* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 Heredity, Mitosis and Meiosis
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
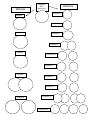
Unit 4 Heredity and Meiosis Study Guide Test = Wednesday 2/8 Completing this study guide is NOT optional. It is a big part of your grade. Please see me if you have questions or need help. Use the notes, journals, PowerPoint Notes labs, worksheets, heredity reading packets, and if all else fails the book to help you find the answers. Vocabulary - Know these words and how they relate to each other (what does one have to do with the other) (Use your vocabulary charts and heredity notes to create your own definitions) 1. Gene : The sections of DNA that contain heredity information. They are passed down from parent to offspring. Each gene has at least 2 forms or alleles. They determine our traits like blond hair or chin shape). 2. Allele: These are forms of a trait. Each gene has different alleles. Alleles are represented by a capital letter like B for a dominant trait or lower case letter like b for recessive traits. Two alleles together make up a persons genotype – BB or Bb or bb. 3. Heredity 4. Phenotype 5. Genotype 6. Characteristic 7. Trait 8. Homozygous 9. Heterozygous 10. Hybrid 1 11. Purebred Answer the following questions in complete sentences. Use vocabulary terms you have learned and drawings to help explain. The more details and connections you make the more credit you will receive – including extra credit. Staple extra papers to this study guide if you need more space to answer. 12. In Mendel’s pea plants 1 trait was controlled by 1 gene that had only 2 forms (alleles) which were either dominant or recessive. Give some examples where heredity can be more complex than Mendel’s explanation (exceptions to Mendel’s rules). (book 184 – 186, reading packet 2, and heredity notes) 13. What is the difference between a dominant and recessive trait? (heredity notes, journals, and heredity reading packets) (Be sure to use alleles, genotypes, phenotypes, and Mendel’s experiments to help you explain.) 14. Who was Mendel and what is he known for? (heredity notes, heredity reading packets, book 174 -187) (Explain his experiments, what he worked with, and how he studied traits) 15. What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction and why is meiosis so important for sexual reproduction? (meiosis notes, book 188 -193) (be sure to answer both parts and use examples) 2 Brown eyes are dominant and represented by a “B”. Blue eyes are recessive and represented by a “b”. Solve the following Punnett square question and use it to answer the questions that follow. (heredity notes , journals, heredity reading packets, and Punnett squares worksheets) 16. What would the genotypes be for the offspring of a heterozygous mother and a blue eyed father? (draw a Punnett square below and use it to determine the possible genotypes for all of the possible offspring) 17. What is the genotype of the mother? 18. What is the probability that an offspring would be homozygous dominant? 19. What are the possible phenotypes for the offspring? 20. Draw the chromosomes of fruit fly gametes as they meet and the egg is fertilized. Write the number of chromosomes next to each cell (find the number of chromosomes in question 21 use colors to show homologous pairs). (meiosis notes) Fertilized Egg Fruit Fly Sperm Fruit Fly Egg 21. Fruit flies have a diploid number of 4 chromosomes or 2 homologous pairs. On the next page draw what happens to the chromosomes in a fruit fly cell during mitosis and then what happens when a fruit fly germ cell goes through meiosis to create haploid gametes (“s” cells or reproductive cells). Draw clearly the chromosomes in each bubble or cell. Use colors if it will help you make your drawings clear. Write the number of chromosomes in each cell next to the cell. (book 188 -193 and meiosis and mitosis notes, and meiosis flipbook) ANSWER THIS ON THE NEXT PAGE 3 mitosis Interphase DNA Replicated meiosis Prophase I Prophase Metaphase I Metaphase Anaphase I Telophase I Anaphase Cytokinesis I Prophase II Telophase Metaphase II Anaphase II Cytokinesis Telophase II Cytokinesis II 4