ a substance by comparing the properties of the substance to unknown substances. CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL CHANGES: ______________________changes do not change the composition of a substance, only the physical properties. Change in ______________________ of matter Change in _________________ or ______________________ ___________________________ changes result in the formation of one or more new substances with new chemical and physical properties. The four types of evidence that show a chemical change/reaction has occurred are a change in _________________, a change in __________, formation of a _______, or formation of a ___________________. reactions occur at different rates, slow to fast, and that reaction rates can be changed by changing the ____________________ of reactants, the _______________, the surface areas of solids, and by using a catalyst. solutions can be acidic, basic, or neutral. The pH scale is used to classify solutions. Neutral solutions have a pH of 7. Acids have a pH of _________________ than 7. Bases have a pH of _________________ than 7. Look at each example below. If the change is chemical, write a C, if it is physical, write a P ____ Ice cream melts ____ sugar dissolves ____ water boils ____ Water evaporates ____ wood burns to ash ____ Ice melts ____ Iron Rusts ____ Apple browns in air ____ paper is wrinkled ____ vinegar/baking soda bubble ____ metal is dented ____ sublimation CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND BALANCING EQUATIONS: A ______________________________can be used to represent a chemical reaction that has occurred. An __________________________is used to distinguish between the substance that are broken apart or combined, and can be understood as meaning “yields” or “makes”. ___________________are the substances broken apart or combined in a chemical reaction and that they are located on the left side of the arrow in a chemical equation. o _____________________________are new substances formed in a chemical reaction and that they are located on the right side of the arrow in a chemical equation. Label each part of the chemical equation: 2H2 + O2 --> 2H20. ______________________ ________________________ when materials ______________ with each other, many changes can take place, but that in every case the total amount of matter _________________ is the same as ________________. balanced chemical equation supports the law of conservation of matter. What does the Law of conservation of Matters state? 28. Balance the following reaction: ____NaCl + ____I2 ____ NaI + ____Cl2 30. 2 grams of sodium are mixed with 2 grams of chlorine. They undergo a chemical reaction. What is the mass of the product, sodium chloride?