* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 9 Day 1 Notes
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Marine life wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
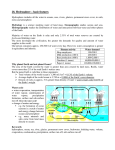
Unit 9 Day 1 Notes The Oceans •There are general hypotheses about the origin of the Earth’s oceans #1 • and the planet and release water •Meteorites generally contain that impact water #2 • early in Earth’s history released significant amounts of water vapor among the other gasses to form the early atmosphere VA SOL •SOL 11 The student will investigate and understand that oceans are complex, interactive physical, , and biological systems and are subject to longand short-term variations. Key concepts include a. physical and chemical changes (tides, waves, currents, sea level and ice cap variations, , and variations). Objective 1. Discuss the origin of the oceans and describe the distribution of oceans and seas 2. Describe the composition of sea water and variations in salinity concentrations 3. Explain ocean layering and effects of 4. Describe variations in •The water vapor and to form the oceans and ice caps The Oceans •Since prehistoric times man has utilized the worlds oceans for obtain , and to •It wasn’t until the late 1800’s when the British Distribution of Oceans expedition was the first to use sophisticated devices to study the oceans •The oceans contain Origin of the Oceans •Several geologic clues indicate that the oceans have existed geologic history of Earth’s water Distribution of Oceans of •The other is either locked up in over the poles and in and 7 •The percentage of ice on Earth has varied by as much •It borders North and South America to the west and as 10 % over geologic time as periods of climate alternated. Europe and Africa to the east The Major Oceans and •Sea Level is the level of the ocean’s surfaces and has risen and fallen by response to and in glaciers •The is located mainly in the . •The •The is the north of the arctic circle (Southern Ocean) is the region surrounding Antarctica • as a response to tectonic activity will also affect sea level •A •Currently sea level is rising causes a per year in response to melting glaciers as the global climate enters a • Seas are smaller than oceans and are partly or mostly •The seas and oceans (with a few notable exceptions) belong to one global ocean whose waters are •The is located between The Major Oceans •The oceans cover of Earth’s surface. The landmasses are like islands completely surrounded by water. •It was the first sea to be explored and mapped by ancient peoples such as the and •The •The oceans are really one vast, body of water. • is the contains about half of the Earth’s seawater is located to the southeast of North America and •The separates Alaska and Siberia •It borders North America to the East and Asia to the West •The the arctic circle is the and extends from Antarctica to 8