* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The element, hydrogen, symbolized by H, is #1 on the periodic table
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
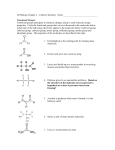
Some notes on pH and it's importance in living systems (this information is for use with the related lecture material) The element, hydrogen, symbolized by H, is #1 on the periodic table. A H atom has one electron and a nucleus containing only one proton (no neutron). So the atom is neutral. If the electron is stripped away, a proton (the nucleus) is all that remains; that H nucleus would have a charge = +1. That H nucleus is also called a hydrogen ion and is symbolized as H+. pH is a number, between 0 and 14, that expresses the H+ concentration of a solution. Brackets are used to mean "concentration of." Therefore, [H+] means "concentration of hydrogen ions." Then pH = log (1 / [H+]). Stated in words, pH of a solution is equal to the common logarithm of the reciprocal of the H+ concentration of the solution. From studying logarithms in the past you know that this expression can also be written as: pH = -log [H+]. That is, pH is equal to the negative logarithm of the H+ concentration. On the pH scale, pH = 7 is called "neutrality." A pH 7 solution is "neutral." Values above 7.0 are "basic," sometimes called "alkaline." Values below 7.0 are "acidic." Values far from neutrality are called very (or strongly) acidic or very basic. The equation above says that pH is inversely related to [H+]. That is, as [H+] increases, pH decreases; also, as [H+] decreases, pH increases. Think of it this way too: If you add an acid (which increases the [H+]) to a solution, you drive the pH value down. Your first lab's guidesheets showed you that there are various ways of expressing concentrations. For pH, the [H+] is expressed as molarity, symbolized by M. Example: If a solution has [H+] = 10-7 M, then pH = -log 10-7 which is -(-7) = 7. Or you can say that a solution of pH = 7 has hydrogen ion concentration equal to 10-7 M. Example: If [H+] = 10-2 M, then pH = -log 10-2 = -(-2) = 2. Example: If [H+] = 5 X 10-4 M, then pH = -log 0.0005 = 3.3. You can check this with your pocket calculator. Note what the logarithmic relationship means: a difference of one pH unit (2 versus 3, for example) means a factor of 10 difference in [H+]. This factor of 10 is also called one order of magnitude. Therefore, if you raise a solution's [H+] by a factor of 100 (2 orders of magnitude), you are decreasing it's pH by 2. And if you lower a solution's [H+] by a factor of 1000 (3 orders of magnitude), you are increasing its pH by a factor of 3. Remember: the relationship is logarithmic and reciprocal. The solutions that exist within living organisms usually have pH values near 7: saliva, blood, tears, and interstitial fluid (the fluid surrounding/bathing tissues of the body), for example. [[Gastric fluid's very low pH is an exception, but that fluid's acidity is necessary to denature dietary proteins. So, for gastric fluid, a very low pH is "normal."]] 1 It is essential in living organisms that the pH of the biological solutions be maintained relatively constant and not be allowed to change significantly. Biological solutions (the bloodstream or the solution in a cell, e.g.) contain proteins that do the work of cells and tissues; and each protein's function depends on the protein having a specific shape. The pH of the solution is an important factor in every protein molecule's shape. If the pH of a solution changes significantly, the shapes of proteins in the solution will change, and that will result in loss of function of the proteins. This radical change in shape of a protein is called "denaturation." This is why strong acids or bases can damage tissues, by destroying the proteins' functioning. As just noted, the low pH of the stomach's gastric fluid denatures dietary proteins as a necessary step in preparing those proteins for chemical breakdown in the small intestine. Anything that significantly changes the [H+] of a biological solution may have a harmful effect on proteins. So, biological solutions contain molecules some of whose functional groups have the ability to (1) remove H+ (by binding them) when their concentration is too high and (2) release H+ when their concentration is too low. Such functional groups are reversibly dissociable. "Dissociation" means "to come apart." In this context that means that a H+ can come loose (dissociate) from a functional group. "Reversible" means that the H+ can come loose from and reattach to the functional group. "Reassociate" means to reattach. There are several reversibly dissociable functional groups. As the lectures stress, three of these are particularly important at the pH values usually found in biological solutions: the carboxyl group, the amino group, the phoshate group. A -COOH group has only one proton to lose, and in the molecules we will study the amino group also has only one proton to lose, as shown below. -COOH ↔ -COO- + H+ (pH < 4 ) (pH > 4) -NH3+ ↔ (pH < 9) -NH2 + H+ (pH > 9) It is the pH of the solution that determines whether a functional group is in the dissociated form (-COO- and -NH2) or the undissociated form (-COOH and -NH3+). Recall that "dissociated" means the H+ has come loose (-COO- and -NH2) and that undissociated means the proton is still attached. So the carboxyl group is neutral (no charge) if undissociated (at pH values below 4 approximately) and bears a negative charge if it's dissociated (pH above 4 approximately). The -COOH cannot bear a positive charge. The undissociated amino group bears a positive charge (at pH values below 9 approximately), but the dissociated form is neutral (at pH above 9 approximately). A short simplification: at pH 7, as in most biological solutions, carboxyl groups within molecules will usually be dissociated (negatively charged) whereas amino groups within molecules will usually be undissociated (positively charged). Note that these pH values of 4 and 9 are only approximations, because the rest of a molecule, other than the carboxyl or amino group, influences how readily the H+ will dissociate and reassociate. 2 Presence of such charges on functional groups within molecules is important for several reasons. In particular these charged functional groups contribute to the proper shape of proteins and influence whether molecules can readily pass through membranes. Biological solutions contain complex mixtures of molecules which contain these functional groups. Thus, if a bit of acid or base were added to the solution, these functional groups could either release H+ to the solution in response or remove H+ from solution in response. Either way, the result would be to prevent change of the [H+]; that is, pH of the solution would remain relatively constant and no damage would be done to the functioning proteins in the solution. A solution that thus resists change in pH is called a buffer. We say that biological solutions are buffered or that they possess buffering capacity. The phosphate group is a bit more complicated, but for our purposes whenever we encounter it at pH around 7 (as in living systems), it will be negatively charged (dissociated). 3